The tutorial shows how to quickly create, filter and customize pivot charts in Excel, so you can make the most of your data.
If you've ever felt overwhelmed by a large and cluttered spreadsheet, you're not alone. Fortunately, Excel pivot charts provide an easy way to create stunning visualizations of your data. Pivot charts are like magic: they let you summarize, analyze and explore your data with just a few clicks. By the end of this tutorial, you'll be able to make your own pivot graphs and impress your boss, your colleagues and even yourself with your data skills. Ready to get started? Let's dive in!
What is pivot chart?
Pivot Chart is a dynamic visualization tool that works together with Excel PivotTables. While PivotTables provide a way to summarize and analyze large datasets, PivotCharts offer a graphical representation of that summarized data, making trends and patterns easier to spot.
The beauty of pivot charts lies in their interactivity and flexibility. Like pivot tables, pivot charts are dynamic, meaning they can be easily manipulated to display different aspects of the data.
Pivot graphs are particularly useful for presenting complex data in a clear and concise manner. They enable users to identify trends, compare data points, and draw insights quickly. For example, with a pivot chart, you can easily visualize how sales vary across different geographical regions, product categories, or specific time periods.
You can create different types of charts, such as pie, bar, line or scatter, and customize them to suit your needs. You can also change their layout and appearance by applying different filters, fields, and formats. A pivot chart is linked to the pivot table that it is based on, so any changes you make to the pivot table will be reflected in the graph.
In essence, a pivot chart serves as a visual storyteller, transforming raw data into meaningful insights that are easy to understand and act upon.

How to make a pivot chart in Excel
Before you start creating a pivot chart, it's important to make sure your data is well-organized and structured. Each column should represent a different variable or category, and each row should contain a unique record. Don't forget to remove any blank rows or columns and double-check your data for errors or inconsistencies.
Tip. If you want your graph to automatically include new records, then format your source data as a table.
With your source data ready, follow these steps to create a pivot chart:
Step 1. Insert a pivot chart
- Select any cell in your dataset.
- On the Insert tab, in the Charts group, click PivotChart.

- The Create PivotChart dialog window will pop up, automatically selecting the entire data range or table. It will then prompt you to choose where to insert your visual - either in a new worksheet or an existing one. Select your preferred location and click OK.

Note. Inserting a pivot chart will automatically include a pivot table alongside it, as these two things are closely related.
Step 2. Configure pivot chart
Now that you have a blank pivot table and pivot chart ready, it's time to set them up to display your data trends. In the PivotChart pane that appears on the left, you'll find a list of all the fields from your dataset. Select the fields you want to display in the graph, and then drag and drop them into the corresponding areas:
- Filters - add filters to display or hide certain data.
- Axis (Categories) – define what data categories to display along the horizontal axis (placed in pivot table rows).
- Legend (Series) – indicate what data series to display (placed in pivot table columns).
- Values – define the values that will be depicted in the chart.
For example, to visualize the total revenue for different project types and statuses, you could drag the "Status" field to the Legend area, "Project type" to the Axis area, and "Total revenue" to the Values area.

Tip. With a Copilot subscription, you can use the AI to create a desired graph simply by expressing your request in a natural language. For more details, see How to visualize with Copilot.
How to create a chart from a pivot table
If you already have a pivot table set up, here's how you can easily create a graph from it:
- Select any cell within your PivotTable.
- Navigate to the Insert tab on the Excel ribbon and click on the PivotChart button.

- In the dialog box that appears, choose the type of graph you want to create. Here are some recommendations:
- Bar charts are ideal for comparing values across different categories or time periods.
- Line charts work well for illustrating trends over time or continuous data series.
- Pie charts are effective for showing the proportion of each category in a dataset.
- Scatter plots are useful for visualizing the relationship between two variables and identifying any correlations or patterns.
- Once you've selected your desired type, click OK.

You will find the visual in the same worksheet next to your PivotTable. You can move it to a different location by dragging and change its size using the resize handles, just as you would with any other graph in Excel.

Pivot chart shortcut key
To swiftly make a graph based on a pivot table, you can use the following keyboard shortcuts:
- Select any cell within the pivot table.
- Press the F11 key to create a graph in a new Chart sheet.
- Alternatively, use the Alt + F1 shortcut to insert a chart on the active sheet.
The newly created pivot chart will automatically use the default type. From there, you can easily modify it to suit your preferences by selecting a different chart type.
How to filter a pivot chart in Excel
By default, a pivot chart comes with a filter at the bottom, allowing you to filter the Axis data categories. In some cases, an additional filter may be available on the right side for the Legend, enabling you to hide or show different data series.
To add more filters to a pivot chart, follow these steps:
- Click anywhere within your graph to display the Fields pane.
- Drag the desired fields to the Filter area.
The added filters will appear at the top of the chart, as illustrated in the image below:

It's important to note that default and custom filters offer different options. The built-in filter automatically included for data categories provides all sorting and filtering options available in Excel:

On the other hand, the custom filter that you add to the Filter area only provides basic filter functionality. By default, it allows selecting just one item. To select multiple items, check the corresponding box at the bottom of the filter window:

Tips:
- To simplify filtering, try using slicers - interactive buttons that let you change the data displayed in the chart with a click.
- To filter your graph by different time periods, such as years, quarters, months, or days, consider adding a timeline.
- Since the pivot table and pivot chart are closely interconnected, any filters applied to the pivot table will automatically be reflected in the graph, and vice versa.
How to modify a pivot chart
Pivot charts are not just powerful visualization tools; they're also incredibly flexible, allowing you to tweak nearly every aspect to suit your needs.
To show, hide or format graph elements like axes, labels, and legend, simply click the Chart Elements button (a plus sign) at the upper right corner of the graph:

For changing the chart style, click the Style icon at the upper right corner and choose from various predefined styles:

For more options to adjust colors and styles, explore the Design and Format tabs on the ribbon. These tabs offer additional settings and tools to fine-tune your pivot chart to perfection.

For more information, please refer to How to customize Excel graphs.
How to change pivot chart type
You can change the type of your pivot graph at any time after you make it. Here are the steps:
- Click anywhere within your graph to activate the pivot chats tabs on the ribbon.
- On the Design tab, in the Type group, click Change Chart Type.

- Select the desired chart type from the options provided, and then click OK.

With these simple steps, you can quickly change the appearance of your pivot graph to better suit your data visualization goals.
How to remove fields buttons from pivot chart
When you create a pivot chart in Excel, it automatically includes the so-called "field buttons" to help you interact with your data:
- Value field button in the upper left
- Axis field button in the lower left for filtering data categories
- Legend filed button on the right for filtering data series

By hiding unnecessary field buttons, you can get a cleaner and more focused visualization of your data.
To remove a specific field button, right click that button and then select "Hide Value Fields Buttons on Chart" or "Hide Axis Fields Buttons" or "Hide Legend Fields Buttons", depending on which button you clicked.
If you want to remove all field buttons at once, simply right-click on any button and choose Hide All Field Buttons on Chart.

Another way to hide and show field buttons in a pivot chart is through the Field Buttons options on the PivotChart Analyze tab, in the Show/Hide group:
- To hide a specific field button, click on the corresponding item in the dropdown list to remove the checkmark.
- To show a hidden field button, click on the unchecked item in the dropdown list.
- To hide all field buttons in the pivot chart, click Hide All. To make all field buttons, click Hide All once again.

Change how to summarize values in pivot chart
By default, numeric values in a pivot chart are summed, while non-numeric values are counted. To adjust how data is summarized, Excel offers the following customization option:
- Right-click the Value field button.
- Choose Value Field Settings… from the context menu.
- Select the desired summary function.

How to change pivot chart data source
When dealing with large datasets in Excel, you may have multiple pivot tables covering different regions or time periods. Imagine you've meticulously set up a pivot chart for one table with specific design and formatting. It would be nice to replicate that visual for another table without redoing all the work. The solution lies in changing the source data for a graph.
- If you wish to preserve the original chart, then copy the worksheet containing it.
- On the copied sheet, select the graph.
- On the PivotChart Analyze tab, in the Data group, click Change Data Source.

- In the dialog box that pops up, choose the Select a table or a range option, then select the new source data for your graph, and click OK.

In some cases, the pivot chart may appear broken as the fields used in the original graph do not exist in the new data source. For example, when changing from Q1 source data to Q2 data, you may get a blank visual.

To fix this, simply select the Q2 field and drag it to the Values area. Your nicely formatted pivot graph will now display the Q2 data.

To confirm this change, select the graph, click the Change Data Source button on the Analyze tab, and you will see that it is now based on the Q2 table.
Note. Changing the pivot chart data source also alters the data source for the related pivot table.
Move pivot chart to new sheet
Similar to a standard graph, you can relocate your Excel pivot chart to another worksheet. Here's how:
- Right-click the pivot graph and select Move Chart from the context menu. Alternatively, click the Move Chart button on the Analyze tab, in the Actions group.
- In the dialog window that appears, choose one of the following options:
- New sheet - this will create a new Chart sheet and move the visual there.
- Object in – this will move the graph as an object to any existing worksheet.
- Click OK.
You can also easily move your graph back to its original sheet using the same steps.

How to refresh pivot chart in Excel
Refreshing a pivot chart is just like refreshing a pivot table. There are two main methods:
Refresh pivot chart manually
To manually refresh a pivot chart, you have several options:
- Select the graph to activate its ribbon tabs. Then, navigate to the PivotChart Analyze tab and click the Refresh button.
- Alternatively, press ALT + F5 to refresh the worksheet containing the chart.
- Another way is to right-click the graph, and then click Refresh from the context menu.
Choose the method that suits you best to ensure your graph displays the latest data.

Refresh pivot chart automatically when opening the workbook
To ensure your graph stays up-to-date every time you open your workbook, follow these steps:
- Right-click the graph and choose PivotChart Options… from the context menu.
- In the dialog box that appears, go to the Data tab, and check the box labeled Refresh data when opening the file.

Note. The settings you select in this dialog will apply to both the chart and the associated pivot table.
That's how you can create, filter and modify pivot charts in Excel. Experiment with different graph types, layouts, and customization options to find the visualization that suits your data best. With a little practice, you'll be able to create dynamic and informative pivot graphs that effectively communicate your insights.
Practice workbook for download
Excel PivotChart - examples (.xlsx file)
위 내용은 Excel에서 피벗 차트를 작성하고 사용자 정의하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
 Excel의 중간 공식 - 실제 예Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
Excel의 중간 공식 - 실제 예Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM이 튜토리얼은 중간 기능을 사용하여 Excel에서 수치 데이터의 중앙값을 계산하는 방법을 설명합니다. 중앙 경향의 주요 척도 인 중앙값은 데이터 세트의 중간 값을 식별하여 Central Tenden의보다 강력한 표현을 제공합니다.
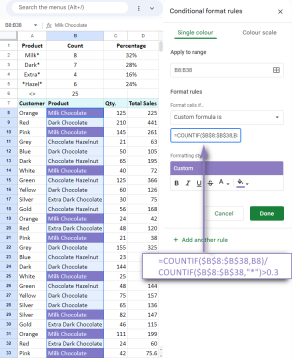 Google 스프레드 시트 Countif 기능은 공식 예제와 함께합니다Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google 스프레드 시트 Countif 기능은 공식 예제와 함께합니다Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM마스터 Google Sheets Countif : 포괄적 인 가이드 이 안내서는 Google 시트의 다목적 카운티프 기능을 탐색하여 간단한 셀 카운팅 이외의 응용 프로그램을 보여줍니다. 우리는 정확하고 부분적인 경기에서 Han에 이르기까지 다양한 시나리오를 다룰 것입니다.
 Excel 공유 통합 문서 : 여러 사용자를위한 Excel 파일을 공유하는 방법Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel 공유 통합 문서 : 여러 사용자를위한 Excel 파일을 공유하는 방법Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM이 튜토리얼은 다양한 방법, 액세스 제어 및 갈등 해결을 다루는 Excel 통합 문서 공유에 대한 포괄적 인 안내서를 제공합니다. Modern Excel 버전 (2010, 2013, 2016 및 이후) 협업 편집을 단순화하여 M에 대한 필요성을 제거합니다.
 Excel을 JPG로 변환하는 방법 - 이미지 파일로 .xls 또는 .xlsx를 저장Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
Excel을 JPG로 변환하는 방법 - 이미지 파일로 .xls 또는 .xlsx를 저장Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM이 자습서는 .xls 파일을 .jpg 이미지로 변환하는 다양한 방법을 탐색하여 내장 된 Windows 도구와 무료 온라인 변환기를 모두 포함합니다. 프레젠테이션을 만들거나 스프레드 시트 데이터를 단단히 공유하거나 문서를 디자인해야합니까? YO를 변환합니다
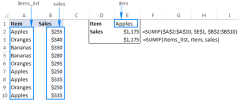 Excel 이름 및 명명 범위 : 공식에서 정의 및 사용 방법Apr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Excel 이름 및 명명 범위 : 공식에서 정의 및 사용 방법Apr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM이 튜토리얼은 Excel 이름의 기능을 명확히하고 셀, 범위, 상수 또는 공식의 이름을 정의하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 또한 정의 된 이름을 편집, 필터링 및 삭제하는 것도 다룹니다. Excel 이름은 엄청나게 유용하지만 종종 오버로입니다
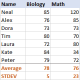 표준 편차 Excel : 기능 및 공식 예제Apr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
표준 편차 Excel : 기능 및 공식 예제Apr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM이 튜토리얼은 표준 편차와 평균의 표준 오차의 차이점을 명확히하여 표준 편차 계산을위한 최적의 Excel 함수를 안내합니다. 설명 통계에서 평균 및 표준 편차는 Intrinsi입니다.
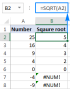 Excel의 제곱근 : SQRT 기능 및 기타 방법Apr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Excel의 제곱근 : SQRT 기능 및 기타 방법Apr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM이 Excel 튜토리얼은 정사각형 뿌리와 Nth 뿌리를 계산하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 제곱근을 찾는 것은 일반적인 수학적 작동이며 Excel은 몇 가지 방법을 제공합니다. Excel에서 사각형 뿌리를 계산하는 방법 : SQRT 기능 사용 : the
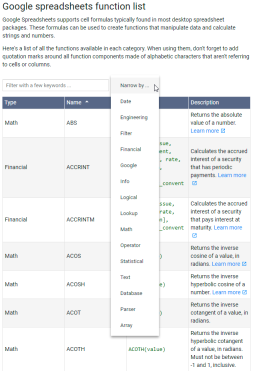 Google Sheets Basics : Google 스프레드 시트에서 작업하는 방법을 배우십시오.Apr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google Sheets Basics : Google 스프레드 시트에서 작업하는 방법을 배우십시오.Apr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AMGoogle Sheets : 초보자 가이드의 힘을 잠금 해제하십시오 이 튜토리얼은 MS Excel에 대한 강력하고 다양한 대안 인 Google Sheets의 기본 사항을 소개합니다. 스프레드 시트를 쉽게 관리하고, 주요 기능을 활용하며, 협업하는 방법에 대해 알아보십시오.


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

맨티스BT
Mantis는 제품 결함 추적을 돕기 위해 설계된 배포하기 쉬운 웹 기반 결함 추적 도구입니다. PHP, MySQL 및 웹 서버가 필요합니다. 데모 및 호스팅 서비스를 확인해 보세요.

Eclipse용 SAP NetWeaver 서버 어댑터
Eclipse를 SAP NetWeaver 애플리케이션 서버와 통합합니다.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 맥
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

VSCode Windows 64비트 다운로드
Microsoft에서 출시한 강력한 무료 IDE 편집기

SublimeText3 Linux 새 버전
SublimeText3 Linux 최신 버전















