커피 한잔 사주세요😄
*메모:
- 내 게시물에서는 RandomRotation()에 대해 설명합니다.
- 내 게시물에서는 RandomAffine()에 대해 설명합니다.
- 내 게시물에서는 RandomHorizontalFlip()에 대해 설명합니다.
- 내 게시물에서는 RandomVerticalFlip()에 대해 설명합니다.
- 내 게시물에는 OxfordIIITPet()에 대한 설명이 나와 있습니다.
RandomPerspective()는 아래와 같이 0개 이상의 이미지에 대해 원근 변환을 수행할 수 있습니다.
*메모:
- 초기화를 위한 첫 번째 인수는istortion_scale(Optional-Default:0.5-Type:int or float)입니다.
*메모:
- 관점 전환이 가능합니다.
- 0
- 초기화를 위한 두 번째 인수는 p(Optional-Default:0.5-Type:int or float)입니다.
*메모:
- 각 이미지가 원근 변환으로 완성되었는지 아닌지에 대한 확률입니다.
- 0
- 초기화를 위한 세 번째 인수는 보간(Optional-Default:InterpolationMode.BILINEAR-Type:InterpolationMode)입니다.
- 초기화를 위한 네 번째 인수는 fill(Optional-Default:0-Type:int, float 또는 tuple/list(int 또는 float))입니다.
*메모:
- 이미지의 배경을 변경할 수 있습니다. *이미지의 원근 변환 시 배경이 보일 수 있습니다.
- 튜플/리스트는 3개 요소를 포함하는 1D여야 합니다.
- 첫 번째 인수(필수 유형:PIL 이미지 또는 텐서(int))가 있습니다. *3D 텐서여야 합니다.
- v2는 V1 또는 V2에 따라 사용하는 것이 좋습니다? 어느 것을 사용해야 합니까?.
from torchvision.datasets import OxfordIIITPet
from torchvision.transforms.v2 import RandomPerspective
from torchvision.transforms.functional import InterpolationMode
randompers = RandomPerspective()
randompers = RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.5,
p=0.5,
interpolation=InterpolationMode.BILINEAR,
fill=0)
randompers
# RandomPerspective(p=0.5,
# distortion_scale=0.5,
# interpolation=InterpolationMode.BILINEAR,
# fill=0)
randompers.distortion_scale
# 0.5
randompers.p
# 0.5
randompers.interpolation
# <interpolationmode.bilinear:>
randompers.fill
# 0
origin_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=None
# transform=RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0)
# transform=RandomPerspective(p=0)
)
dis02p1_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.2, p=1)
)
dis06p1_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.6, p=1)
)
dis1p1_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=1, p=1)
)
p1_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(p=1)
)
p05_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(p=0.5)
)
p1fillgray_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(p=1, fill=150)
)
p1fillpurple_data = OxfordIIITPet(
root="data",
transform=RandomPerspective(p=1, fill=[160, 32, 240])
)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def show_images1(data, main_title=None):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=0.8, fontsize=14)
for i, (im, _) in zip(range(1, 6), data):
plt.subplot(1, 5, i)
plt.imshow(X=im)
plt.xticks(ticks=[])
plt.yticks(ticks=[])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
show_images1(data=origin_data, main_title="origin_data")
show_images1(data=dis02p1_data, main_title="dis02p1_data")
show_images1(data=dis06p1_data, main_title="dis06p1_data")
show_images1(data=dis1p1_data, main_title="dis1p1_data")
show_images1(data=p1_data, main_title="p1_data")
show_images1(data=p05_data, main_title="p05_data")
show_images1(data=p1fillgray_data, main_title="p1fillgray_data")
show_images1(data=p1fillpurple_data, main_title="p1fillpurple_data")
# ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ The code below is identical to the code above. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
def show_images2(data, main_title=None, d=0.5, prob=0.5, f=0):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=0.8, fontsize=14)
for i, (im, _) in zip(range(1, 6), data):
plt.subplot(1, 5, i)
rp = RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=d, p=prob, fill=f) # Here
plt.imshow(X=rp(im)) # Here
plt.xticks(ticks=[])
plt.yticks(ticks=[])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="origin_data", d=0)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="dis02p1_data", d=0.2, prob=1)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="dis06p1_data", d=0.6, prob=1)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="dis1p1_data", d=1, prob=1)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="p1_data", prob=1)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="p05_data", prob=0.5)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="p1fillgray_data", prob=1, f=150)
show_images2(data=origin_data, main_title="p1fillpurple_data", prob=1,
f=[160, 32, 240])
</interpolationmode.bilinear:>



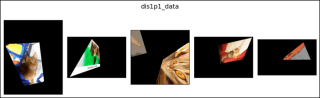




위 내용은 PyTorch의 RandomPerspective의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
 배열이 숫자 데이터를 저장하는 목록보다 일반적으로 더 메모리 효율적인 이유는 무엇입니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:15 AM
배열이 숫자 데이터를 저장하는 목록보다 일반적으로 더 메모리 효율적인 이유는 무엇입니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:15 AMArraysareGenerallyMorememory- 효율적 인 thanlistsortingnumericaldataduetotheirfixed-sizenatureanddirectmemoryAccess.1) ArraysStoreElementsInacontiguousBlock, retoneverHead-fompointerSormetAdata.2) 목록, 종종 implementededymamamicArraysorlinkedStruct
 파이썬 목록을 파이썬 어레이로 어떻게 변환 할 수 있습니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AM
파이썬 목록을 파이썬 어레이로 어떻게 변환 할 수 있습니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AMToconvertapyThonlisttoAnarray, usethearraymodule : 1) importThearrayModule, 2) CreateAlist, 3) Usearray (typecode, list) toconvertit, thetypecodelike'i'forintegers
 동일한 Python 목록에 다른 데이터 유형을 저장할 수 있습니까? 예를 들어보세요.May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AM
동일한 Python 목록에 다른 데이터 유형을 저장할 수 있습니까? 예를 들어보세요.May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython 목록은 다양한 유형의 데이터를 저장할 수 있습니다. 예제 목록에는 정수, 문자열, 부동 소수점 번호, 부울, 중첩 목록 및 사전이 포함되어 있습니다. 목록 유연성은 데이터 처리 및 프로토 타이핑에서 가치가 있지만 코드의 가독성과 유지 관리를 보장하기 위해주의해서 사용해야합니다.
 파이썬의 배열과 목록의 차이점은 무엇입니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:06 AM
파이썬의 배열과 목록의 차이점은 무엇입니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:06 AMPythondoesnothaveBuilt-inarrays; Usethearraymoduleformory- 효율적인 호모 유전자 도자기, whilistsareversartileformixedDatatypes.arraysareefficiTiveDatasetsophesAty, whereferfiblityAndareAsiErtouseFormixOrdorSmallerSmallerSmallerSMATASETS.
 파이썬에서 배열을 만드는 데 일반적으로 사용되는 모듈은 무엇입니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:02 AM
파이썬에서 배열을 만드는 데 일반적으로 사용되는 모듈은 무엇입니까?May 05, 2025 am 12:02 AMthemoscommonLyusedModuleForraySinisThonisNumpy.1) NumpyProvideseficileditionToolsForArrayOperations, IdealFornumericalData.2) ArrayscanBecreatedUsingnp.array () for1dand2dsuctures.3) Numpyexcelsinlement-wiseOperations Numpyexcelscelslikemea
 Python 목록에 요소를 어떻게 추가합니까?May 04, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Python 목록에 요소를 어떻게 추가합니까?May 04, 2025 am 12:17 AMtoAppendElementStoapyThonList, usetHeappend () MethodForsingleElements, extend () formultipleements, andinsert () forspecificpositions.1) useappend () foraddingOneElementatateend.2) usextend () toaddmultipleementsefficially
 파이썬 목록을 어떻게 만드나요? 예를 들어보세요.May 04, 2025 am 12:16 AM
파이썬 목록을 어떻게 만드나요? 예를 들어보세요.May 04, 2025 am 12:16 AMTo TeCreateAtheThonList, usequareBrackets [] andseparateItemswithCommas.1) ListSaredynamicandCanholdMixedDatAtatypes.2) useappend (), remove () 및 SlicingFormAnipulation.3) listlisteforences;) ORSL
 수치 데이터의 효율적인 저장 및 처리가 중요한 경우 실제 사용 사례에 대해 토론하십시오.May 04, 2025 am 12:11 AM
수치 데이터의 효율적인 저장 및 처리가 중요한 경우 실제 사용 사례에 대해 토론하십시오.May 04, 2025 am 12:11 AM금융, 과학 연구, 의료 및 AI 분야에서 수치 데이터를 효율적으로 저장하고 처리하는 것이 중요합니다. 1) 금융에서 메모리 매핑 파일과 Numpy 라이브러리를 사용하면 데이터 처리 속도가 크게 향상 될 수 있습니다. 2) 과학 연구 분야에서 HDF5 파일은 데이터 저장 및 검색에 최적화됩니다. 3) 의료에서 인덱싱 및 파티셔닝과 같은 데이터베이스 최적화 기술은 데이터 쿼리 성능을 향상시킵니다. 4) AI에서 데이터 샤딩 및 분산 교육은 모델 교육을 가속화합니다. 올바른 도구와 기술을 선택하고 스토리지 및 처리 속도 간의 트레이드 오프를 측정함으로써 시스템 성능 및 확장 성을 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

PhpStorm 맥 버전
최신(2018.2.1) 전문 PHP 통합 개발 도구

SecList
SecLists는 최고의 보안 테스터의 동반자입니다. 보안 평가 시 자주 사용되는 다양한 유형의 목록을 한 곳에 모아 놓은 것입니다. SecLists는 보안 테스터에게 필요할 수 있는 모든 목록을 편리하게 제공하여 보안 테스트를 더욱 효율적이고 생산적으로 만드는 데 도움이 됩니다. 목록 유형에는 사용자 이름, 비밀번호, URL, 퍼징 페이로드, 민감한 데이터 패턴, 웹 셸 등이 포함됩니다. 테스터는 이 저장소를 새로운 테스트 시스템으로 간단히 가져올 수 있으며 필요한 모든 유형의 목록에 액세스할 수 있습니다.





