그래프의 최소 스패닝 트리는 총 가중치가 최소인 스패닝 트리입니다.
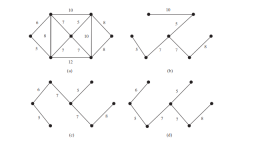
그래프에는 여러 개의 스패닝 트리가 있을 수 있습니다. 가장자리에 가중치가 부여되어 있다고 가정합니다. 최소 스패닝 트리는 최소 총 가중치를 갖습니다. 예를 들어 아래 그림 b, c, d의 트리는 그림 a의 그래프에 대한 스패닝 트리입니다. 그림 c와 d의 트리는 최소 신장 트리입니다.
최소 스패닝 트리를 찾는 문제는 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다. 여러 도시에 지점이 있는 회사를 생각해 보세요. 회사는 모든 지점을 함께 연결하기 위해 전화선을 임대하려고 합니다. 전화 회사는 여러 쌍의 도시를 연결하기 위해 서로 다른 금액을 청구합니다. 모든 지점을 함께 연결하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다. 가장 저렴한 방법은 총 비율이 최소인 스패닝 트리를 찾는 것입니다.
최소 스패닝 트리 알고리즘
최소 스패닝 트리는 어떻게 찾나요? 이를 수행하기 위한 몇 가지 잘 알려진 알고리즘이 있습니다. 이번 섹션에서는 Prim의 알고리즘을 소개합니다. Prim의 알고리즘은 임의의 정점을 포함하는 스패닝 트리 T로 시작합니다. 알고리즘은 이미 트리에 있는 정점에 최저 비용 가장자리가 있는 정점을 반복적으로 추가하여 트리를 확장합니다. 프림의 알고리즘은 그리디 알고리즘이며, 아래 코드에 설명되어 있습니다.
Input: A connected undirected weighted G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: MST (a minimum spanning tree)
1 MST minimumSpanningTree() {
2 Let T be a set for the vertices in the spanning tree;
3 Initially, add the starting vertex to T;
4
5 while (size of T
<p>알고리즘은 <strong>T</strong>에 시작 정점을 추가하는 것으로 시작됩니다. 그런 다음 <strong>V – T</strong>의 정점(예: <strong>v</strong>)을 <strong>T</strong>에 계속 추가합니다. <strong>v</strong>는 가장자리에서 가중치가 가장 작은 <strong>T</strong>의 정점에 인접한 정점입니다. 예를 들어 아래 그림과 같이 <strong>T</strong>와 <strong>V – T</strong>의 정점을 연결하는 5개의 간선이 있고, (<strong>u</strong>, <strong>v</strong> )의 무게가 가장 작은 것입니다.</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172557408574612.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Minimum Spanning Trees"></p>
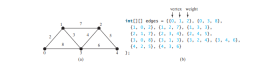
<p>아래 그림의 그래프를 살펴보세요. 알고리즘은 다음 순서로 <strong>T</strong>에 정점을 추가합니다.</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172557408660759.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Minimum Spanning Trees"></p>
<ol>
<li>
<strong>T</strong>에 정점 <strong>0</strong>을 추가합니다.</li>
<li>정점 <strong>5</strong>을 <strong>T</strong>에 추가합니다. <strong>Edge(5, 0, 5)</strong>는 T<strong>, 그림 a와 같습니다. </strong>0<strong>에서 </strong>5<strong>까지의 화살표는 </strong>0<strong>이 </strong>5<strong></strong>의 상위임을 나타냅니다.
</li>정점 <li>1<strong>을 </strong>T<strong>에 추가합니다. </strong>Edge(1, 0, 6)<strong>은 T</strong>, 그림 b와 같습니다.<strong>
</strong>
</li>T<li>에 정점 <strong>6</strong>을 추가합니다. <strong>Edge(6, 1, 7)</strong>은 T<strong>, 그림 c와 같습니다.</strong>
<strong></strong>T</li>에 정점 <li>2<strong>를 추가합니다. </strong>Edge(2, 6, 5)<strong>는 T</strong>, 그림 d와 같습니다.<strong>
</strong><strong>T</strong>에 정점 </li>4<li>를 추가합니다. <strong>Edge(4, 6, 7)</strong>은 T<strong>, 그림 e와 같습니다.</strong>
<strong>정점 </strong>3<strong>을 </strong>T</li>에 추가합니다. <li>Edge(3, 2, 8)<strong>은 T</strong>, 그림 f와 같습니다.<strong>
</strong>
<strong>최소 스패닝 트리는 고유하지 않습니다. 예를 들어 아래 그림의 (c)와 (d)는 모두 그림 a의 그래프에 대한 최소 신장 트리입니다. 그러나 가중치가 서로 다른 경우 그래프에는 고유한 최소 스패닝 트리가 있습니다.</strong>
<strong></strong>
</li>
</ol>그래프가 연결되어 있고 방향이 없다고 가정합니다. 그래프가 연결되지 않거나 방향이 지정되지 않으면 알고리즘이 작동하지 않습니다. 방향이 지정되지 않은 그래프에 대한 확장 포리스트를 찾기 위해 알고리즘을 수정할 수 있습니다. 스패닝 포레스트(Spanning Forest)는 연결된 각 구성 요소가 트리인 그래프입니다.<p>
</p><h2>
Refining Prim’s MST Algorithm
</h2>
<p>To make it easy to identify the next vertex to add into the tree, we use <strong>cost[v]</strong> to store the cost of adding a vertex <strong>v</strong> to the spanning tree <strong>T</strong>. Initially <strong>cost[s]</strong> is <strong>0</strong> for a starting vertex and assign infinity to <strong>cost[v]</strong> for all other vertices. The algorithm repeatedly finds a vertex <strong>u</strong> in <strong>V – T</strong> with the smallest <strong>cost[u]</strong> and moves <strong>u</strong> to <strong>T</strong>. The refined version of the alogrithm is given in code below.<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">Input: A connected undirected weighted G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: a minimum spanning tree with the starting vertex s as the root
1 MST getMinimumSpanngingTree(s) {
2 Let T be a set that contains the vertices in the spanning tree;
3 Initially T is empty;
4 Set cost[s] = 0; and cost[v] = infinity for all other vertices in V;
5
6 while (size of T w(u, v)) { // Adjust cost[v]
11 cost[v] = w(u, v); parent[v] = u;
12 }
13 }
14 }
Implementation of the MST Algorithm
The getMinimumSpanningTree(int v) method is defined in the WeightedGraph class. It returns an instance of the MST class, as shown in Figure below.

The MST class is defined as an inner class in the WeightedGraph class, which extends the Tree class, as shown in Figure below.

The Tree class was shown in Figure below. The MST class was implemented in lines 141–153 in WeightedGraph.java.

The refined version of the Prim’s algoruthm greatly simplifies the implementation. The getMinimumSpanningTree method was implemented using the refined version of the Prim’s algorithm in lines 99–138 in Listing 29.2. The getMinimumSpanningTree(int startingVertex) method sets cost[startingVertex] to 0 (line 105) and cost[v] to infinity for all other vertices (lines 102–104). The parent of startingVertex is set to -1 (line 108). T is a list that stores the vertices added into the spanning tree (line 111). We use a list for T rather than a set in order to record the order of the vertices added to T.
Initially, T is empty. To expand T, the method performs the following operations:
- Find the vertex u with the smallest cost[u] (lines 118–123 and add it into T (line 125).
- After adding u in T, update cost[v] and parent[v] for each v adjacent to u in V-T if cost[v] > w(u, v) (lines 129–134).
After a new vertex is added to T, totalWeight is updated (line 126). Once all vertices are added to T, an instance of MST is created (line 137). Note that the method will not work if the graph is not connected. However, you can modify it to obtain a partial MST.
The MST class extends the Tree class (line 141). To create an instance of MST, pass root, parent, T, and totalWeight (lines 144-145). The data fields root, parent, and searchOrder are defined in the Tree class, which is an inner class defined in AbstractGraph.
Note that testing whether a vertex i is in T by invoking T.contains(i) takes O(n) time, since T is a list. Therefore, the overall time complexity for this implemention is O(n3).
The code below gives a test program that displays minimum spanning trees for the graph in Figure below and the graph in Figure below a, respectively.
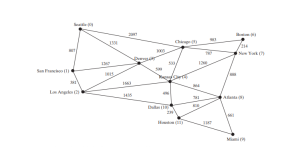
package demo;
public class TestMinimumSpanningTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097},
{1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267},
{2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435},
{3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003},
{4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496},
{5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787},
{6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214},
{7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888},
{8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810},
{9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187},
{10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239},
{11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239}
};
WeightedGraph<string> graph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
WeightedGraph<string>.MST tree1 = graph1.getMinimumSpanningTree();
System.out.println("Total weight is " + tree1.getTotalWeight());
tree1.printTree();
edges = new int[][]{
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<integer> graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5);
WeightedGraph<integer>.MST tree2 = graph2.getMinimumSpanningTree(1);
System.out.println("\nTotal weight is " + tree2.getTotalWeight());
tree2.printTree();
}
}
</integer></integer></string></string>
Total weight is 6513.0
Root is: Seattle
Edges: (Seattle, San Francisco) (San Francisco, Los Angeles)
(Los Angeles, Denver) (Denver, Kansas City) (Kansas City, Chicago)
(New York, Boston) (Chicago, New York) (Dallas, Atlanta)
(Atlanta, Miami) (Kansas City, Dallas) (Dallas, Houston)
Total weight is 14.0
Root is: 1
Edges: (1, 0) (3, 2) (1, 3) (2, 4)
程式為上圖第 27 行建立一個加權圖。然後呼叫 getMinimumSpanningTree()(第 28 行)回傳一個 MST,它表示圖形。在 MST 物件上呼叫 printTree()(第 30 行)會顯示樹中的邊緣。注意,MST 是 Tree 的子類別。 printTree() 方法定義在 Tree 類別中。
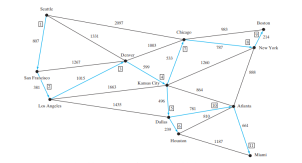
最小生成樹的圖示如下圖所示。頂點按以下順序添加到樹中:西雅圖、舊金山、洛杉磯、丹佛、堪薩斯城、達拉斯、休士頓、芝加哥、紐約、波士頓、亞特蘭大和邁阿密。
위 내용은 최소 스패닝 트리의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
 Java 플랫폼은 어떻게 독립적입니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Java 플랫폼은 어떻게 독립적입니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava는 JVM (Java Virtual Machines) 및 바이트 코드에 의존하는 "Write Once, Everywhere 어디에서나 Run Everywhere"디자인 철학으로 인해 플랫폼 독립적입니다. 1) Java Code는 JVM에 의해 해석되거나 로컬로 계산 된 바이트 코드로 컴파일됩니다. 2) 라이브러리 의존성, 성능 차이 및 환경 구성에주의하십시오. 3) 표준 라이브러리를 사용하여 크로스 플랫폼 테스트 및 버전 관리가 플랫폼 독립성을 보장하기위한 모범 사례입니다.
 Java의 플랫폼 독립성에 대한 진실 : 정말 간단합니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Java의 플랫폼 독립성에 대한 진실 : 정말 간단합니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AMjava'splatformincceldenceisisnotsimple; itinvolvescomplex
 Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 웹 응용 프로그램의 장점May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 웹 응용 프로그램의 장점May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AMJava'SplatformIndenceBenefitsWebApplicationScodetorUnonySystemwithajvm, simplifyingDeploymentandScaling.Itenables : 1) EasyDeploymentAcrossDifferentservers, 2) SeamlessScalingAcrossCloudPlatforms, 3))
 JVM 설명 : Java Virtual Machine에 대한 포괄적 인 가이드May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JVM 설명 : Java Virtual Machine에 대한 포괄적 인 가이드May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMthejvmistheruntimeenvironmenmentforexecutingjavabytecode, Crucialforjava의 "WriteOnce, runanywhere"capability.itmanagesmemory, executesThreads, andensuressecurity, makingestement ofjavadeveloperStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandSmetsmentsMemory
 Java의 주요 기능 : 왜 최고의 프로그래밍 언어로 남아 있는지May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Java의 주요 기능 : 왜 최고의 프로그래밍 언어로 남아 있는지May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMjavaremainsatopchoicefordevelopersdueToitsplatformindence, 객체 지향 데 디자인, 강력한, 자동 메모리 관리 및 compehensiveStandardlibrary
 Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 개발자에게 무엇을 의미합니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 개발자에게 무엇을 의미합니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AMJava'splatforminceldenceMeansdeveloperscanwriteCodeOnceAndrunitonAnyDevicewithoutRecompiling.thisiSocievedTheRoughthejavirtualMachine (JVM), thisTecodeIntomachine-specificinstructions, hallyslatslatsplatforms.howev
 첫 번째 사용을 위해 JVM을 설정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AM
첫 번째 사용을 위해 JVM을 설정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AMJVM을 설정하려면 다음 단계를 따라야합니다. 1) JDK 다운로드 및 설치, 2) 환경 변수 설정, 3) 설치 확인, 4) IDE 설정, 5) 러너 프로그램 테스트. JVM을 설정하는 것은 단순히 작동하는 것이 아니라 메모리 할당, 쓰레기 수집, 성능 튜닝 및 오류 처리를 최적화하여 최적의 작동을 보장하는 것도 포함됩니다.
 내 제품의 Java 플랫폼 독립성을 어떻게 확인할 수 있습니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
내 제품의 Java 플랫폼 독립성을 어떻게 확인할 수 있습니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AMToensureJavaplatform Independence, followthesesteps : 1) CompileIndrunyourApplicationOnMultiplePlatformsUsingDifferentOnsandjvMversions.2) Utilizeci/CDPIPELINES LICKINSORTIBACTIONSFORAUTOMATES-PLATFORMTESTING


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

SublimeText3 영어 버전
권장 사항: Win 버전, 코드 프롬프트 지원!

SublimeText3 Linux 새 버전
SublimeText3 Linux 최신 버전

Eclipse용 SAP NetWeaver 서버 어댑터
Eclipse를 SAP NetWeaver 애플리케이션 서버와 통합합니다.

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

안전한 시험 브라우저
안전한 시험 브라우저는 온라인 시험을 안전하게 치르기 위한 보안 브라우저 환경입니다. 이 소프트웨어는 모든 컴퓨터를 안전한 워크스테이션으로 바꿔줍니다. 이는 모든 유틸리티에 대한 액세스를 제어하고 학생들이 승인되지 않은 리소스를 사용하는 것을 방지합니다.





