두 정점 사이의 최단 경로는 총 가중치가 최소인 경로입니다.
모서리에 음수가 아닌 가중치가 있는 그래프가 주어지면 네덜란드 컴퓨터 과학자인 Edsger Dijkstra가 두 정점 사이의 최단 경로를 찾는 잘 알려진 알고리즘을 발견했습니다. 정점 s에서 정점 v까지의 최단 경로를 찾기 위해 Dijkstra의 알고리즘은 s에서 모든 정점까지의 최단 경로를 찾습니다. 그래서 Dijkstra의 알고리즘은 단일 소스 최단 경로 알고리즘으로 알려져 있습니다. 알고리즘은 cost[v]를 사용하여 정점 v에서 소스 정점 s까지의 최단 경로 비용을 저장합니다. 비용은 0입니다. 처음에는 다른 모든 정점에 대해 cost[v]에 무한대를 할당합니다. 알고리즘은 V – T에서 cost[u]가 가장 작은 정점 u를 반복적으로 찾아 u를 T로 이동합니다. .
알고리즘은 아래 코드에 설명되어 있습니다.
Input: a graph G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: a shortest path tree with the source vertex s as the root
1 ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(s) {
2 Let T be a set that contains the vertices whose
3 paths to s are known; Initially T is empty;
4 Set cost[s] = 0; and cost[v] = infinity for all other vertices in V;
5
6 while (size of T cost[u] + w(u, v)) {
11 cost[v] = cost[u] + w(u, v); parent[v] = u;
12 }
13 }
14 }
이 알고리즘은 최소 스패닝 트리를 찾는 Prim의 알고리즘과 매우 유사합니다. 두 알고리즘 모두 정점을 T 및 V - T의 두 세트로 나눕니다. Prim의 알고리즘의 경우 T 세트에는 이미 트리에 추가된 정점이 포함됩니다. Dijkstra의 경우 세트 T에는 소스까지의 최단 경로가 발견된 정점이 포함됩니다. 두 알고리즘 모두 V – T에서 정점을 반복적으로 찾아 T에 추가합니다. Prim 알고리즘의 경우 정점은 가장자리의 가중치가 최소인 집합의 일부 정점과 인접해 있습니다. Dijkstra 알고리즘에서 정점은 소스에 대한 총 비용이 최소인 집합의 일부 정점과 인접해 있습니다.
알고리즘은 cost[s]를 0(4번째 줄)으로 설정하고 다른 모든 정점에 대해 cost[v]를 무한대로 설정하는 것으로 시작합니다. 그런 다음 V – T의 정점(예: u)을 비용[u]이 가장 작은 T에 계속해서 추가합니다(7행 – 8) 아래 그림과 같이 a. T에 u를 추가한 후 알고리즘은 각 vcost[v] 및 parent[v]를 업데이트합니다. > T에 없음 (u, v)가 T에 있고 cost[v] > 비용[u] + w(u, v) (라인 10–11).

1이라고 가정합니다. 따라서 아래 그림 b에 표시된 것처럼 cost[1] = 0이고 다른 모든 꼭짓점의 비용은 초기에 입니다. parent[i]를 사용하여 경로에서 i의 부모를 나타냅니다. 편의상 소스 노드의 상위 노드를 -1으로 설정합니다.

T는 비어 있습니다. 알고리즘은 비용이 가장 작은 정점을 선택합니다. 이 경우 정점은 1입니다. 알고리즘은 아래 그림과 같이 T에 1을 추가합니다. 이후 1에 인접한 각 정점의 비용을 조정합니다. 이제 아래 그림 b와 같이 꼭지점 2, 0, 6, 3과 해당 부모의 비용이 업데이트됩니다.

2, 0, 6, 3은 원본 정점에 인접하고 정점 2는 V-T에서 비용이 가장 작은 항목이므로 아래 그림과 같이 T에 2를 추가하고 정점의 비용과 부모를 업데이트합니다. V-T이고 2에 인접합니다. cost[0]는 이제 6으로 업데이트되고 해당 상위 항목은 2로 설정됩니다. 1에서 2까지의 화살표 선은 2가 추가된 후 1이 2의 상위임을 나타냅니다. ㅇ.
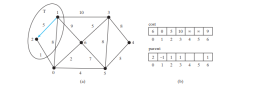
이제 T에는 {1, 2}이 포함됩니다. Vertex 0은 V-T에서 cost가 가장 작은 Vertex 0이므로 아래 그림과 같이 T에 0을 추가하고 V-T에 있고 해당하는 경우 0에 인접한 정점에 대한 비용 및 부모입니다. cost[5]는 이제 10으로 업데이트되고 상위 항목은 0으로 설정되며 cost[6]은 이제 cost[6]으로 업데이트됩니다. 🎜>8
이고 해당 상위 항목은0 으로 설정됩니다.
으로 설정됩니다.
이제 T에는 {1, 2, 0}이 포함됩니다. Vertex 6은 V-T에서 cost가 가장 작은 Vertex 6이므로 아래 그림과 같이 T에 6
을 추가하고V-T 에 있고 해당하는 경우
에 있고 해당하는 경우
에 인접한 정점에 대한 비용 및 부모입니다. 이제 T에는 {1, 2, 0, 6}이 포함됩니다. Vertex 3 또는 5는 V-T에서 비용이 가장 작은 것입니다. T에 3 또는 5을 추가할 수 있습니다. 아래 그림과 같이 T에 3을 추가하고 V-T에 있고 3에 인접한 정점에 대한 비용과 부모를 업데이트하겠습니다. 해당되는 경우. cost[4]
는 이제18 으로 업데이트되고 해당 상위 항목은
으로 업데이트되고 해당 상위 항목은
으로 설정됩니다. 현재 T에는 {1, 2, 0, 6, 3}. Vertex 5는 V-T에서 cost가 가장 작은 Vertex 5이므로 아래 그림과 같이 T에 5를 추가하고 V-T에 있고 해당하는 경우 5에 인접한 정점에 대한 비용 및 부모입니다.
cost[4]는 이제  10
10
5으로 설정됩니다. 현재 T에는 {1, 2, 0, 6, 3, 5}. Vertex 4는 V-T
에서 cost가 가장 작은 Vertex4 이므로 아래 그림과 같이
이므로 아래 그림과 같이
에 4를 추가합니다. 보시다시피 이 알고리즘은 본질적으로 소스 꼭짓점에서 모든 최단 경로를 찾아 소스 꼭짓점에 뿌리를 둔 트리를 생성합니다. 우리는 이 트리를 단일 소스 모든 최단 경로 트리(또는 간단히 최단 경로 트리)라고 부릅니다. 이 트리를 모델링하려면 아래 그림과 같이 Tree
클래스를 확장하는ShortestPathTree 라는 클래스를 정의하세요.
라는 클래스를 정의하세요.
는 WeightedGraph.java의 200~224행에 있는 WeightedGraph의 내부 클래스로 정의됩니다. getShortestPath(int sourceVertex) 메소드는 WeightedGraph.java의 156~197행에서 구현되었습니다. 이 메서드는 cost[sourceVertex]를 0(162행)으로 설정하고 다른 모든 정점(159~161행)에 대해 cost[v]를 무한대로 설정합니다. sourceVertex의 부모는 -1
으로 설정됩니다(166행).T는 최단 경로 트리(169행)에 추가된 정점을 저장하는 목록입니다. T에 추가되는 정점의 순서를 기록하기 위해 세트가 아닌 T
에 대한 목록을 사용합니다. 처음에는 T가 비어 있습니다. T를 확장하기 위해 메서드는 다음 작업을 수행합니다.- Find the vertex u with the smallest cost[u] (lines 175–181) and add it into T (line 183).
- After adding u in T, update cost[v] and parent[v] for each v adjacent to u in V-T if cost[v] > cost[u] + w(u, v) (lines 186–192).
Once all vertices from s are added to T, an instance of ShortestPathTree is created (line 196).
The ShortestPathTree class extends the Tree class (line 200). To create an instance of ShortestPathTree, pass sourceVertex, parent, T, and cost (lines 204–205). sourceVertex becomes the root in the tree. The data fields root, parent, and searchOrder are defined in the Tree class, which is an inner class defined in AbstractGraph.
Note that testing whether a vertex i is in T by invoking T.contains(i) takes O(n) time, since T is a list. Therefore, the overall time complexity for this implemention is O(n^3).
Dijkstra’s algorithm is a combination of a greedy algorithm and dynamic programming. It is a greedy algorithm in the sense that it always adds a new vertex that has the shortest distance to the source. It stores the shortest distance of each known vertex to the source and uses it later to avoid redundant computing, so Dijkstra’s algorithm also uses dynamic programming.
The code below gives a test program that displays the shortest paths from Chicago to all other cities in Figure below and the shortest paths from vertex 3 to all vertices for the graph in Figure below a, respectively.
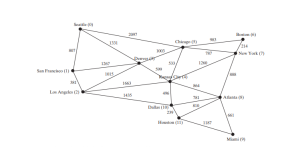
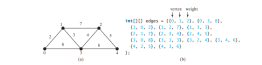
package demo;
public class TestShortestPath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097},
{1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267},
{2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435},
{3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003},
{4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496},
{5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787},
{6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214},
{7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888},
{8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810},
{9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187},
{10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239},
{11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239}
};
WeightedGraph<string> graph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
WeightedGraph<string>.ShortestPathTree tree1 = graph1.getShortestPath(graph1.getIndex("Chicago"));
tree1.printAllPaths();
// Display shortest paths from Houston to Chicago
System.out.println("Shortest path from Houston to Chicago: ");
java.util.List<string> path = tree1.getPath(graph1.getIndex("Houston"));
for(String s: path) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
edges = new int[][]{
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<integer> graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5);
WeightedGraph<integer>.ShortestPathTree tree2 = graph2.getShortestPath(3);
System.out.println("\n");
tree2.printAllPaths();
}
}
</integer></integer></string></string></string>
All shortest paths from Chicago are:
A path from Chicago to Seattle: Chicago Seattle (cost: 2097.0)
A path from Chicago to San Francisco:
Chicago Denver San Francisco (cost: 2270.0)
A path from Chicago to Los Angeles:
Chicago Denver Los Angeles (cost: 2018.0)
A path from Chicago to Denver: Chicago Denver (cost: 1003.0)
A path from Chicago to Kansas City: Chicago Kansas City (cost: 533.0)
A path from Chicago to Chicago: Chicago (cost: 0.0)
A path from Chicago to Boston: Chicago Boston (cost: 983.0)
A path from Chicago to New York: Chicago New York (cost: 787.0)
A path from Chicago to Atlanta:
Chicago Kansas City Atlanta (cost: 1397.0)
A path from Chicago to Miami:
Chicago Kansas City Atlanta Miami (cost: 2058.0)
A path from Chicago to Dallas: Chicago Kansas City Dallas (cost: 1029.0)
A path from Chicago to Houston:
Chicago Kansas City Dallas Houston (cost: 1268.0)
Shortest path from Houston to Chicago:
Houston Dallas Kansas City Chicago
All shortest paths from 3 are:
A path from 3 to 0: 3 1 0 (cost: 5.0)
A path from 3 to 1: 3 1 (cost: 3.0)
A path from 3 to 2: 3 2 (cost: 4.0)
A path from 3 to 3: 3 (cost: 0.0)
A path from 3 to 4: 3 4 (cost: 6.0)
The program creates a weighted graph for Figure above in line 27. It then invokes the getShortestPath(graph1.getIndex("Chicago")) method to return a Path object that contains all shortest paths from Chicago. Invoking printAllPaths() on the ShortestPathTree object displays all the paths (line 30).
The graphical illustration of all shortest paths from Chicago is shown in Figure below. The shortest paths from Chicago to the cities are found in this order: Kansas City, New York, Boston, Denver, Dallas, Houston, Atlanta, Los Angeles, Miami, Seattle, and San Francisco.
위 내용은 최단 경로 찾기의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
 Java 플랫폼은 어떻게 독립적입니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Java 플랫폼은 어떻게 독립적입니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava는 JVM (Java Virtual Machines) 및 바이트 코드에 의존하는 "Write Once, Everywhere 어디에서나 Run Everywhere"디자인 철학으로 인해 플랫폼 독립적입니다. 1) Java Code는 JVM에 의해 해석되거나 로컬로 계산 된 바이트 코드로 컴파일됩니다. 2) 라이브러리 의존성, 성능 차이 및 환경 구성에주의하십시오. 3) 표준 라이브러리를 사용하여 크로스 플랫폼 테스트 및 버전 관리가 플랫폼 독립성을 보장하기위한 모범 사례입니다.
 Java의 플랫폼 독립성에 대한 진실 : 정말 간단합니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Java의 플랫폼 독립성에 대한 진실 : 정말 간단합니까?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AMjava'splatformincceldenceisisnotsimple; itinvolvescomplex
 Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 웹 응용 프로그램의 장점May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 웹 응용 프로그램의 장점May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AMJava'SplatformIndenceBenefitsWebApplicationScodetorUnonySystemwithajvm, simplifyingDeploymentandScaling.Itenables : 1) EasyDeploymentAcrossDifferentservers, 2) SeamlessScalingAcrossCloudPlatforms, 3))
 JVM 설명 : Java Virtual Machine에 대한 포괄적 인 가이드May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JVM 설명 : Java Virtual Machine에 대한 포괄적 인 가이드May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMthejvmistheruntimeenvironmenmentforexecutingjavabytecode, Crucialforjava의 "WriteOnce, runanywhere"capability.itmanagesmemory, executesThreads, andensuressecurity, makingestement ofjavadeveloperStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandStandSmetsmentsMemory
 Java의 주요 기능 : 왜 최고의 프로그래밍 언어로 남아 있는지May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Java의 주요 기능 : 왜 최고의 프로그래밍 언어로 남아 있는지May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMjavaremainsatopchoicefordevelopersdueToitsplatformindence, 객체 지향 데 디자인, 강력한, 자동 메모리 관리 및 compehensiveStandardlibrary
 Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 개발자에게 무엇을 의미합니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java 플랫폼 독립성 : 개발자에게 무엇을 의미합니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AMJava'splatforminceldenceMeansdeveloperscanwriteCodeOnceAndrunitonAnyDevicewithoutRecompiling.thisiSocievedTheRoughthejavirtualMachine (JVM), thisTecodeIntomachine-specificinstructions, hallyslatslatsplatforms.howev
 첫 번째 사용을 위해 JVM을 설정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AM
첫 번째 사용을 위해 JVM을 설정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AMJVM을 설정하려면 다음 단계를 따라야합니다. 1) JDK 다운로드 및 설치, 2) 환경 변수 설정, 3) 설치 확인, 4) IDE 설정, 5) 러너 프로그램 테스트. JVM을 설정하는 것은 단순히 작동하는 것이 아니라 메모리 할당, 쓰레기 수집, 성능 튜닝 및 오류 처리를 최적화하여 최적의 작동을 보장하는 것도 포함됩니다.
 내 제품의 Java 플랫폼 독립성을 어떻게 확인할 수 있습니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
내 제품의 Java 플랫폼 독립성을 어떻게 확인할 수 있습니까?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AMToensureJavaplatform Independence, followthesesteps : 1) CompileIndrunyourApplicationOnMultiplePlatformsUsingDifferentOnsandjvMversions.2) Utilizeci/CDPIPELINES LICKINSORTIBACTIONSFORAUTOMATES-PLATFORMTESTING


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

PhpStorm 맥 버전
최신(2018.2.1) 전문 PHP 통합 개발 도구

SublimeText3 영어 버전
권장 사항: Win 버전, 코드 프롬프트 지원!

mPDF
mPDF는 UTF-8로 인코딩된 HTML에서 PDF 파일을 생성할 수 있는 PHP 라이브러리입니다. 원저자인 Ian Back은 자신의 웹 사이트에서 "즉시" PDF 파일을 출력하고 다양한 언어를 처리하기 위해 mPDF를 작성했습니다. HTML2FPDF와 같은 원본 스크립트보다 유니코드 글꼴을 사용할 때 속도가 느리고 더 큰 파일을 생성하지만 CSS 스타일 등을 지원하고 많은 개선 사항이 있습니다. RTL(아랍어, 히브리어), CJK(중국어, 일본어, 한국어)를 포함한 거의 모든 언어를 지원합니다. 중첩된 블록 수준 요소(예: P, DIV)를 지원합니다.

MinGW - Windows용 미니멀리스트 GNU
이 프로젝트는 osdn.net/projects/mingw로 마이그레이션되는 중입니다. 계속해서 그곳에서 우리를 팔로우할 수 있습니다. MinGW: GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)의 기본 Windows 포트로, 기본 Windows 애플리케이션을 구축하기 위한 무료 배포 가능 가져오기 라이브러리 및 헤더 파일로 C99 기능을 지원하는 MSVC 런타임에 대한 확장이 포함되어 있습니다. 모든 MinGW 소프트웨어는 64비트 Windows 플랫폼에서 실행될 수 있습니다.

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구





