집 >백엔드 개발 >C#.Net 튜토리얼 >C#의 피보나치 수열
C#의 피보나치 수열
- 王林원래의
- 2024-09-03 15:34:44885검색
피보나치 시리즈 중 C#의 피보나치 시리즈는 유명한 시퀀스 시리즈 중 하나입니다. 순서는 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8… 피보나치 수열은 0과 1부터 시작하며 다음 숫자는 이전 두 숫자의 합입니다. 피보나치 수열은 13세기세기에 레오나르도 피사노 비골로(Leonardo Pisano Bigollo)가 창안했다고 합니다. 피보나치 수열은 일부 시나리오에 유용합니다. 기본적으로 이것은 원래 토끼 문제, 즉 한 쌍에서 태어난 토끼의 수를 해결하는 데 사용되었습니다. 피보나치 수열이 유용한 다른 문제도 있습니다.
피보나치 수열 논리
피보나치 수열과 마찬가지로 숫자는 이전 두 숫자의 합입니다. 따라서 피보나치 수열이 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21이라고 말하면… 이 다음 숫자에 따르면 13과 21과 같은 이전 두 숫자의 합이 됩니다. 따라서 다음 숫자는 13입니다. +21=34.
피보나치 수열을 생성하는 논리는 다음과 같습니다
F(n)= F(n-1) +F(n-2)
F(n)은 항 번호이고 F(n-1) +F(n-2)는 이전 값의 합입니다.
그래서 시리즈 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89…
논리에 따르면 F(n)= F(n-1) +F(n-2)
F(n)= 55+89
F(n)= 144
다음 학기는 144입니다.
피보나치 수열을 만드는 다양한 방법
피보나치 수열은 다양한 방법으로 생성할 수 있습니다.
1. 반복적 접근
이 방법이 시리즈를 생성하는 가장 쉬운 방법입니다.
코드:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespaceFibonacciDemo
{
classProgram
{
staticint Fibonacci(int n)
{
intfirstnumber = 0, secondnumber = 1, result = 0;
if (n == 0) return 0; //It will return the first number of the series
if (n == 1) return 1; // it will return the second number of the series
for (int i = 2; i<= n; i++) // main processing starts from here
{
result = firstnumber + secondnumber;
firstnumber = secondnumber;
secondnumber = result;
}
return result;
}
staticvoid Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Length of the Fibonacci Series: ");
int length = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
for(int i = 0; i< length; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", Fibonacci(i));
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2. 재귀적 방법
이 문제를 해결하는 또 다른 방법입니다.
방법 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespaceFibonacciDemo
{
classProgram
{
staticint Fibonacci(int n)
{
intfirstnumber = 0, secondnumber = 1, result = 0;
if (n == 0) return 0; //it will return the first number of the series
if (n == 1) return 1; // it will return the second number of the series
return Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2);
}
staticvoid Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Length of the Fibonacci Series: ");
int length = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
for(int i = 0; i< length; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", Fibonacci(i));
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
방법 2
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace FibonacciSeries
{
class Program
{
public static void Fibonacci
(
int firstnumber,
int secondnumber,
int count,
int length,
)
{
if (count <= length)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", firstnumber);
Fibonacci(secondnumber, firstnumber + secondnumber, count + 1, length);
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Length of the Fibonacci Series: ");
int length = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Fibonacci(0, 1, 1, length);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
출력:
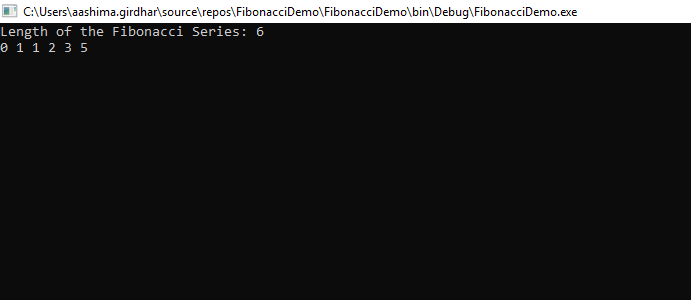
3. 배열을 이용한 피보나치
코드:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
public class Program
{
public static int[] Fibonacci(int number)
{
int[] a = new int[number];
a[0] = 0;
a[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < number; i++)
{
a[i] = a[i - 2] + a[i - 1];
}
return a;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var b = Fibonacci(10);
foreach (var elements in b)
{
Console.WriteLine(elements);
}
}
}
출력:
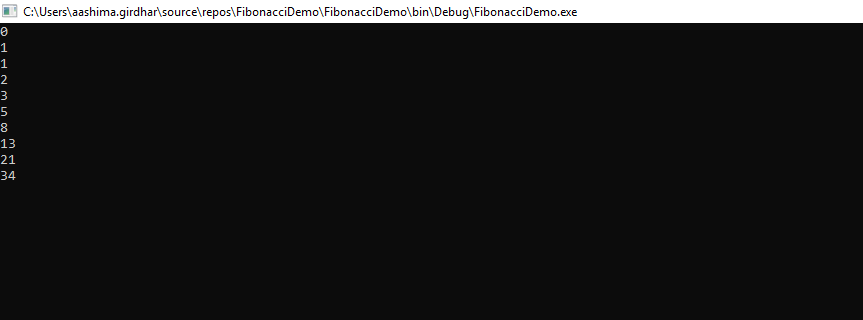
피보나치 수열의 N번째 항을 찾는 방법은 무엇인가요?
방법은 다음과 같습니다
방법 1
코드:
using System;
namespace FibonacciSeries
{
class Program {
public static int NthTerm(int n)
{
if ((n == 0) || (n == 1))
{
return n;
}
else
{
return (NthTerm(n - 1) + NthTerm(n - 2));
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Enter the nth term of the Fibonacci Series: ");
int number = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
number = number - 1;
Console.Write(NthTerm(number));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
위 코드는 피보나치 수열의 n번째 항을 찾는 코드입니다. 예를 들어, 시리즈에서 12번째 용어를 찾으려면 결과는 89가 됩니다.
방법 2
(O(Log t) 시간).
t번째 피보나치 수를 찾는 데 사용할 수 있는 또 다른 반복 공식이 있습니다. t가 짝수이면 = t/2:
F(t) = [2*F(k-1) + F(k)]*F(k)
t가 홀수이면 k = (t + 1)/2
F(t) = F(k)*F(k) + F(k-1)*F(k-1)
피보나치 행렬
행렬을 얻은 후에는 (-1)t = Ft+1Ft-1 – Ft2를 얻습니다.
FmFt + Fm-1Ft-1 = Fm+t-1
t = t+1이라고 하면
FmFt+1 + Fm-1Ft = Fm+t
m = t
F2t-1 = Ft2 + Ft-12
F2t = (Ft-1 + Ft+1)Ft = (2Ft-1 + Ft)Ft
공식을 얻기 위해 다음을 수행합니다
t가 짝수이면 k = t/2를 입력하세요
t가 홀수이면 k = (t+1)/2를 입력하세요
이러한 숫자를 정렬하면 STACK의 메모리 공간이 지속적으로 사용되는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다. 이는 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 제공합니다. 재귀 알고리즘은 효율성이 떨어집니다.
코드:
int f(n) : if( n==0 || n==1 ) return n; else return f(n-1) + f(n-2)
이제 위의 알고리즘이 n=4에 대해 실행될 때
fn(4)
f(3) f(2)
f(2) f(1) f(1) f(0)
f(1) f(0)
그럼 나무군요. f(4)를 계산하려면 f(3)과 f(2) 등을 계산해야 합니다. 4라는 작은 값의 경우 f(2)는 두 번 계산되고 f(1)은 세 번 계산됩니다. 이 추가 항목 수는 대량으로 증가할 것입니다.
f(n)을 계산하는데 필요한 덧셈의 개수는 f(n+1)-1이라는 추측이 있습니다.
결론
여기서 반복 방법은 이러한 종류의 문제를 해결하는 데 더 빠른 접근 방식을 제공하므로 항상 선호됩니다. 여기서는 이전 숫자와 이전 숫자(두 개의 변수)에 피보나치 수열의 첫 번째와 두 번째 숫자를 저장하고 또한 현재 숫자를 사용하여 피보나치 수를 저장합니다.
위 내용은 C#의 피보나치 수열의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

