집 >백엔드 개발 >C#.Net 튜토리얼 >C# 다차원 배열
C# 다차원 배열
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB원래의
- 2024-09-03 15:12:21788검색
C#에서 직사각형 배열 또는 다차원 배열은 행렬 형식의 요소 구성을 나타냅니다. 다차원 배열은 2차원 또는 3차원만 가능합니다. 배열의 차원은 변수에 있는 데이터의 구성 형식을 나타냅니다. 따라서 다차원 배열은 요소를 행이나 열로 직렬 또는 순서로 구성한 것으로 정의할 수 있습니다.
구문:
다음은 다차원 배열의 구문입니다.
2차원 배열 선언.
int[,] x=new int[1,2];
3차원 배열 선언.
int[,,] x=new int[1,2,3];
위 구문은 2차원 배열과 3차원 배열(x)을 선언하는 형식을 지정합니다. 첫 번째 배열에는 1과 2라는 두 요소가 포함되어 있는 반면, 3차원 배열에는 1,2,3 요소가 포함되어 있습니다.
다차원 배열 초기화
다차원 배열은 세 가지 방법으로 초기화할 수 있습니다
1. 선언 완료
int[,] x = new int[6,6];
위 사양은 배열 유형, 배열 크기, new 연산자 사용을 포함하여 2차원 배열을 완전히 초기화합니다.
2. 새 연산자를 사용하지 않고 초기화
int[,] x = { { 3,2,1 }, { 6,5,4 }, { 9,8,7 } };
3. 크기를 선언하지 않고 배열 초기화
int[,] x = new int[,]{ { 3,2,1 }, { 6,5,4 }, { 9,8,7 } };
C# 다차원 배열의 예
다음은 C#의 다차원 배열의 예입니다.
예시 #1
다차원 배열의 선언 및 초기화를 설명하는 프로그램입니다. 아래 예에서는 C#에서 다차원 배열을 생성하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
코드:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] x = { { 3, 2, 1 }, { 6, 5, 4 }, { 9, 8, 7 } };
for (int a = 0; a < 3; a++)
{
for (int b = 0; b < 3; b++)
{
Console.Write(x[a, b] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
출력:

예시 #2
초기화, 2차원 배열 선언, 요소 액세스를 설명하는 프로그램
코드:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* declaring and initialising a two dimensional array*/
int[,] b = new int[6, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 6 }, { 8,7 }, { 9 , 10 }, { 2, 3 } };
int i, j;
/* accessing each of the elements value for the array */
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, b[i, j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
출력:

위 프로그램은 다차원 배열의 배열 요소에 액세스하기 위한 위치 표시로 인덱스를 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
예시 #3
두 개의 다차원 배열을 추가하는 프로그램
코드:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[,] array1 = new int[3, 3];
int[,] array2 = new int[3, 3];
int[,] resultArray = new int[3, 3];
int i, j;
Console.WriteLine("specify the members of the first array: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
array1[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
Console.WriteLine("elements of the array1: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", array1[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
Console.WriteLine("specify the members of the array2: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
array2[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
Console.WriteLine("elements of the array2: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", array2[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
resultArray[i, j] = array1[i, j] + array2[i, j];
}
}
Console.WriteLine("resultArray of the array1 and array2 looks as below : ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", resultArray[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
}
}
출력:
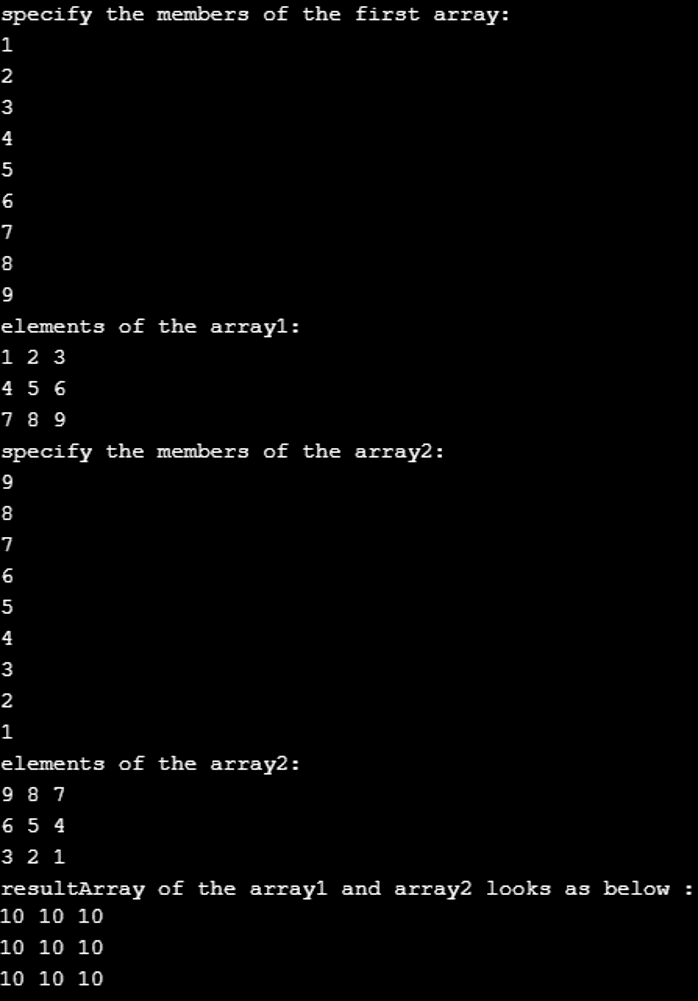
위 프로그램을 사용하여 첫 번째 배열의 각 요소를 두 번째 배열의 카운터 요소에 추가하여 배열에 대한 추가 작업을 완료했습니다. 예를 들어, array1의 첫 번째 요소는 1입니다. 마찬가지로 array2의 첫 번째 요소는 9입니다. 덧셈의 결과에는 첫 번째 요소가 10인 배열이 포함되어야 합니다.
장점 및 단점
다음은 다차원 배열의 장점과 단점입니다.
장점
- 다차원 배열을 사용하면 배열 내의 데이터 하위 그룹을 구성할 수 있습니다. 다차원 배열은 포인터 배열에 데이터 메모리 주소를 저장하는 데에도 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 프로그램에서 다차원 배열은 처음에 정적 크기와 초기화를 갖습니다. 크기를 확장하려면 초기화 중에 관련 크기를 지정해야 합니다.
- 다차원 배열을 사용하면 행렬 연산을 수행하고 동일한 변수 할당 하에서 큰 데이터 값을 유지할 수 있습니다.
- 다차원 배열은 스택, 힙, 큐, 해시 테이블을 구현하는 데 사용됩니다.
단점
- 요소는 배열의 연속 메모리 위치에 있습니다. 따라서 요소의 삽입 및 삭제는 단일 요소에 대한 유사한 작업보다 더 복잡합니다.
- 또한 배열 중간에 요소를 삽입할 수 없습니다.
- 정적 할당은 필요한 것보다 더 많은 메모리를 할당하는 경우 낭비를 야기하고 사용되지 않은 메모리를 해제하지 못할 수 있습니다. 이는 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
- 다차원 배열은 1차원 배열에 비해 속도가 느릴 수 있다는 점이 큰 단점입니다. 이를 극복하기 위해 들쭉날쭉한 배열을 다차원 배열로 대체할 수 있습니다.
위 내용은 C# 다차원 배열의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

