효율성이 높고 라벨이 필요 없는 Google 팀은 AI를 사용하여 임상 데이터를 마이닝하고 유전자 발견 및 질병 예측을 개선하며 Nature 하위 저널에 게재됩니다.
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB원래의
- 2024-07-19 21:45:12551검색

Editor | ScienceAI
현대 의료 시스템은 폐 기능 맵, 광용적맥파(PPG), 심전도(ECG) 기록, CT 스캔, MRI 영상과 같은 대량의 고차원 임상 데이터(HDCD)를 생성합니다. 데이터는 단일 이진수 또는 연속 숫자로 요약될 수 없습니다.
게놈과 HDCD 사이의 연관성을 이해하는 것은 질병에 대한 이해를 향상시킬 뿐만 아니라 질병 치료법 개발에도 중요합니다.
최근 Google Research의 유전체학 팀은 HDCD를 사용하여 질병과 생물학적 특성을 특성화하는 데 진전을 이루었습니다.
연구팀은 유전자 변이와 HDCD 사이의 연관성을 발견하기 위해 비지도 딥러닝 모델인 REGLE(Representation Learning for Low-Dimensional Embedding Gene Discovery)을 제안했습니다.
REGLE은 새로운 유전자 발견 방법으로 고차원 임상 데이터에 숨겨진 정보를 활용할 수 있고, 계산적으로 효율적이며, 질병 라벨이 필요하지 않으며, 전문가가 정의한 지식의 정보를 통합할 수 있습니다.
전반적으로 REGLE에는 기존 전문가가 정의한 시그니처로 포착한 것 이상의 임상적으로 관련 있는 정보가 포함되어 있어 유전자 발견 및 질병 예측이 향상됩니다.
관련 연구는 "고차원 임상 데이터에 대한 비지도 표현 학습이 게놈 발견 및 예측을 향상시킵니다"라는 제목으로 "Nature Genetics"에 7월 8일 게재되었습니다.

논문 링크: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-024-01831-6
HDCD에 숨겨진 정보를 밝히다
유전자와 HDCDA의 연관성 연구 간단한 접근 방식은 각 데이터 좌표에 대해 GWAS를 수행하는 것입니다. 예를 들어 의료 이미지의 각 픽셀 값 변화를 연구할 수 있습니다. 이 접근 방식은 계산 비용이 많이 들고 인접한 좌표 간의 높은 상관 관계와 큰 다중 테스트 부담으로 인해 중요한 연관성을 감지하는 데 성능이 낮습니다.
보다 일반적인 접근 방식은 HDCD에서 추출된 소수의 전문가 정의 특징(EDF)에 GWAS의 대상 특징 또는 표현형으로 집중하는 것입니다. EDF에는 폐활량 측정법의 강제 폐활량(FVC) 또는 1초 강제 호기량(FEV1)과 같은 임상적으로 알려진 기능이 포함될 수 있습니다.
이러한 EDF는 전문가가 발견한 중요한 기능이지만 HDCD에 인코딩된 신호를 완전히 캡처하지 못할 수도 있으므로 이러한 신호에서 GWAS를 실행하면 HDCD의 잠재력을 최대한 활용하지 못할 수 있습니다.
REGLE은 VAE(변형 자동 인코더) 모델을 사용하여 이러한 한계를 극복하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 이 방법은 세 가지 주요 단계로 구성됩니다.
(1) VAE를 통해 HDCD의 비선형, 저차원, 분리된 표현(즉, 인코딩 또는 임베딩)을 학습합니다.
(2) 각 인코딩된 좌표에 대해 독립적으로 GWAS를 수행합니다.
(3) 코딩 좌표의 PRS(다유전적 위험 점수)를 일반적인 생물학적 기능에 대한 유전 점수로 사용한 다음 잠재적으로 이러한 점수를 결합하여 특정 질병 또는 형질에 대한 PRS를 생성합니다(질병 라벨 수가 적음). 특히 REGLE은 수정된 VAE 아키텍처의 디코더 입력에 관련 EDF를 선택적으로 포함할 수 있도록 하여 인코더가 EDF로 표시되지 않는 잔여 신호만 학습하도록 장려합니다.
폐 및 순환 기능에 대한 새로운 유전자좌 검출
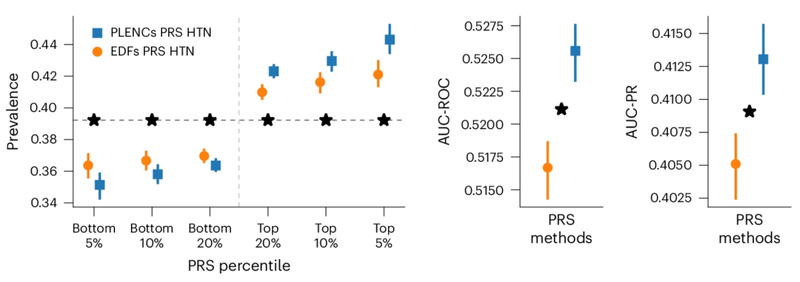
연구원들은 폐 기능을 측정하는 폐활량 측정법과 심혈관 기능을 측정하는 폐활량 측정법이라는 두 가지 고차원 임상 데이터 형식을 사용하여 REGLE의 강력함을 입증했습니다. .PPG. 둘 다 진료소나 소비자 웨어러블 기기에서 비침습적으로 비교적 저렴하게 수집할 수 있으며 두 방식 모두 잘 알려진 특성을 가지고 있습니다. 동일한 차원의 폐활량 측정법 및 PPG 시그니처를 사용한 게놈 전체 연관 연구와 비교하여, 학습된 코딩에 대한 REGLE의 연구는 폐 및 순환 기능과 관련된 알려진 유전적 유전자좌의 대부분을 복구하는 동시에 다른 부위(예: , PPG의 중요 사이트가 45% 증가했습니다. 이러한 사이트가 추가 분석 및 습식 실험실 실험에서 검증되면 새로운 약물 표적이 될 가능성이 있습니다. 향상된 유전적 위험 점수다유전자 위험 점수(PRS)는 특정 특성에 대한 많은 유전적 변이의 예상 영향을 요약한 것으로 단일 숫자로 표시됩니다. REGLE 임베딩에 대한 게놈 차원의 연관 연구를 통해 생성된 PRS는 몇 가지 질병 특징만을 사용하여 결합되어 해당 특정 질병에 대한 PRS를 생성할 수 있습니다.Researchers observed that lung function PRS created from spirometry coding improved COPD and asthma prediction compared to existing methods such as expert-defined features, PCA, and PRS, and outperformed feature PRS at both ends of the risk spectrum Stratify risk groups more efficiently. Statistically significant improvements in multiple metrics (AUC-ROC, AUC-PR, and Pearson correlation) across multiple independent datasets (COPDGene, eMERGE III, Indiana Biobank, and EPIC-Norfolk) for asthma and COPD, as follows Show.

Similarly, PRS derived from the REGLE embedding of PPG improves hypertension and systolic blood pressure (SBP) predictions. Hypertension and SBP PRS generated by PPG encoding and PPG signatures were evaluated in three independent datasets (COPDGene, eMERGE III and EPIC-Norfolk) as well as in the UK Biobank held-out test set.
Observed that across multiple datasets, there is a consistent trend of improvement using PRS from PPG coding over using PRS from expert-defined features, for both hypertension and SBP.

Partially Interpretable Embeddings
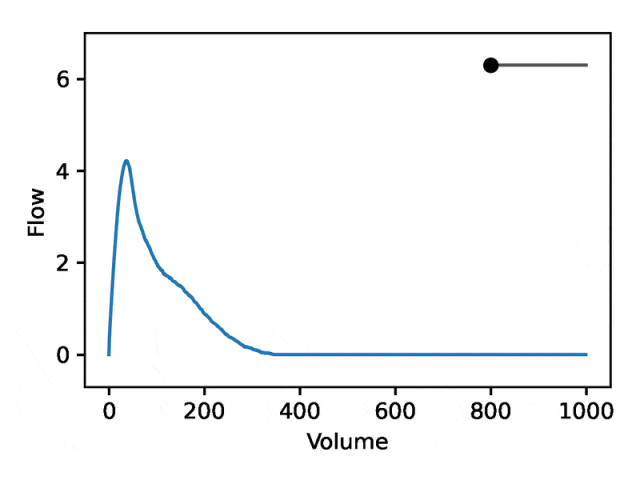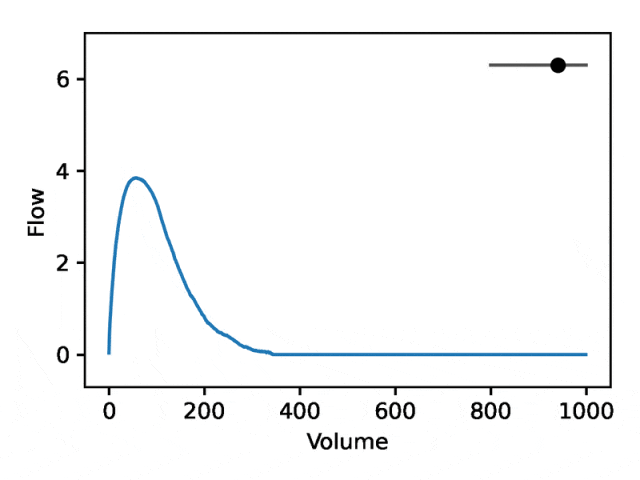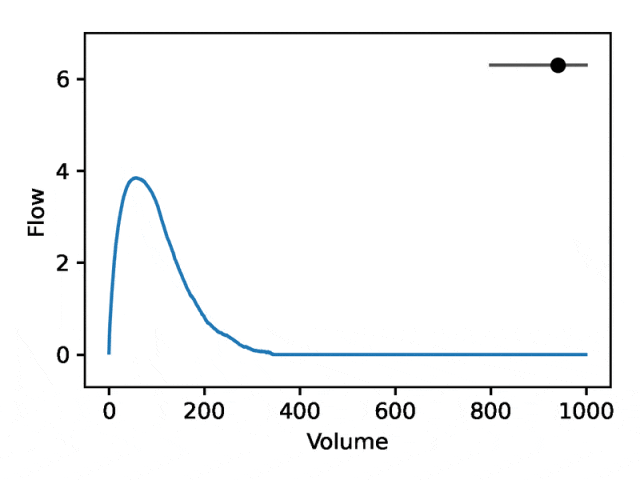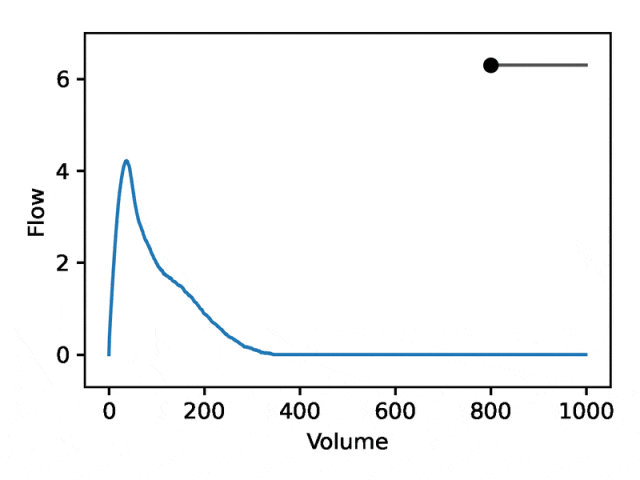
Taking advantage of the generative properties of REGLE, we study the effect of encoding coordinates on spirometry by fixing the value of expert-defined features and changing one encoding coordinate while keeping the other encoding coordinates zero. Effect of shape. Then, the corresponding spirometry map is generated using only the decoder part of the trained model.
A typical flow-volume spirometry consists of two distinct parts: (1) the relatively short section to reach peak flow, where flow increases monotonically with increasing volume; (2) the main part of the spirometry section, where the flow rate decreases monotonically.
The image below shows that changing the first coordinate is equivalent to expanding or shrinking the second part (negative slope) while keeping the first part relatively fixed. In fact, the concavity in the second part of the curve, which pulmonologists refer to as a dip, is an indicator of airway obstruction that is not well represented by the standard EDF.
Elucidating the genetic basis of human traits and diseases
REGLE is an unsupervised learning method that performs genetic analysis, improved novel locus discovery, and risk prediction. Since EDFs are difficult to discover manually at scale, unsupervised learning of HDCD representations is attractive for genome discovery.
The REGLE framework also supports the principled use of these features in modeling by modifying traditional VAE architectures. REGLE is demonstrated in two clinical data modalities (spirometry and PPG), which can be measured routinely in clinical settings or passively and non-invasively via smartphones or wearable devices.
REGLE provides a mechanism to identify genetic influences on organ function without labeled data and allows the incorporation of expert features into the model. It also provides a way to create disease- and trait-specific PRS using few labels. In the future, approaches like this will increasingly be used to further elucidate the genetic basis of human traits and diseases.
Reference content: https://research.google/blog/harnessing-hidden-genetic-information-in-clinical-data-with-regle/
위 내용은 효율성이 높고 라벨이 필요 없는 Google 팀은 AI를 사용하여 임상 데이터를 마이닝하고 유전자 발견 및 질병 예측을 개선하며 Nature 하위 저널에 게재됩니다.의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

