Java basic syntax
A Java program can be thought of as a collection of objects that work together by calling each other's methods. The following briefly introduces the concepts of classes, objects, methods and instance variables.
Object: An object is an instance of a class and has state and behavior. For example, a dog is an object. Its status includes: color, name, and breed; its behaviors include: wagging its tail, barking, eating, etc.
Class: A class is a template that describes the behavior and status of a type of object.
Method: Method is behavior, and a class can have many methods. Logical operations, data modification, and all actions are completed in methods.
Instance variables: Each object has unique instance variables, and the state of the object is determined by the values of these instance variables.
The first Java program
Look at a simple Java program that will print a stringHello World
Instance
public class HelloWorld {
/* 第一个Java程序
* 它将打印字符串 Hello World
*/
public static void main(String []args) {
System.out.println("Hello World"); // 打印 Hello World
}
}Run Instance»
Click the "Run Instance" button to view the online instance
The following will introduce step by step how to save, compile and run this program:
Open Notepad and add the above code;
Save the file name as: HelloWorld.java;
Open the cmd command window and enter the location of the target file, assuming it is C:\
Type javac HelloWorld.java in the command line window and press enter to compile the code. If there are no errors in the code, the cmd command prompt will go to the next line. (Assuming the environment variables are all set).
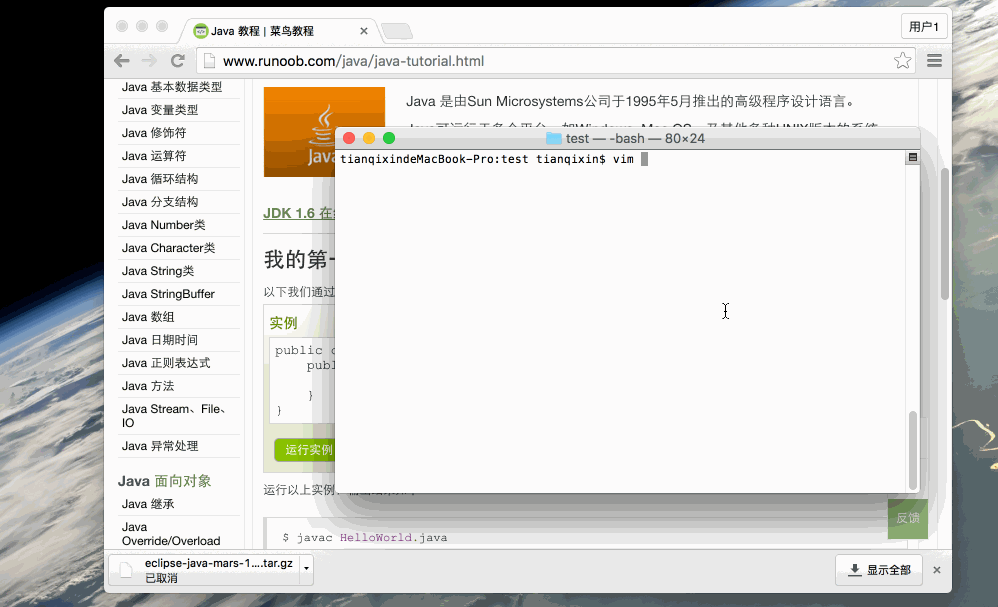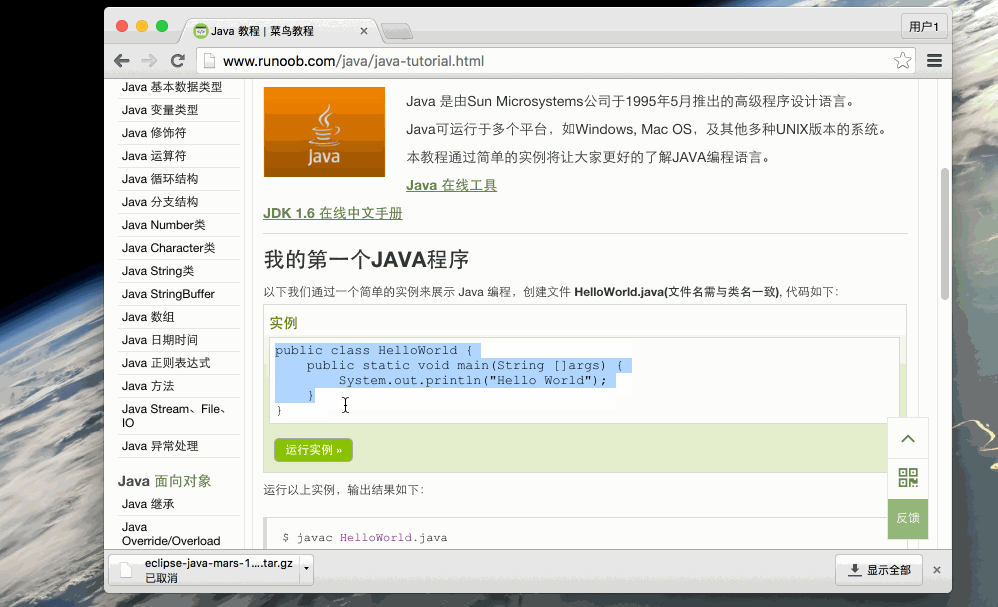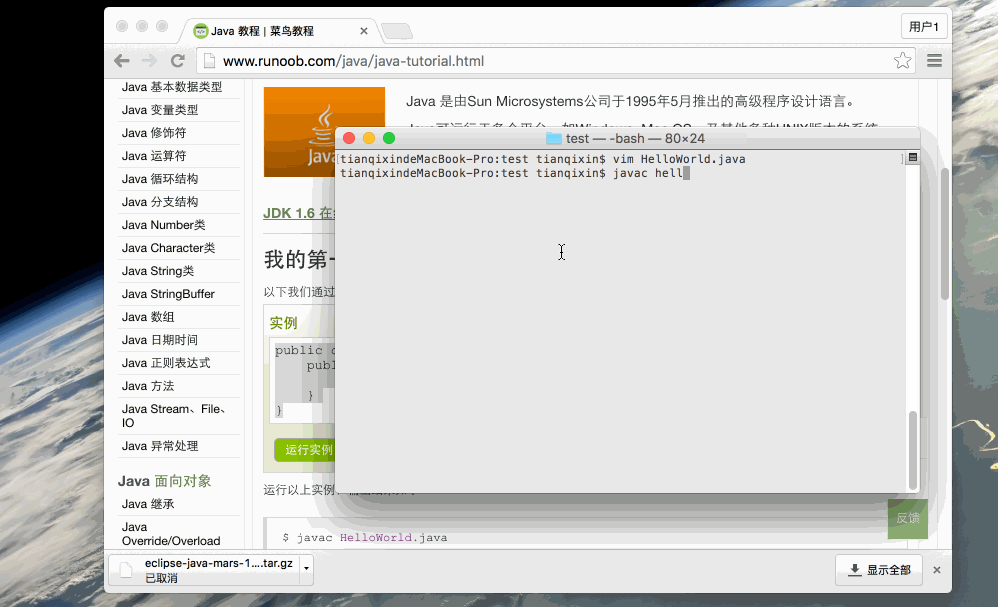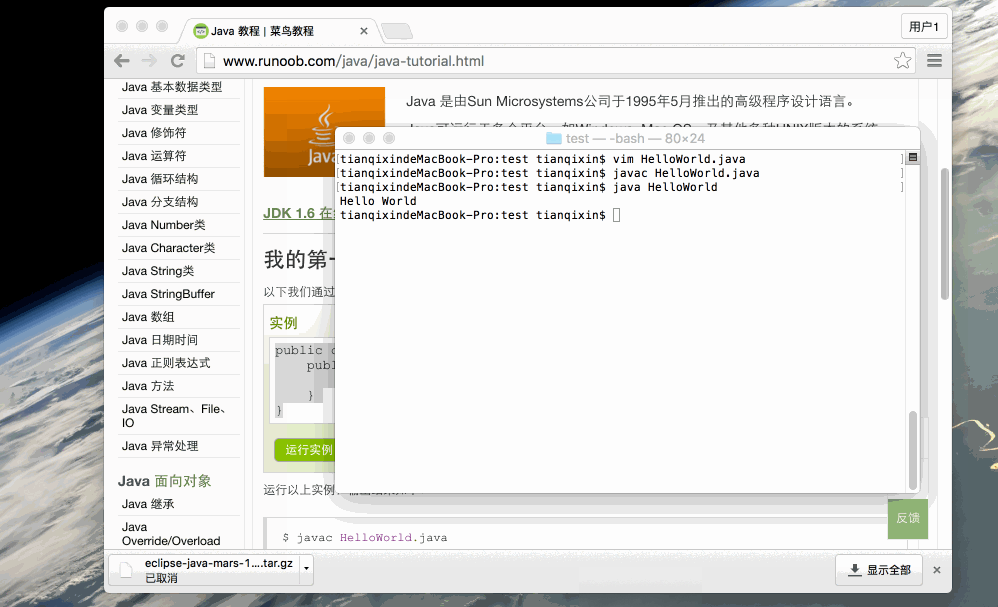
Then type java HelloWorld and press the Enter key to run the program
You will see Hello World
C : > javac HelloWorld.java C : > java HelloWorld Hello World
Gif picture demonstration in the window:
Basic syntax
When writing Java programs, you should pay attention to the following points:
Case sensitive: Java is Case-sensitive, which means that the identifiers Hello and hello are different.
Class name: For all classes, the first letter of the class name should be capitalized. If the class name consists of several words, the first letter of each word should be capitalized, for example, MyFirstJavaClass .
Method name: All method names should start with a lowercase letter. If the method name contains several words, the first letter of each subsequent word is capitalized.
Source file name: The source file name must be the same as the class name. When saving the file, you should use the class name as the filename (remember Java is case-sensitive) and the filename suffix .java. (If the file name and class name are different, a compilation error will occur).
Main method entrance: All Java programs start execution from the public static void main(String []args) method.
Java identifier
All components of Java require names. Class names, variable names, and method names are all called identifiers.
Regarding Java identifiers, there are the following points to note:
All identifiers should start with a letter (A-Z or a-z), a dollar sign ($), or an underscore (_)
After the first character, there can be any combination of characters
Keywords cannot be used as identifiers
Identifiers are case sensitive
Examples of legal identifiers: age, $salary, _value, __1_value
- ## Examples of illegal identifiers: 123abc, -salary
Java modifier Like other languages, Java can use modifiers to modify methods and properties in classes. There are two main types of modifiers:
- Accessible modifiers: default, public, protected, private
- Inaccessible modifiers: final, abstract, strictfp
Java variables
There are mainly the following types of variables in Java
- Local variables
- Class variables (static variables)
- Member variables (non-static variables)
Java arrayArrays are objects stored on the heap and can store multiple variables of the same type. In later chapters, we will learn how to declare, construct, and initialize an array.
Java EnumerationJava 5.0 introduced enumeration, which limits variables to preset values. Using enumerations can reduce bugs in your code. For example, we design a program for a juice shop that will limit juice to small, medium, and large cups. That means it doesn't allow customers to order juices other than those three sizes.
Example
class FreshJuice {
enum FreshJuiceSize{ SMALL, MEDUIM, LARGE }
FreshJuiceSize size;
}
public class FreshJuiceTest {
public static void main(String []args){
FreshJuice juice = new FreshJuice();
juice.size = FreshJuice. FreshJuiceSize.MEDUIM ;
}
}
Note: Enumerations can be declared individually or inside a class. Methods, variables, and constructors can also be defined in enumerations.
Java KeywordsJava reserved words are listed below. These reserved words cannot be used in the names of constants, variables, and any identifiers. ##default Default branch in switch statement#doLoop statement, the loop body will be executed at least oncedouble64-bit double precision floating point numberelseThe branch executed when the condition is not trueenumEnumeration typeextendsIndicates that one class is a subclass of another classfinalIndicates that a value cannot be changed after initializationfinallyDesigned to complete the execution of the code, mainly for the robustness and integrity of the program, the code will be executed regardless of whether an exception occurs. float32-bit single precision floating point numberforfor loop statementgotoNot usedifConditional statementimplementsIndicates that a class implements the interfaceimportImport classinstanceofTest whether an object is an instance of a classint32-bit integerinterfaceInterface, an abstract type with only definitions of methods and constantslong64-bit integernativeIndicates that the method is implemented in non-java codenewAllocates a new class instancepackageA series of related classes form a packageprivateIndicates private fields, methods, etc. Can only be accessed from within the classprotectedIndicates that the field can only be accessed through the class or its subclassespublicIndicates shared properties or methodsreturnMethod return valueshort16-digit numberstatic represents a strictfpFloating point comparison uses strict rulessuperRepresents the base classswitchSelect statementsynchronizedRepresents a code block that can only be accessed by one thread at the same timethis means calling the current instance
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| abstract | Abstract method, abstract class modifier |
| assert | Assert whether the condition is met |
| boolean | Boolean data type |
| break | Break out of the loop or label code segment |
| byte | 8-bit signed data type |
| case | A condition of the switch statement |
| catch | Combined with try to capture exception information |
| char | 16-bit Unicode character data type |
| class | Definition class |
| const | Unused |
| continue | Do not execute the remainder of the loop |
| Indicates that a method cannot be overridden, or a class cannot have subclasses | |
| Subclasses or other classes in the same package | |
| defined at the class level and shared by all instances | |
| Or call another constructor | |
| throw | throws exception |
| throws | define method possible Thrown exception |
| transient | Modify fields not to be serialized |
| try | Indicates the code If the block needs to handle exceptions or cooperate with finally to indicate whether an exception is thrown, the code in finally will be executed |
| void | The marked method does not return any value |
| volatile | Marked fields may be accessed by multiple threads at the same time without synchronization |
| while | while loop |
Java comments
Similar to C/C++, Java also supports single-line and multi-line comments. Characters in comments will be ignored by the Java compiler.
public class HelloWorld {
/* 这是第一个Java程序
*它将打印Hello World
* 这是一个多行注释的示例
*/
public static void main(String []args){
// 这是单行注释的示例
/* 这个也是单行注释的示例 */
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}Java Blank lines
Blank lines or lines with comments will be ignored by the Java compiler.
Inheritance
In Java, a class can be derived from other classes. If you are creating a class and there is already a class that has the properties or methods you need, then you can inherit the newly created class from that class.
Using inheritance methods, you can reuse methods and properties of existing classes without having to rewrite these codes. The inherited class is called a super class, and the derived class is called a subclass.
Interface
In Java, an interface can be understood as a protocol for communication between objects. Interfaces play a very important role in inheritance.
The interface only defines the methods to be used by the derived class, but the specific implementation of the method completely depends on the derived class.
The next section introduces classes and objects in Java programming. Afterwards you will have a clearer understanding of classes and objects in Java.








