Original title: RoadBEV: Road Surface Reconstruction in Bird's Eye View
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.06605.pdf
Code link: https ://github.com/ztsrxh/RoadBEV
Author affiliation: Tsinghua University, University of California, Berkeley

## Paper idea:
Road surface conditions, especially geometric contours, greatly affect the driving ability of autonomous vehicles. Vision-based online road reconstruction is expected to capture road information in advance. Existing solutions such as monocular depth estimation and stereo vision estimation have their limitations. Recent bird's-eye view (BEV) perception technology provides tremendous motivation for more reliable and accurate reconstruction. This paper uniformly proposes two effective BEV road elevation reconstruction models, named RoadBEV-mono and RoadBEV-stereo respectively, which are different from the use of monocular and binocular images for road elevation estimation. The former estimates road elevation directly from a single image, while the latter estimates road elevation using left and right volumetric views. In-depth analysis reveals their consistency and differences with the perspectives. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the model. The elevation errors of RoadBEV-mono and RoadBEV-stereo are 1.83 meters and 0.56 meters respectively. The performance of BEV estimation based on monocular images is improved by 50%. The model in this article is expected to provide a valuable reference in vision-based autonomous driving technology.Main contributions:
This paper demonstrates for the first time the necessity and superiority of road surface reconstruction from a bird's-eye perspective from both theoretical and experimental aspects. This article introduces two models, named RoadBEV-mono and RoadBEV-stereo. For monocular and stereo based schemes, this article explains their mechanisms in detail. This paper comprehensively tests and analyzes the performance of the proposed model, providing valuable insights and prospects for future research.Network Design:
In recent years, the rapid development of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) has put forward higher requirements for vehicle-mounted perception systems. Real-time understanding of the driving environment and conditions is crucial for accurate motion planning and control [1]-[3]. For vehicles, roads are the only medium of contact with the physical world. Road surface conditions determine many vehicle characteristics and drivability [4]. As shown in Figure 1(a), road irregularities, such as bumps and potholes, will exacerbate the riding experience of the vehicle, which is intuitively perceptible. Real-time road surface condition perception, especially geometric elevation, greatly helps improve ride comfort [5], [6]. Compared with other perception tasks in unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) such as segmentation and detection, road surface reconstruction (RSR) is an emerging technology that has received increasing attention recently. Similar to existing perception processes, RSR typically utilizes onboard LiDAR and camera sensors to retain road surface information. LiDAR directly scans road contours and derives point clouds [7], [8]. Road elevation on vehicle trajectories can be extracted directly without complex algorithms. However, the high cost of lidar sensors limits their application in economical mass-produced vehicles. Unlike larger traffic objects such as vehicles and pedestrians, road irregularities are typically small in magnitude, so the accuracy of the point cloud is critical. Motion compensation and filtering are required on real-time road scanning, which further requires high-precision positioning at the centimeter level. Image-based road surface reconstruction (RSR), as a three-dimensional vision task, is more promising than LiDAR in terms of accuracy and resolution. It also retains the road surface texture, making the road perception more comprehensive. Vision-based road elevation reconstruction is actually a depth estimation problem. For monocular cameras, monocular depth estimation can be implemented based on a single image, or multi-view stereo (MVS) can be implemented based on sequences to directly estimate depth [9]. For binocular cameras, binocular matching regresses disparity maps, which can be converted to depth [10], [11]. Given the camera parameters, the road point cloud in the camera coordinate system can be recovered. Through a preliminary post-processing process, road structure and elevation information are finally obtained. Under the guidance of ground-truth (GT) labels, high-precision and reliable RSR can be achieved.However, road surface reconstruction (RSR) from the image perspective has inherent shortcomings. The depth estimation for a specific pixel is actually to find optimal bins along the direction perpendicular to the image plane (shown as the orange point in Figure 1(b)). There is a certain angular deviation between the depth direction and the road surface. Changes and trends in road profile features are inconsistent with changes and trends in the search direction. Information cues about road elevation changes are sparse in the depth view. Furthermore, the depth search range is the same for each pixel, causing the model to capture global geometric hierarchy rather than local surface structure. Due to the global but coarse depth search, fine road elevation information is destroyed. Since this paper focuses on elevation in the vertical direction, the effort in the depth direction is wasted. In perspective views, texture details at long distances are lost, which further poses challenges for efficient depth regression unless further a priori constraints are introduced [12].
Estimating road elevation from a top view (i.e., bird's eye view, BEV) is a natural idea because elevation essentially describes vibrations in the vertical direction. Bird's eye view is an effective paradigm for representing multi-modal and multi-view data in unified coordinates [13], [14]. Recent state-of-the-art performance on 3D object detection and segmentation tasks was achieved by approaches based on bird's-eye views [15], as opposed to perspective views, which are performed by introducing estimated heads on view-transformed image features. Figure 1 illustrates the motivation for this paper. Instead of focusing on the global structure in the image view, the reconstruction in the bird's-eye view directly identifies road features within a specific small range in the vertical direction. Road features projected in a bird's-eye view densely reflect structural and contour changes, facilitating efficient and refined searches. The influence of perspective effects is also suppressed because roads are represented uniformly on a plane perpendicular to the viewing angle. Road reconstruction based on bird's-eye view features is expected to achieve higher performance.
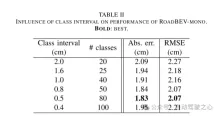
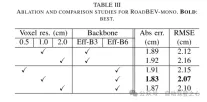
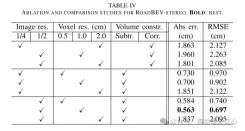
This paper reconstructs the road surface under BEV to solve the problems identified above. In particular, this paper focuses on road geometry, namely elevation. In order to utilize monocular and binocular images and demonstrate the broad feasibility of bird's-eye view perception, this paper proposes two sub-models named RoadBEV-mono and RoadBEV-stereo. Following the paradigm of a bird's eye view, this paper defines voxels of interest covering potential road relief. These voxels query pixel features through 3D-2D projection. For RoadBEV-mono, this paper introduces a height estimation head on the reshaped voxel features. The structure of RoadBEV-stereo is consistent with binocular matching in image views. Based on the left and right voxel features, a 4D cost volume is constructed in the bird's-eye view, which is aggregated through 3D convolution. Elevation regression is considered as a classification of predefined bins to enable more efficient model learning. This paper validates these models on a real-world dataset previously published by the authors, showing that they have huge advantages over traditional monocular depth estimation and stereo matching methods.
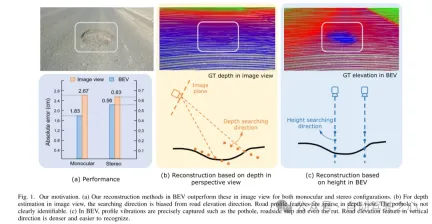
Figure 1. Motivation for this article. (a) Regardless of monocular or binocular configuration, our reconstruction method in bird's-eye view (BEV) outperforms the method in image view. (b) When performing depth estimation in the image view, the search direction is biased from the road elevation direction. In the depth view, road outline features are sparse. Potholes are not easily identified. (c) In a bird's-eye view, contour vibrations such as potholes, curb steps and even ruts can be accurately captured. Road elevation features in the vertical direction are denser and easier to identify.
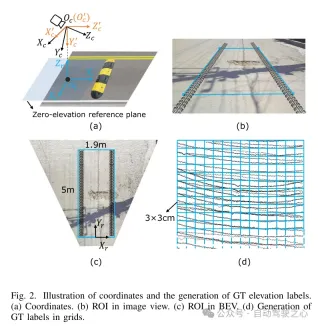
Figure 2. Coordinate representation and generation of true value (GT) elevation labels. (a) Coordinates (b) Region of interest (ROI) in image view (c) Region of interest (ROI) in bird's eye view (d) Generating ground truth (GT) labels in grid

Figure 3. Example of road image and ground truth (GT) elevation map.
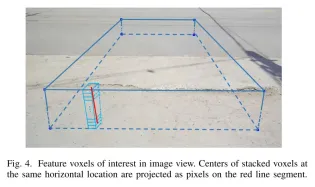
Figure 4. Feature voxels of interest in image view. The centers of stacked voxels located at the same horizontal position are projected to pixels on the red line segment.
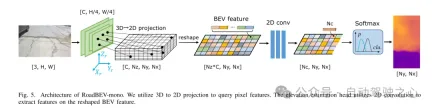
Figure 5. Architecture of RoadBEV-mono. This paper uses 3D to 2D projection to query pixel features. The elevation estimation head uses 2D convolution to extract features on the reshaped Bird's Eye View (BEV) features.
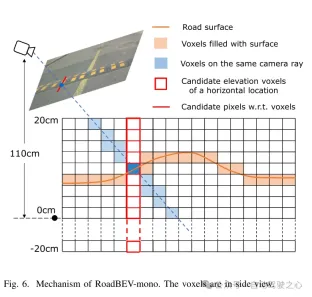
図6. RoadBEV-monoの仕組み。ボクセルは側面図で表示されます。
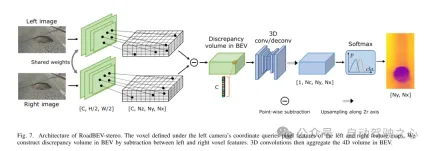
図 7. RoadBEV ステレオ アーキテクチャ。左カメラ座標系で定義されたボクセルは、左右の特徴マップのピクセル特徴を照会します。この論文では、左右のボクセル特徴間の減算を通じて鳥瞰図 (BEV) の差分ボリュームを構築します。次に、3D コンボリューションにより、鳥瞰図で 4D ボリュームが集約されます。
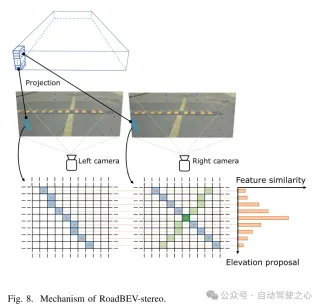
図 8. RoadBEV ステレオのメカニズム。
実験結果:
図 9. (a) RoadBEV モノラルと (b) RoadBEV ステレオのトレーニング損失。
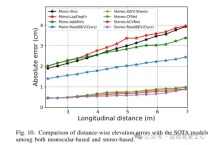
図 10. 単眼と両眼に基づく SOTA モデルとの距離方向の標高誤差の比較。
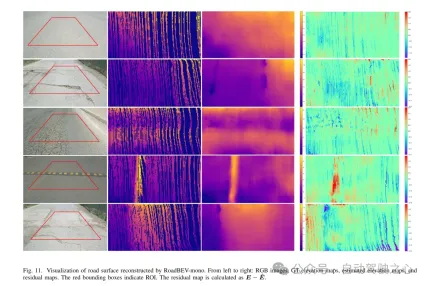
図 11. RoadBEV-mono によって再構築された路面の可視化。
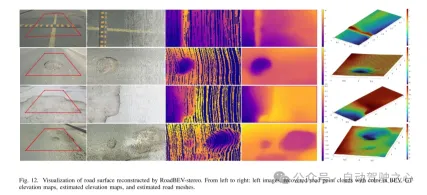
図 12. RoadBEV ステレオによって再構築された路面の視覚化。
要約:
本稿では初めて路面の高さを鳥瞰図で再現しました。この論文では、それぞれ RoadBEV-mono と RoadBEV-stereo と名付けられた、単眼画像と両眼画像に基づく 2 つのモデルを提案し、分析します。この論文では、BEV における単眼推定と両眼マッチングは透視図と同じメカニズムであり、探索範囲を狭め、標高方向に直接特徴をマイニングすることで改善されることを発見しました。現実世界のデータセットでの包括的な実験により、提案された BEV ボリューム、推定ヘッド、パラメーター設定の実現可能性と優位性が検証されます。単眼カメラの場合、BEV での再構成パフォーマンスは、透視図と比較して 50% 向上します。同時に、BEVでは、双眼カメラを使用した場合の性能が単眼カメラの3倍になります。この記事では、モデルに関する詳細な分析とガイダンスを提供します。この記事の画期的な探求は、BEV 知覚、3D 再構成、および 3D 検出に関連するさらなる研究と応用のための貴重な参考資料も提供します。
以上が清華の最新作! RoadBEV: BEV で路面の再構築をどのように実現するか?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
 Microsoft Work Trend Index 2025は、職場の容量の緊張を示していますApr 24, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Microsoft Work Trend Index 2025は、職場の容量の緊張を示していますApr 24, 2025 am 11:19 AMAIの急速な統合により悪化した職場での急成長能力の危機は、増分調整を超えて戦略的な変化を要求します。 これは、WTIの調査結果によって強調されています。従業員の68%がワークロードに苦労しており、BURにつながります
 AIは理解できますか?中国の部屋の議論はノーと言っていますが、それは正しいですか?Apr 24, 2025 am 11:18 AM
AIは理解できますか?中国の部屋の議論はノーと言っていますが、それは正しいですか?Apr 24, 2025 am 11:18 AMジョン・サールの中国の部屋の議論:AIの理解への挑戦 Searleの思考実験は、人工知能が真に言語を理解できるのか、それとも真の意識を持っているのかを直接疑問に思っています。 チャインを無知な人を想像してください
 中国の「スマート」AIアシスタントは、マイクロソフトのリコールのプライバシーの欠陥をエコーしますApr 24, 2025 am 11:17 AM
中国の「スマート」AIアシスタントは、マイクロソフトのリコールのプライバシーの欠陥をエコーしますApr 24, 2025 am 11:17 AM中国のハイテク大手は、西部のカウンターパートと比較して、AI開発の別のコースを図っています。 技術的なベンチマークとAPI統合のみに焦点を当てるのではなく、「スクリーン認識」AIアシスタントを優先しています。
 Dockerは、おなじみのコンテナワークフローをAIモデルとMCPツールにもたらしますApr 24, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Dockerは、おなじみのコンテナワークフローをAIモデルとMCPツールにもたらしますApr 24, 2025 am 11:16 AMMCP:AIシステムに外部ツールにアクセスできるようになります モデルコンテキストプロトコル(MCP)により、AIアプリケーションは標準化されたインターフェイスを介して外部ツールとデータソースと対話できます。人類によって開発され、主要なAIプロバイダーによってサポートされているMCPは、言語モデルとエージェントが利用可能なツールを発見し、適切なパラメーターでそれらを呼び出すことができます。ただし、環境紛争、セキュリティの脆弱性、一貫性のないクロスプラットフォーム動作など、MCPサーバーの実装にはいくつかの課題があります。 Forbesの記事「人類のモデルコンテキストプロトコルは、AIエージェントの開発における大きなステップです」著者:Janakiram MSVDockerは、コンテナ化を通じてこれらの問題を解決します。 Docker Hubインフラストラクチャに基づいて構築されたドキュメント
 6億ドルのスタートアップを構築するために6つのAIストリートスマート戦略を使用するApr 24, 2025 am 11:15 AM
6億ドルのスタートアップを構築するために6つのAIストリートスマート戦略を使用するApr 24, 2025 am 11:15 AM最先端のテクノロジーと巧妙なビジネスの洞察力を活用して、コントロールを維持しながら非常に収益性の高いスケーラブルな企業を作成する先見の明のある起業家によって採用された6つの戦略。このガイドは、建設を目指している起業家向けのためのものです
 Googleフォトの更新は、すべての写真の見事なウルトラHDRのロックを解除しますApr 24, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Googleフォトの更新は、すべての写真の見事なウルトラHDRのロックを解除しますApr 24, 2025 am 11:14 AMGoogle Photosの新しいウルトラHDRツール:画像強化のゲームチェンジャー Google Photosは、強力なウルトラHDR変換ツールを導入し、標準的な写真を活気のある高ダイナミックレンジ画像に変換しました。この強化は写真家に利益をもたらします
 Descopeは、AIエージェント統合の認証フレームワークを構築しますApr 24, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Descopeは、AIエージェント統合の認証フレームワークを構築しますApr 24, 2025 am 11:13 AM技術アーキテクチャは、新たな認証の課題を解決します エージェントアイデンティティハブは、AIエージェントの実装を開始した後にのみ多くの組織が発見した問題に取り組んでいます。
 Google Cloud Next2025と現代の仕事の接続された未来Apr 24, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Google Cloud Next2025と現代の仕事の接続された未来Apr 24, 2025 am 11:12 AM(注:Googleは私の会社であるMoor Insights&Strategyのアドバイザリークライアントです。) AI:実験からエンタープライズ財団まで Google Cloud Next 2025は、実験機能からエンタープライズテクノロジーのコアコンポーネント、ストリームへのAIの進化を紹介しました


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

Dreamweaver Mac版
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

VSCode Windows 64 ビットのダウンロード
Microsoft によって発売された無料で強力な IDE エディター

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser は、オンライン試験を安全に受験するための安全なブラウザ環境です。このソフトウェアは、あらゆるコンピュータを安全なワークステーションに変えます。あらゆるユーティリティへのアクセスを制御し、学生が無許可のリソースを使用するのを防ぎます。

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

ホットトピック
 7694
7694 15
15 1640
1640 14
14 1393
1393 52
52 1287
1287 25
25 1229
1229 29
29



