ループスケジューリング用のCプログラム
- 王林転載
- 2023-09-25 17:09:02989ブラウズ
n 個のプロセスと、それらに対応するバースト時間とタイム クォンタムが与えられます。タスクは、平均待機時間と平均ターンアラウンド タイムを見つけて、結果を表示することです。
ラウンド ロビンとはスケジューリング?
ラウンド ロビンは、特にタイム シェアリング システム用に設計された CPU スケジューリング アルゴリズムです。これは、FCFS スケジューリング アルゴリズムに似ていますが、ラウンド ロビン プロセスでは量子時間サイズで制限される点が 1 つ変更されています。小さな時間単位は、タイム クォンタムまたはタイム スライスとして知られています。タイム クォンタムの範囲は 10 ~ 100 ミリ秒です。 CPU は、レディ キューを、指定されたタイム スライスでプロセスを実行するための循環キューとして扱います。プロセスに固定時間が割り当てられるため、プリエンプティブなアプローチに従います。唯一の欠点は、コンテキスト切り替えのオーバーヘッドです。
何を計算する必要がありますか?
完了時間は、プロセスに必要な時間です。実行を完了するまでの時間です。
ターンアラウンド タイムは、プロセスの送信から完了までの時間間隔です。
ターンアラウンド タイム = プロセスの完了 - プロセスの送信
待機時間はターンアラウンド タイムとバースト タイムの差です。
待機時間 = ターンアラウンド タイム – バースト タイム
例
3 つのプロセスが与えられています。 P1、P2、および P3 (対応するバースト時間は 24、3、および 3)
| バースト時間 | |
|---|---|
| 24 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |
平均待ち時間 = 17/3 = 5.66 ミリ秒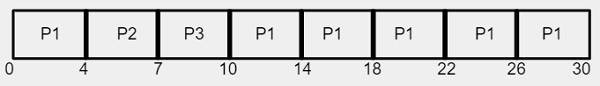
アルゴリズム
Start
Step 1-> In function int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i]
return 1
Step 2-> In function int waitingtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int quantum)
Declare rem_bt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rem_bt[i] = bt[i]
Set t = 0
Loop While (1)
Set done = true
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
If rem_bt[i] > 0 then,
Set done = false
If rem_bt[i] > quantum then,
Set t = t + quantum
Set rem_bt[i] = rem_bt[i] - quantum
Else
Set t = t + rem_bt[i]
Set wt[i] = t - bt[i]
Set rem_bt[i] = 0
If done == true then,
Break
Step 3->In function int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int quantum)
Declare and initialize wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call function waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum)
Call function turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat)
Print "Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time "
Loop For i=0 and i<n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print the value i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]
Print "Average waiting time = total_wt / n
Print "Average turnaround time =total_tat / n
Step 4-> In function int main()
Delcare and initialize processes[] = { 1, 2, 3}
Declare and initialize n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0]
Declare and initialize burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12}
Set quantum = 2
Call function findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum)例 例の演示
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate turn around time
int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int tat[]) {
// calculating turnaround time by adding
// bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i];
return 1;
}
// Function to find the waiting time for all
// processes
int waitingtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int quantum) {
// Make a copy of burst times bt[] to store remaining
// burst times.
int rem_bt[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
rem_bt[i] = bt[i];
int t = 0; // Current time
// Keep traversing processes in round robin manner
// until all of them are not done.
while (1) {
bool done = true;
// Traverse all processes one by one repeatedly
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// If burst time of a process is greater than 0
// then only need to process further
if (rem_bt[i] > 0) {
done = false; // There is a pending process
if (rem_bt[i] > quantum) {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t += quantum;
// Decrease the burst_time of current process
// by quantum
rem_bt[i] -= quantum;
}
// If burst time is smaller than or equal to
// quantum. Last cycle for this process
else {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t = t + rem_bt[i];
// Waiting time is current time minus time
// used by this process
wt[i] = t - bt[i];
// As the process gets fully executed
// make its remaining burst time = 0
rem_bt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// If all processes are done
if (done == true)
break;
}
return 1;
}
// Function to calculate average time
int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[],
int quantum) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all processes
waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum);
// Function to find turn around time for all processes
turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat);
// Display processes along with all details
printf("Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time</p><p>");
// Calculate total waiting time and total turn
// around time
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
printf("\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d</p><p>",i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]);
}
printf("Average waiting time = %f", (float)total_wt / (float)n);
printf("</p><p>Average turnaround time = %f</p><p>", (float)total_tat / (float)n);
return 1;
}
// main function
int main() {
// process id's
int processes[] = { 1, 2, 3};
int n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0];
// Burst time of all processes
int burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12};
// Time quantum
int quantum = 2;
findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum);
return 0;
}出力
以上がループスケジューリング用のCプログラムの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

