フローチャートと手順を使用して、C で意思決定の概念を説明します。
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB転載
- 2023-09-15 11:05:041467ブラウズ
以下は決定ステートメントです-
- 単純な if ステートメント
- if-else ステートメント
- ネストされた if else ステートメント
- else – ifladder
- switch ステートメント
単純 – if ステートメント
「if」キーワードは、論理条件が true の場合に一連のステートメントを実行するために使用されます。
構文
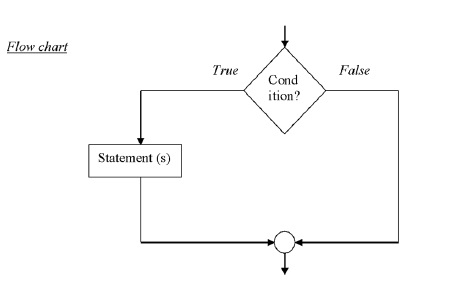
if (condition){
Statement (s)
}
例
次の例では、数値が 50 より大きいかどうかを確認します。
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a;
printf (“enter any number:</p><p>”);
scanf (“%d”, &a);
if (a>50)
printf (“%d is greater than 50”, a);
}出力
1) enter any number: 60 60 is greater than 50 . 2) enter any number 20 no output
if else ステートメント
if else ステートメントは True または False の条件を受け入れます。
構文
if (condition){
True block statement(s)
}
else{
False block statement(s)
}フローチャート
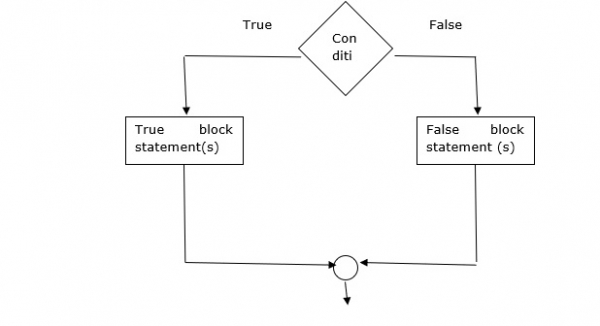
例
次は、奇数と偶数をチェックするプログラムです-
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int n;
printf (“enter any number:</p><p>”);
scanf (“%d”, &n);
if (n%2 ==0)
printf (“%d is even number”, n);
else
printf( “%d is odd number”, n);
}出力
1) enter any number: 10 10 is even number
ネストされた if - else ステートメント
ここでは、「if」が別の if (または) else-
構文の中に配置されています
if (condition1){
if (condition2)
stmt1;
else
stmt2;
}
else{
if (condition3)
stmt3;
else
stmt4;
}フローチャート
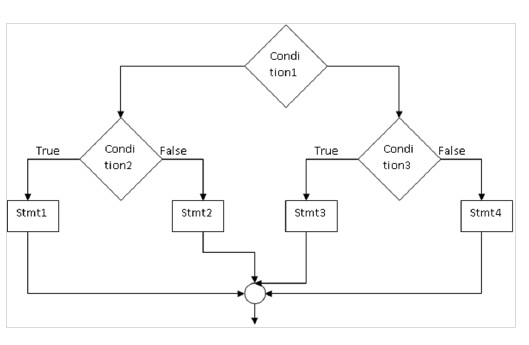
例
次の例は、指定された数値の最大 3 桁を出力します。
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a,b,c;
printf (“enter 3 numbers”);
scanf (“%d%d%d”, &a, &b, &c);
if (a>b){
if (a>c)
printf (“%d is largest”, a);
else
printf (“%d is largest”, c);
} else {
if (b>c)
printf (“%d is largest”, b);
else
printf (“%d is largest”, c);
}
}出力
enter 3 numbers = 10 20 30 30 is largest
Else – ifladder
これは多方向の決定条件です。
構文
if (condition1) stmt1; else if (condition2) stmt2; - - - - - - - - - - else if (condition n) stmt n; else stmt x;
フローチャート
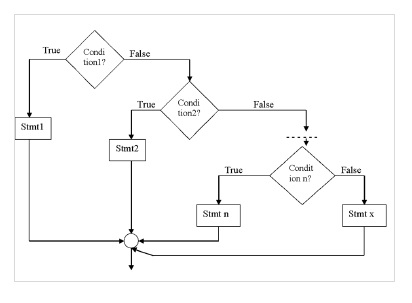
例
次の例では、二次方程式の根を求めます。
#include <math.h>
main (){
int a,b,c,d;
float r1, r2
printf ("enter the values a b c");
scanf (“%d%d%d”, &a, &b, &c);
d= b*b – 4*a*c ;
if (d>0){
r1 = (-b+sqrt(d)) / (2*a);
r2 = (-b-sqrt(d)) / (2*a);
printf (“root1 ,root2 =%f%f”, r1, r2);
}
else if (d== 0){
r1 = -b / (2*a);
r2 = -b/ (2*a);
printf (“root1, root2 = %f%f”, r1, r2);
}
else
printf ("roots are imaginary”);
}出力
1) enter the values of a b c : 1 4 3 Root 1 = -1 Root 2 = -3
Switchステートメント
複数の決定から1つを選択するのに役立ちます。
文法
switch (expression){
case value1 : stmt1;
break;
case value2 : stmt2;
break;
- - - - - -
default : stmt – x;
}文法
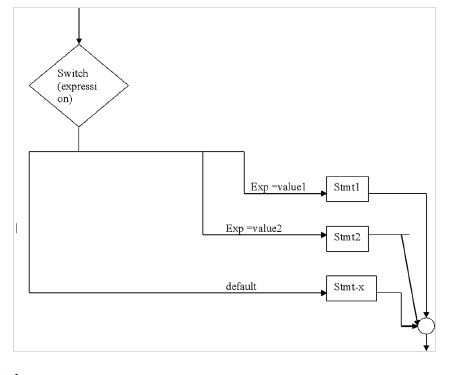
例
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int n;
printf (“enter a number”);
scanf (“%d”, &n);
switch (n){
case 0 : printf (“zero”)
break;
case 1 : printf (‘one”);
break;
default : printf (‘wrong choice”);
}
}出力
enter a number 1 One
以上がフローチャートと手順を使用して、C で意思決定の概念を説明します。の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
声明:
この記事はtutorialspoint.comで複製されています。侵害がある場合は、admin@php.cn までご連絡ください。

