C 言語では、指定されたインデックスのリンク リスト ノードを出力します。
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB転載
- 2023-08-26 21:21:041180ブラウズ
指定されたインデックスにあるリンク リストのノードのデータを出力する必要があります。配列とは異なり、リンク リストには通常インデックスがないため、リンク リスト全体を走査し、特定のデータに到達したときにデータを出力する必要があります。
リストにはノード 29、34、43、56 が含まれているとします。 88 でインデックスの値が 1、2、4 の場合、出力はこれらのインデックスのノード 34、43、88 になります。
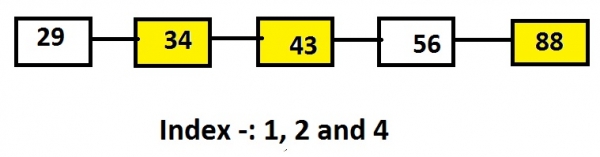
Example
Linked list: 29->34->43->56->88 Input: 1 2 4 Output: 34 43 88
上記のリンク リストの表現では、黄色で強調表示されたノードは、出力されるノード、または特定のインデックスにあるノードです。
ここで使用されるアプローチには、1 つのポインターと 1 つのカウンタ変数を初期化することが含まれます。ノードを通過するたびに増加する 1。カウンタはキーの値と一致します。キーがカウンタ値と一致すると、ノード構造を指すポインタがノードのデータを出力し、次のノードにインクリメントされるなどして、特定のキーのノードが得られます。
以下のコードは、次の C 実装を示しています。与えられたアルゴリズム。
アルゴリズム
START
Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure
Declare int data
Declare pointer of type node using *next
Step 2 -> create struct node* intoList(int data)
Create newnode using malloc
Set newnode->data = data
newnode->next = NULL
return newnode
step 3 -> Declare function void displayList(struct node *catchead)
create struct node *temp
IF catchead = NULL
Print list is empty
return
End
Set temp = catchead
Loop While (temp != NULL)
print temp->data
set temp = temp->next
End
Step 4 -> Declare Function int search(int key,struct node *head)
Set int index
Create struct node *newnode
Set index = 0 and newnode = head
Loop While (newnode != NULL & newnode->data != key)
Set index++
Set newnode = newnode->next
End
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1
step 5 -> In Main()
create node using struct node* head = intoList(9)
call displayList(head)
set index = search(24,head)
IF (index >= 0)
Print index
Else
Print not found in the list
EndIF
STOP例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* intoList(int data) {
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//funtion to display list
void displayList(struct node *catchead) {
struct node *temp;
if (catchead == NULL) {
printf("List is empty.</p><p>");
return;
}
printf("elements of list are : ");
temp = catchead;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("</p><p>");
}
//function to search element
int search(int key,struct node *head) {
int index;
struct node *newnode;
index = 0;
newnode = head;
while (newnode != NULL && newnode->data != key) {
index++;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1;
}
int main() {
int index;
struct node* head = intoList(9); //inserting elements into a list
head->next = intoList(76);
head->next->next = intoList(13);
head->next->next->next = intoList(24);
head->next->next->next->next = intoList(55);
head->next->next->next->next->next = intoList(109);
displayList(head);
index = search(24,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d</p><p>", 24, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.</p><p>", 24);
index=search(55,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d</p><p>", 55, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.</p><p>", 55);
}出力
上のプログラムを実行すると、以下の出力が生成されます。
以上がC 言語では、指定されたインデックスのリンク リスト ノードを出力します。の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
声明:
この記事はtutorialspoint.comで複製されています。侵害がある場合は、admin@php.cn までご連絡ください。

