ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Javaで手書き配布スノーフレークを利用してIDを生成する方法 SnowFlake
Javaで手書き配布スノーフレークを利用してIDを生成する方法 SnowFlake
- PHPz転載
- 2023-04-24 21:34:161113ブラウズ
SnowFlake アルゴリズム
SnowFlake アルゴリズムが ID を生成した結果は 64 ビットの整数であり、その構造は次のとおりです:
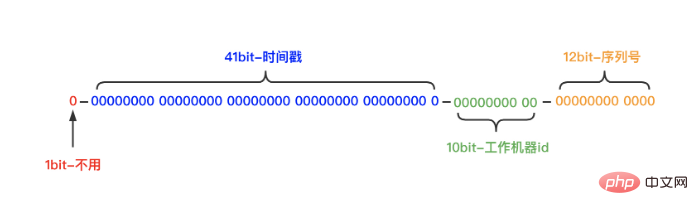
それは分割されます4 つのセクションに分かれています:
最初の段落: ビット 1 は使用されず、常に 0 に固定されます。
(バイナリの最上位ビットは符号ビットであるため、1 は負の数を表し、0 は正の数を表します。生成される ID は通常正の整数であるため、最上位ビットは 0 に固定されます)
2 番目のセグメント: 41 ビットはミリ秒時間 (41 ビットの長さは 69 年間使用できます)
3 番目のセグメント: 10 ビットは workerId (10 ビットの長さは、最大 1024 ノード)
(ここでの 10 桁は 2 つの部分に分かれています。最初の部分の 5 桁はデータセンター ID (0 ~ 31) を表し、2 番目の部分の 5 桁はマシンを表します。 ID (0-31))
4 番目の段落: 12 桁のミリ秒以内のカウント (12 ビットのカウント シーケンス番号は、ミリ秒ごとに 4096 ID シリアル番号を生成する各ノードをサポートします)
コード実装:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class SnowFlake {
//时间 41位
private static long lastTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//数据中心ID 5位(默认0-31)
private long datacenterId = 0;
private long datacenterIdShift = 5;
//机房机器ID 5位(默认0-31)
private long workerId = 0;
private long workerIdShift = 5;
//随机数 12位(默认0~4095)
private AtomicLong random = new AtomicLong();
private long randomShift = 12;
//随机数的最大值
private long maxRandom = (long) Math.pow(2, randomShift);
public SnowFlake() {
}
public SnowFlake(long workerIdShift, long datacenterIdShift){
if (workerIdShift < 0 ||
datacenterIdShift < 0 ||
workerIdShift + datacenterIdShift > 22) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不匹配");
}
this.workerIdShift = workerIdShift;
this.datacenterIdShift = datacenterIdShift;
this.randomShift = 22 - datacenterIdShift - workerIdShift;
this.maxRandom = (long) Math.pow(2, randomShift);
}
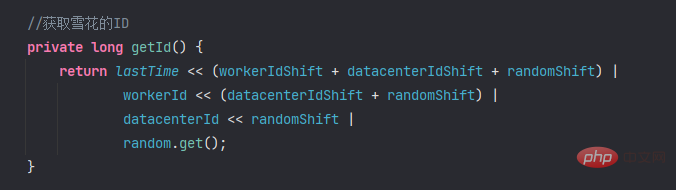
//获取雪花的ID
private long getId() {
return lastTime << (workerIdShift + datacenterIdShift + randomShift) |
workerId << (datacenterIdShift + randomShift) |
datacenterId << randomShift |
random.get();
}
//生成一个新的ID
public synchronized long nextId() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
//如果当前时间和上一次时间不在同一毫秒内,直接返回
if (now > lastTime) {
lastTime = now;
random.set(0);
return getId();
}
//将最后的随机数,进行+1操作
if (random.incrementAndGet() < maxRandom) {
return getId();
}
//自选等待下一毫秒
while (now <= lastTime) {
now = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
lastTime = now;
random.set(0);
return getId();
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
SnowFlake snowFlake = new SnowFlake();
HashSet<Long> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
set.add(snowFlake.nextId());
}
System.out.println(set.size());
}
}コード内の ID を取得するメソッドはビット操作を使用して実装されています
1 | 41 1011 1110 10001001 01011100 00|00000|0 0000 |0000 00000000 / /41 桁の時刻 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|10001|0 0000|0000 00000000 //5 桁のデータセンター ID 0|0000000 0000 0000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|1 1001|0000 00000000 //5 桁のマシン ID または 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|0 0000|000 0 00000000 //12桁のシーケンス生成されたすべての ID時間傾向に従って分散され、分散全体が増加します。 システム内で重複 ID が生成されません (区別するための datacenterId と workerId があるため) SnowFlake の欠点: SnowFlake はタイムスタンプに強く依存しているため、時間の変化はSnowFlake のアルゴリズムでエラーが発生します。------------------------------------------------ -------------------------------------------------- -- 0 |0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|10001|1 1001|0000 00000000 //結果: 910499571847892992
SnowFlake の利点:
以上がJavaで手書き配布スノーフレークを利用してIDを生成する方法 SnowFlakeの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
声明:
この記事はyisu.comで複製されています。侵害がある場合は、admin@php.cn までご連絡ください。

