ロング ポーリングの実装方法を分析する
現在、主要なミドルウェアはすべてロング ポーリング データ インタラクション方式を採用していますが、現在よく使われているのは Nacos コンフィギュレーション センターや RocketMQ Pull (プル モード) メッセージなどです。 、それらはすべてロングポーリング方式を使用して実装されます。たとえば、Nacos 構成センターでは、サーバーはどのようにして構成の変更を感知し、リアルタイムでクライアントにプッシュできるのでしょうか?
ロング ポーリングとショート ポーリング
ロング ポーリングと言えば、その逆もあるはずです。ここではショート ポーリングと呼びましょう。ショート ポーリングについて簡単に紹介します。
ショートポーリングもプルモードです。これは、サーバーのデータが更新されているかどうかに関係なく、クライアントは一定期間ごとにデータのプルを要求することを意味し、更新されたデータが返される場合もあれば、何も返されない場合もあります。構成センターがこの方法を使用すると、次のような問題が発生します。
構成データは頻繁には変更されないため、常にリクエストが送信されると、必然的にサーバーに大きな負荷がかかります。また、データのプッシュにも遅延が発生します (例: 構成は 10 秒ごとに要求されます。構成が 11 秒目に更新される場合、プッシュは 9 秒遅れ、次の要求を待機します。
#)## は、サーバーの圧力と 2 つの間のプッシュ Neutralize で遅延することはできません。ポーリング間隔を短くすると、遅延が減少し、圧力が増加します。ポーリング間隔を増加すると、圧力が減少し、遅延が増加します。
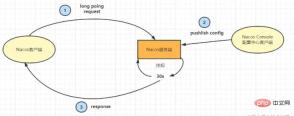
ロング ポーリングショート ポーリングの問題を解決するために、クライアントはロング ポーリングを開始します。サーバー上のデータが変更されない場合、リクエストはサーバー上のデータが変更されるまで保留されます。サーバーが変更されるか、一定時間待ってから戻ってください。戻った後、クライアントはリッスンする次のロング ポーリング リクエストを開始します。
この設計の利点:- 低遅延と比較して、クライアントは長いポーリングを開始し、サーバーはデータの変更を感知した後すぐに応答を返すことができます。 。 クライアント。
- サーバーへの負荷が軽減され、クライアントは長いポーリングを開始します。データが変更されない場合、サーバーはクライアントのリクエストを保留します。リクエストを保留する時間は次のとおりです。通常は 30 秒または 60 秒に設定され、サーバーはサーバー リソースをあまり消費せずにリクエストを保持します。

- まず、クライアントはロング セッションを開始します。ポーリング要求。サーバーがクライアントの要求を受信すると、クライアントの要求を一時停止します。サーバーが設計した 30 秒以内に変更がない場合、サーバーはデータが変更されていないことをクライアントに応答し、クライアントはリクエストを送信し続けます。
- サービス データが 30 秒以内に変更されると、サーバーは変更されたデータをクライアントにプッシュします。 #構成センターのロングポーリング設計
 アイデア全体を上で紹介しました。コードで実装してみましょう:
アイデア全体を上で紹介しました。コードで実装してみましょう:
- まず、クライアントは HTTP リクエストをサーバーに送信します。サーバーは非同期スレッドを開きます。データに変更がない場合、現在のリクエストは一時停止されます (Tomcat には 200 スレッドがあり、長いラウンドが必要です)クエリによって Tomcat のビジネス スレッドがブロックされるべきではないため、構成センターはロング ポーリングを実装するときに非同期応答をよく使用します。非同期 HTTP をより便利に実装する一般的な方法は、Servlet3.0
- によって提供される
AsyncContext メカニズムです。)
サーバーによって設定されたタイムアウト期間内にデータの変更がない場合は、変更されていない識別子がクライアントに返されます。たとえば、ステータス コード 304 に応答します。 - サーバーによって設定されたタイムアウト期間内にデータ変更があった場合、クライアントによって変更された内容が返されます。
- 構成センターのロング ポーリングの実装
@Slf4j
public class ConfigClientWorker {
private final CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
private final ScheduledExecutorService executorService;
public ConfigClientWorker(String url, String dataId) {
this.executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(runnable -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.setName("client.worker.executor-%d");
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
});
// ① httpClient 客户端超时时间要大于长轮询约定的超时时间
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom().setSocketTimeout(40000).build();
this.httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig).build();
executorService.execute(new LongPollingRunnable(url, dataId));
}
class LongPollingRunnable implements Runnable {
private final String url;
private final String dataId;
public LongPollingRunnable(String url, String dataId) {
this.url = url;
this.dataId = dataId;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
String endpoint = url + "?dataId=" + dataId;
log.info("endpoint: {}", endpoint);
HttpGet request = new HttpGet(endpoint);
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request);
switch (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()) {
case 200: {
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(response.getEntity()
.getContent()));
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = rd.readLine()) != null) {
result.append(line);
}
response.close();
String configInfo = result.toString();
log.info("dataId: [{}] changed, receive configInfo: {}", dataId, configInfo);
break;
}
// ② 304 响应码标记配置未变更
case 304: {
log.info("longPolling dataId: [{}] once finished, configInfo is unchanged, longPolling again", dataId);
break;
}
default: {
throw new RuntimeException("unExcepted HTTP status code");
}
}
executorService.execute(this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new ConfigClientWorker("http://127.0.0.1:8080/listener", "user");
System.in.read();
}
}
# #httpClient クライアントのタイムアウトは、ロング ポーリングで合意されたタイムアウト期間より大きくする必要があります。そうでない場合、サーバーが戻る前にクライアントがタイムアウトになります。
304 応答コード タグの構成は変更されていません;
http://127.0.0.1:8080/listener はサーバー アドレスです。
- ##サーバー側の実装
@RestController @Slf4j @SpringBootApplication public class ConfigServer { @Data private static class AsyncTask { // 长轮询请求的上下文,包含请求和响应体 private AsyncContext asyncContext; // 超时标记 private boolean timeout; public AsyncTask(AsyncContext asyncContext, boolean timeout) { this.asyncContext = asyncContext; this.timeout = timeout; } } // guava 提供的多值 Map,一个 key 可以对应多个 value private Multimap<String, AsyncTask> dataIdContext = Multimaps.synchronizedSetMultimap(HashMultimap.create()); private ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("longPolling-timeout-checker-%d") .build(); private ScheduledExecutorService timeoutChecker = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory); // 配置监听接入点 @RequestMapping("/listener") public void addListener(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { String dataId = request.getParameter("dataId"); // 开启异步!!! AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync(request, response); AsyncTask asyncTask = new AsyncTask(asyncContext, true); // 维护 dataId 和异步请求上下文的关联 dataIdContext.put(dataId, asyncTask); // 启动定时器,30s 后写入 304 响应 timeoutChecker.schedule(() -> { if (asyncTask.isTimeout()) { dataIdContext.remove(dataId, asyncTask); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED); // 标志此次异步线程完成结束!!! asyncContext.complete(); } }, 30000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } // 配置发布接入点 @RequestMapping("/publishConfig") @SneakyThrows public String publishConfig(String dataId, String configInfo) { log.info("publish configInfo dataId: [{}], configInfo: {}", dataId, configInfo); Collection<AsyncTask> asyncTasks = dataIdContext.removeAll(dataId); for (AsyncTask asyncTask : asyncTasks) { asyncTask.setTimeout(false); HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)asyncTask.getAsyncContext().getResponse(); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); response.getWriter().println(configInfo); asyncTask.getAsyncContext().complete(); } return "success"; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigServer.class, args); } }
request.startAsync(request, response) ;
Tomcat スレッドが占有されていないことを確認してください。この時点で、Tomcat スレッドがリリースされます。- asyncContext.complete()
- とともに使用されます。
dataId を非同期リクエスト コンテキストに関連付けて、構成とリリースを容易にし、対応するコンテキストを取得しますdataIdContext.put(dataId, asyncTask); -
Map##Multimap<string asynctask> dataIdContext</string>これは複数値の Map です。1 つのキーは複数の値に対応できます。> timeoutChecker.schedule()タイマーを開始し、30 秒後に 304 応答を書き込みます@RequestMapping("/publishConfig"),配置发布的入口。配置变更后,根据 dataId 一次拿出所有的长轮询,为之写入变更的响应。asyncTask.getAsyncContext().complete();表示这次异步请求结束了。
启动配置监听
先启动 ConfigServer,再启动 ConfigClient。30s之后控制台打印第一次超时之后收到服务端304的状态码
16:41:14.824 [client.worker.executor-%d] INFO cn.haoxiaoyong.poll.ConfigClientWorker - longPolling dataId: [user] once finished, configInfo is unchanged, longPolling again
请求一下配置发布,请求localhost:8080/publishConfig?dataId=user&configInfo=helloworld
服务端打印日志:
2022-08-25 16:45:56.663 INFO 90650 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] cn.haoxiaoyong.poll.ConfigServer : publish configInfo dataId: [user], configInfo: helloworld
以上がJavaで単純なロングポーリングを実装するにはどうすればよいですか?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
 プラットフォームの独立性は、エンタープライズレベルのJavaアプリケーションにどのように利益をもたらしますか?May 03, 2025 am 12:23 AM
プラットフォームの独立性は、エンタープライズレベルのJavaアプリケーションにどのように利益をもたらしますか?May 03, 2025 am 12:23 AMJavaは、プラットフォームの独立性により、エンタープライズレベルのアプリケーションで広く使用されています。 1)プラットフォームの独立性は、Java Virtual Machine(JVM)を介して実装されているため、Javaをサポートする任意のプラットフォームでコードを実行できます。 2)クロスプラットフォームの展開と開発プロセスを簡素化し、柔軟性とスケーラビリティを高めます。 3)ただし、パフォーマンスの違いとサードパーティライブラリの互換性に注意を払い、純粋なJavaコードやクロスプラットフォームテストの使用などのベストプラクティスを採用する必要があります。
 プラットフォームの独立性を考慮して、JavaはIoT(Thingのインターネット)デバイスの開発においてどのような役割を果たしますか?May 03, 2025 am 12:22 AM
プラットフォームの独立性を考慮して、JavaはIoT(Thingのインターネット)デバイスの開発においてどのような役割を果たしますか?May 03, 2025 am 12:22 AMjavaplaysasificanificantduetduetoitsplatformindepence.1)itallowscodetobewrittendunonvariousdevices.2)java'secosystemprovidesutionforiot.3)そのセキュリティフィートルセンハンス系
 Javaでプラットフォーム固有の問題に遭遇したシナリオと、どのように解決したかを説明してください。May 03, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Javaでプラットフォーム固有の問題に遭遇したシナリオと、どのように解決したかを説明してください。May 03, 2025 am 12:21 AMTheSolution to HandlefilepathsaCrosswindossandlinuxinjavaistousepaths.get()fromthejava.nio.filepackage.1)usesystem.getProperty( "user.dir")およびhearterativepathtoconstructurctthefilepath.2)
 開発者にとってJavaのプラットフォーム独立性の利点は何ですか?May 03, 2025 am 12:15 AM
開発者にとってJavaのプラットフォーム独立性の利点は何ですか?May 03, 2025 am 12:15 AMjava'splatformentepenceissificAntiveSifcuseDeverowsDevelowSowRitecodeOdeonceantoniTONAnyPlatformwsajvm.これは「writeonce、runanywhere」(wora)adportoffers:1)クロスプラットフォームの複雑性、deploymentacrossdiferentososwithusisues; 2)re
 さまざまなサーバーで実行する必要があるWebアプリケーションにJavaを使用することの利点は何ですか?May 03, 2025 am 12:13 AM
さまざまなサーバーで実行する必要があるWebアプリケーションにJavaを使用することの利点は何ですか?May 03, 2025 am 12:13 AMJavaは、クロスサーバーWebアプリケーションの開発に適しています。 1)Javaの「Write and、Run Averywhere」哲学は、JVMをサポートするあらゆるプラットフォームでコードを実行します。 2)Javaには、開発プロセスを簡素化するために、SpringやHibernateなどのツールを含む豊富なエコシステムがあります。 3)Javaは、パフォーマンスとセキュリティにおいて優れたパフォーマンスを発揮し、効率的なメモリ管理と強力なセキュリティ保証を提供します。
 JVMは、Javaの「Write and、Run Anywhere」(Wora)機能にどのように貢献しますか?May 02, 2025 am 12:25 AM
JVMは、Javaの「Write and、Run Anywhere」(Wora)機能にどのように貢献しますか?May 02, 2025 am 12:25 AMJVMは、バイトコード解釈、プラットフォームに依存しないAPI、動的クラスの負荷を介してJavaのWORA機能を実装します。 2。標準API抽象オペレーティングシステムの違い。 3.クラスは、実行時に動的にロードされ、一貫性を確保します。
 Javaの新しいバージョンは、プラットフォーム固有の問題にどのように対処しますか?May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Javaの新しいバージョンは、プラットフォーム固有の問題にどのように対処しますか?May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AMJavaの最新バージョンは、JVMの最適化、標準的なライブラリの改善、サードパーティライブラリサポートを通じて、プラットフォーム固有の問題を効果的に解決します。 1)Java11のZGCなどのJVM最適化により、ガベージコレクションのパフォーマンスが向上します。 2)Java9のモジュールシステムなどの標準的なライブラリの改善は、プラットフォーム関連の問題を削減します。 3)サードパーティライブラリは、OpenCVなどのプラットフォーム最適化バージョンを提供します。
 JVMによって実行されたバイトコード検証のプロセスを説明します。May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AM
JVMによって実行されたバイトコード検証のプロセスを説明します。May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AMJVMのバイトコード検証プロセスには、4つの重要な手順が含まれます。1)クラスファイル形式が仕様に準拠しているかどうかを確認し、2)バイトコード命令の有効性と正確性を確認し、3)データフロー分析を実行してタイプの安全性を確保し、検証の完全性とパフォーマンスのバランスをとる。これらの手順を通じて、JVMは、安全で正しいバイトコードのみが実行されることを保証し、それによりプログラムの完全性とセキュリティを保護します。


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

MantisBT
Mantis は、製品の欠陥追跡を支援するために設計された、導入が簡単な Web ベースの欠陥追跡ツールです。 PHP、MySQL、Web サーバーが必要です。デモおよびホスティング サービスをチェックしてください。

WebStorm Mac版
便利なJavaScript開発ツール

SecLists
SecLists は、セキュリティ テスターの究極の相棒です。これは、セキュリティ評価中に頻繁に使用されるさまざまな種類のリストを 1 か所にまとめたものです。 SecLists は、セキュリティ テスターが必要とする可能性のあるすべてのリストを便利に提供することで、セキュリティ テストをより効率的かつ生産的にするのに役立ちます。リストの種類には、ユーザー名、パスワード、URL、ファジング ペイロード、機密データ パターン、Web シェルなどが含まれます。テスターはこのリポジトリを新しいテスト マシンにプルするだけで、必要なあらゆる種類のリストにアクセスできるようになります。

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Eclipse を SAP NetWeaver アプリケーション サーバーと統合します。

Dreamweaver Mac版
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

ホットトピック
 7931
7931 15
15 1652
1652 14
14 1412
1412 52
52 1303
1303 25
25 1250
1250 29
29



