ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Java で HttpServer シミュレートされたフロントエンド インターフェイス呼び出しを実装する方法
Java で HttpServer シミュレートされたフロントエンド インターフェイス呼び出しを実装する方法
- PHPz転載
- 2023-04-17 10:28:39785ブラウズ
実行結果の表示
ここでは 2 つの簡単なテスト表示を示し、最後にさらに多くのテスト例を示します。
ルート ディレクトリにアクセスすると、文 (文字列) が返されます (注: グリーン ドラゴンはブラウザでのみ表示され、画像自体もリクエストに属します) .) Content-Type: application/json
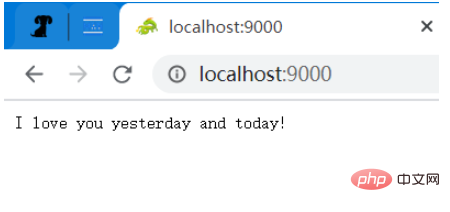
この画像に個別にアクセスすると、戻り値は画像 (バイナリ データ)
リクエストおよびレスポンス設定ファイル
ユーザーが事前にリクエスト情報とレスポンス情報を設定しておけば、特定のリクエストに対して、特定のデータを返すことができます。したがって、この情報を構成するための単純な XML ファイルを設計しました。XML 構成を使用する方が便利です。プロパティ構成ファイルは階層情報を表現できず、単純な構成要件にのみ適用できます。
大きな request_and_responses は多くのリクエストとレスポンスの構成を表し、各 request_and_response ノードは request リクエストと response# を表します## 応答情報。要求と応答に関する基本情報が含まれます。 GET リクエストには主に (method) リクエスト メソッドと (path) リクエスト パスとパラメータが含まれます。 POST メソッドのリクエストには、(param) リクエスト パラメータも含まれています。応答には、content_type (応答コンテンツ タイプ) および value (応答コンテンツ) が含まれます。
GET と POST の違いは、GET のリクエスト パスとリクエスト パラメーターは一緒に (両方ともリクエスト ヘッダー内にあり、リクエスト本文はありません)、POST のリクエスト パラメーターはリクエストボディの場合、リクエストヘッダーとリクエストボディの間に CRLF 分離があります。
xml ファイル<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<request_and_responses>
<!-- & 需要使用转义字符 & -->
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>GET</method>
<path>/</path>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>application/json</content_type>
<value>I love you yesterday and today!</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>GET</method>
<path>/login?account=123&pwd=456</path>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>application/json</content_type>
<value>success</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>GET</method>
<path>/query/龙</path>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>application/json</content_type>
<value>龙是中国等东亚国家古代神话传说生活于海中的神异生物。</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>POST</method>
<path>/login</path>
<param>account=123&pwd=456</param>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>application/json</content_type>
<value>{"result":success}</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>POST</method>
<path>/login</path>
<param>workId=12345</param>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>application/json</content_type>
<value>{"result":"success", "data":{"name":"李工", "sex":"男", "age":35}}</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>GET</method>
<path>/pictures/husky.jpeg</path>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>image/jpeg</content_type>
<value>D:/DB/husky.jpeg</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
<!-- 浏览器访问时的图标 -->
<request_and_response>
<request>
<method>GET</method>
<path>/favicon.ico</path>
</request>
<response>
<content_type>image/webp</content_type>
<value>D:/DB/favicon.ico</value>
</response>
</request_and_response>
</request_and_responses>
xml マップされたエンティティ クラス xml 内の情報がメモリに読み込まれ、エンティティ クラスを使用して情報がカプセル化されます。 package com.dragon;
public class RequestAndResponse {
private String method;
private String path;
private String param;
private String content_type;
private String value;
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getParam() {
return param;
}
public void setParam(String param) {
this.param = param;
}
public String getContent_type() {
return content_type;
}
public void setContent_type(String content_type) {
this.content_type = content_type;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RequestAndResponse [method=" + method + ", path=" + path + ", param=" + param + ", content_type="
+ content_type + ", value=" + value + "]";
}
}xml ファイル パーサー クラスクラスを使用して XML ファイルを Java オブジェクトに解析し、List コレクションを使用してすべてのオブジェクトを保存します。
注: 私は名前を付けるのがあまり得意ではありません。少し長すぎるので、これで間に合わせます。ははは。 注: ここでは、XML 解析用の jar パッケージ dom4j が使用されています。
package com.dragon;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
/**
* 解析 xml 文件中配置的用户请求和响应数据。
* */
public class RequestAndResponseResolver {
private static final String method = "method";
private static final String path = "path";
private static final String param = "param";
private static final String content_type = "content_type";
private static final String value = "value";
public static List<RequestAndResponse> listRequestAndResponse(String filePath) throws DocumentException{
File file = new File(filePath);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(file);
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
//获取根元素下面所有的子元素,利用迭代器方式
Iterator<?> it = root.elementIterator();
List<RequestAndResponse> requestAndResponses = new ArrayList<>();
while (it.hasNext()) {
//取出元素request_and_response
Element e = (Element)it.next();
//依次遍历每一个 request_and_response,获取相应的信息
Element request = e.element("request");
Element response = e.element("response");
RequestAndResponse requestAndResponse = new RequestAndResponse();
requestAndResponse.setMethod(request.elementText(method));
requestAndResponse.setPath(request.elementText(path));
requestAndResponse.setParam(request.elementText(param)); //GET 方式,这个属性为 null
requestAndResponse.setContent_type(response.elementText(content_type));
requestAndResponse.setValue(response.elementText(value));
requestAndResponses.add(requestAndResponse);
}
return requestAndResponses;
}
}リクエストを受信して処理する部分以下は、Socket を使用してリクエストを受信して処理する部分の概要です。 ここで必要な知識は基本的に Socket を使用する場合と同じですが、コンテンツ自体にはデータ部分とデータ以外の部分が含まれるため、コンテンツ自体の処理が異なるだけです。 (HTTP の観点からは、データ部分のみが表示されます。) ソケット プログラミングを使用するということは、単にポートをリッスンし、接続が到着したらそれを処理することを意味します。 (ここでは従来の BIO が使用されています。NIO の部分はわかりません。)
ここでの私の処理は、処理にスレッド プールを使用することであり、各接続は処理に 1 つのスレッドを使用します。このクラス (Server クラス) の完全なコードについては、以下を参照してください。
public void receive() {
//使用线程池处理请求
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_NUMBER);
while (true) {
try {
Socket connection = server.accept();
pool.submit(new UserConnection(connection));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(this.getDate()+" 用户连接断开");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}リクエストを受信するためのコード: サーバー クラスpackage com.dragon;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Server {
private static final int THREAD_NUMBER = 10;
private ServerSocket server;
private int port;
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
//启动服务。
public void start() {
try {
server = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println(this.getDate()+" 服务启动!");
this.receive();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(this.getDate()+" 服务启动失败!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void receive() {
//使用线程池处理请求
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_NUMBER);
while (true) {
try {
Socket connection = server.accept();
pool.submit(new UserConnection(connection));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(this.getDate()+" 用户连接断开");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private String getDate() {
String format = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
Date now = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(format);
return dateFormat.format(now);
}
}
HTTP リクエスト メッセージは TCP レベルからのバイナリ データ ストリーム (ネットワークは階層化されている) であるため、TCP を直接使用して次のことを行うことができます。このストリームを受信します。 バイナリ データ (ファイル アップロードなど) を含むメッセージの解析はより複雑で、その方法がわからないため、ここではバイナリ ファイルを含まない単純なリクエストをテストします。 。 )
注: 具体的な分析も非常に複雑なので、HTTP メッセージの構造に関係しますが、ファイルのアップロードを伴わない場合は、メッセージ全体が文字データであるため、一度に読んでください。次に、リクエスト メッセージは文字列に変換され、その文字列を使用して解析されます。in = connection.getInputStream();
out = connection.getOutputStream();
//这个数字是随便设置的,因为要一次性读取整个请求报文,不能太小。(但是其实这个也很大了)
byte[] b = new byte[5*1024];
BufferedInputStream input = new BufferedInputStream(in);
int count = input.read(b);
String requestMessage = new String(b, 0, count);
System.out.println("====================报文分隔符上界===================");
System.out.println(requestMessage);
System.out.println("====================报文分隔符下界===================");処理リクエストコード:UserConnectionクラス
リクエストとレスポンス情報の初期化 説明:静的初期化ブロックを使用して情報を初期化し、事前にユーザーXMLを設定します前述したように、メモリに読み込まれます。
// 初始化配置好的信息
static {
try {
requestAndResponses = RequestAndResponseResolver.listRequestAndResponse("./src/com/dragon/request_and_response.xml");
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
リクエストの処理と応答情報の取得 これは シミュレートされた呼び出し であるため、主にリクエスト ヘッダー内のデータの 3 つの部分に注目します。 ## リクエストメソッド(method)、リクエストパス(path)、リクエストパラメータ(param) 。 GET メソッドと POST メソッドは別々に処理されます。GET と POST の違いは上で簡単に紹介しました (ただし、十分に詳細ではないため、インターネット上の他の情報を参照すると理解できます)。 このコードにより、GETメソッドの場合、RequestAndResponseオブジェクト内のcontent_type(戻り値のデータ型)とvalue(戻り値のデータ)を取り出し、ローカル変数content_typeとvalueに代入します。
if ("GET".compareTo(method) == 0) {
for (RequestAndResponse r : requestAndResponses) {
//这里需要对 get 方式时的请求进行解码,因为一些非 ASCII 码字符会被编码,比如汉字。
path = URLDecoder.decode(path, ENCODE);
if (r.getMethod().equals(method) && r.getPath().equals(path)) {
content_type = r.getContent_type();
value = r.getValue();
break;
}
}
} else {
//POST 方式,请求参数是在请求体中的,请求头和请求体中间有一个换行符。
String param = requestMessage.substring(requestMessage.lastIndexOf(CRLF) + 2); //这里是不包括 CRLF 的两个字符的。
for (RequestAndResponse r : requestAndResponses) { //因为这个get方式的 参数为空,所以这里必须是 param 在前。
if (r.getMethod().equals(method) && r.getPath().equals(path) && param.equals(r.getParam())) {
content_type = r.getContent_type();
value = r.getValue();
break;
}
}
}这里介绍一个知识:URL 中的字符是特定的,不允许中文等字符的出现,所以发送请求时会对中文等字符进行编码,如果直接使用 equals 方法的,当然不会相等了,所以需要先对数据进行解码,然后再调用 equals 方法进行处理。这个是我们平时广泛使用 的东西,有时候使用浏览器可以看到带很多奇怪字符 URL,它们都是被处理过的。
举一个简单的例子:
String str = "我爱你";
String en_str = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(str, "UTF-8");
String de_str = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(en_str, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("编码字符:" + en_str);
System.out.println("解码字符:" + de_str);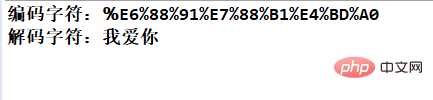
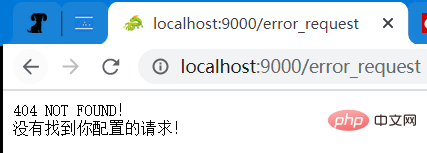
注意:这里有一个特殊的情况,如果发起了没有配置的请求方法和路径,那么程序会出错。所以,这里的 content_type 和 value 有一个默认的值,而且非常有趣!
执行响应 响应信息主要关注几点:响应信息长度(Content-Length)(按字节数计算)、响应内容类型(Content-Type)。
虽然发送的请求里不能带二进制文件,但是响应信息是可以返回文件的,而且使用 Content-Length (一次性发送),不使用 Chunked 分块发送(这里我还不太明白,而且只是模拟,应该使用一些简单的小文件。)。
下面是区分响应类型为 json (字符串) 还是 文件(二进制数据) 的代码:
如果是字符串,则 value 的值是字符串的值,如果是文件,则 value 的值为一个具体的本地路径。(不应该使用网络图片,即使修改程序可以做到也没有必要,因为这样就需要依赖网络了。)
//这里我只处理字符串类和文件类两种响应体
//响应体
int len = 0;
String responseBody = null; //响应值是 json 数据
File file = null; //响应值是 文件
if (content_type.equals("application/json")) { //如果是 json 数据,否则就是 文件类数据(图片、文档或其它文件)
responseBody = value;
len = responseBody.getBytes().length; //响应体的字节数,注意是字节数!
} else {
file = new File(value);
len = (int) file.length();
}然后就可以准备发送响应数据了,下面是发送响应的代码,注意报文的具体结构。
//响应头
responseHeader.append("HTTP/1.1").append(BLANK);
responseHeader.append(200).append(BLANK);
responseHeader.append("OK").append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Server:"+"CrazyDragon").append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Date:").append(BLANK).append(date).append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Content-Type:").append(BLANK).append(content_type).append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Content-Length:").append(BLANK).append(len).append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append(CRLF);
//如果 字符串变量 responseBody 不为空,则说明返回值是 json 数据(字符串)
//否则就是文件类的流了。
if (responseBody != null) {
String response = responseHeader.toString() + responseBody;
out.write(response.getBytes("UTF-8"));
} else {
out.write(responseHeader.toString().getBytes("UTF-8"));
int hasRead = 0;
byte[] data = new byte[4*1024];
try (BufferedInputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
while ((hasRead = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) {
out.write(data, 0, hasRead);
}
}
}
out.flush(); //必要的刷新流操作。User Connection 的完整代码:
package com.dragon;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.TimeZone;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
public class UserConnection implements Runnable{
private static final String BLANK = " ";
private static final String CRLF = "\r\n"; //换行符,不能写反了!
private static final String ENCODE = "UTF-8";
private static final String default_content_type = "application/json"; //当任何匹配路径都没有时。
private static final String default_value = "404 NOT FOUND!\n没有找到你配置的请求!";
private static List requestAndResponses;
private Socket connection;
// 初始化配置好的信息
static {
try {
requestAndResponses = RequestAndResponseResolver.listRequestAndResponse("./src/com/dragon/request_and_response.xml");
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public UserConnection(Socket connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
in = connection.getInputStream();
out = connection.getOutputStream();
//这个数字是随便设置的,因为要一次性读取整个请求报文,不能太小。(但是其实这个也很大了)
byte[] b = new byte[5*1024];
BufferedInputStream input = new BufferedInputStream(in);
int count = input.read(b);
String requestMessage = new String(b, 0, count);
System.out.println("====================报文分隔符上界===================");
System.out.println(requestMessage);
System.out.println("====================报文分隔符下界===================");
//以第一个 换行符 CRLF 为界限取出 请求路径和请求参数
String requestLine = requestMessage.substring(0, requestMessage.indexOf(CRLF));
String[] line = requestLine.split("\\s");
String method = line[0]; //考虑大小写。
String path = line[1];
//这个数组是有三个元素,最后一个是 协议的版本,这里不需要,就不处理了。
String content_type = default_content_type;
String value = default_value;
if ("GET".compareTo(method) == 0) {
// System.out.println("请求方式:" + method + " 请求路径(含参数):" + path);
for (RequestAndResponse r : requestAndResponses) {
//这里需要对 get 方式时的请求进行解码,因为一些非 ASCII 码字符会被编码,比如汉字。
path = URLDecoder.decode(path, ENCODE);
if (r.getMethod().equals(method) && r.getPath().equals(path)) {
content_type = r.getContent_type();
value = r.getValue();
break;
}
}
} else {
//POST 方式,请求参数是在请求体中的,请求头和请求体中间有一个换行符。
String param = requestMessage.substring(requestMessage.lastIndexOf(CRLF) + 2); //这里是不包括 CRLF 的两个字符的。
for (RequestAndResponse r : requestAndResponses) { //因为这个get方式的 参数为空,所以这里必须是 param 在前。
if (r.getMethod().equals(method) && r.getPath().equals(path) && param.equals(r.getParam())) {
content_type = r.getContent_type();
value = r.getValue();
System.out.println(content_type+" "+value);
break;
}
}
}
StringBuilder responseHeader = new StringBuilder();
String date = this.getDate();
//这里我只处理字符串类和文件类两种响应体
//响应体
int len = 0;
String responseBody = null; //响应值是 json 数据
File file = null; //响应值是 文件
if (content_type.equals("application/json")) { //如果是 json 数据,否则就是 文件类数据(图片、文档或其它文件)
responseBody = value;
len = responseBody.getBytes().length; //响应体的字节数,注意是字节数!
} else {
file = new File(value);
len = (int) file.length();
}
//响应头
responseHeader.append("HTTP/1.1").append(BLANK);
responseHeader.append(200).append(BLANK);
responseHeader.append("OK").append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Server:"+"CrazyDragon").append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Date:").append(BLANK).append(date).append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Content-Type:").append(BLANK).append(content_type).append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append("Content-Length:").append(BLANK).append(len).append(CRLF);
responseHeader.append(CRLF);
//如果 字符串变量 responseBody 不为空,则说明返回值是 json 数据(字符串)
//否则就是文件类的流了。
if (responseBody != null) {
String response = responseHeader.toString() + responseBody;
out.write(response.getBytes("UTF-8"));
} else {
out.write(responseHeader.toString().getBytes("UTF-8"));
int hasRead = 0;
byte[] data = new byte[4*1024];
try (BufferedInputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
while ((hasRead = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) {
out.write(data, 0, hasRead);
}
}
}
out.flush(); //必要的刷新流操作。
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (in != null)
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private String getDate() {
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss 'GMT'", Locale.CHINA);
format.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT")); // 设置时区为GMT
return format.format(date);
}
} 主程序类:Main
package com.dragon;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server(9000);
server.start();
}
}更多的测试示例
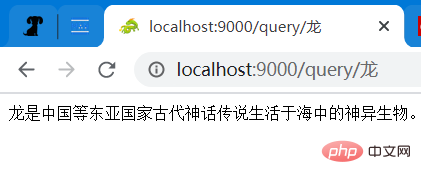
请求方式:GET 请求路径和参数:/query/龙 预期的响应类型:application/json 预期的响应值:龙是中国等东亚国家古代神话传说生活于海中的神异生物。 测试结果:
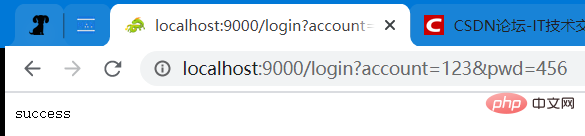
请求方式:GET 请求路径和参数:/login?account=123&pwd=456 预期的响应类型:application/json 预期的响应值:success 测试结果:
请求方式:GET 请求路径和参数:/pictures/husky.jpeg 预期的响应类型:image/jpeg 预期的响应值:一张图片(地址为:D:/DB/husky.jpeg)
请求方式:POST 请求路径:/login 请求参数:account=123&pwd=456 预期的响应类型:application/json 预期的响应值:{“result”:success} 测试结果:
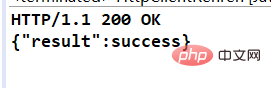
注:这是使用 HttpClient 发送的 POST 请求。

接收到的 POST 请求:
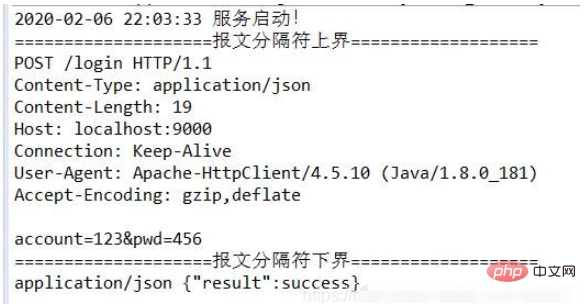
接收到的 GET 请求(含中文参数): /query/龙 注意:“龙” 已经被编码了。
以上がJava で HttpServer シミュレートされたフロントエンド インターフェイス呼び出しを実装する方法の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

