ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >Python チュートリアル >Python の 10 のヒントで、データ分析のニーズの 90% がカバーされます。
Python の 10 のヒントで、データ分析のニーズの 90% がカバーされます。
- 王林転載
- 2023-04-12 08:04:021077ブラウズ
データ アナリストの日常業務には、データの前処理、データ分析、機械学習モデルの作成、モデルのデプロイなど、さまざまなタスクが含まれます。
この記事では、データ分析の問題の 90% をカバーできる 10 の Python 操作を紹介します。いいね、お気に入り、注目を集めましょう。
1. データ セットの読み取り
データの読み取りはデータ分析に不可欠な部分であり、さまざまなファイル形式からデータを読み取る方法を理解することがデータ アナリストの第一歩です。ここでは、pandas を使用して Covid-19 データを含む csv ファイルを読み取る方法の例を示します。
import pandas as pd
# reading the countries_data file along with the location within read_csv function.
countries_df = pd.read_csv('C:/Users/anmol/Desktop/Courses/Python for Data Science/Code/countries_data.csv')
# showing the first 5 rows of the dataframe
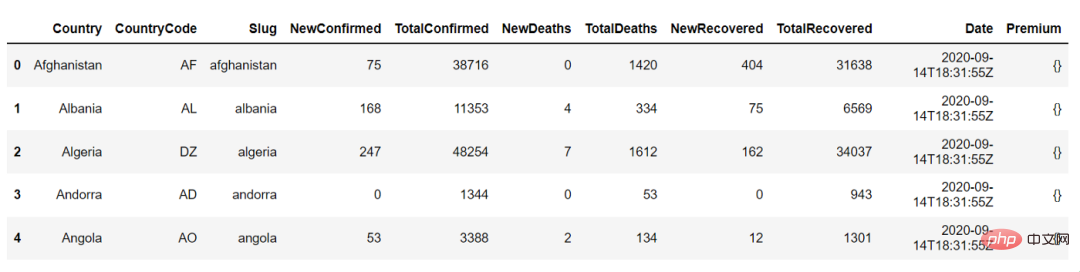
countries_df.head()
以下は、countries_df.head() の出力です。これを使用して、データ フレームの最初の 5 行を表示できます:
2 . 概要統計
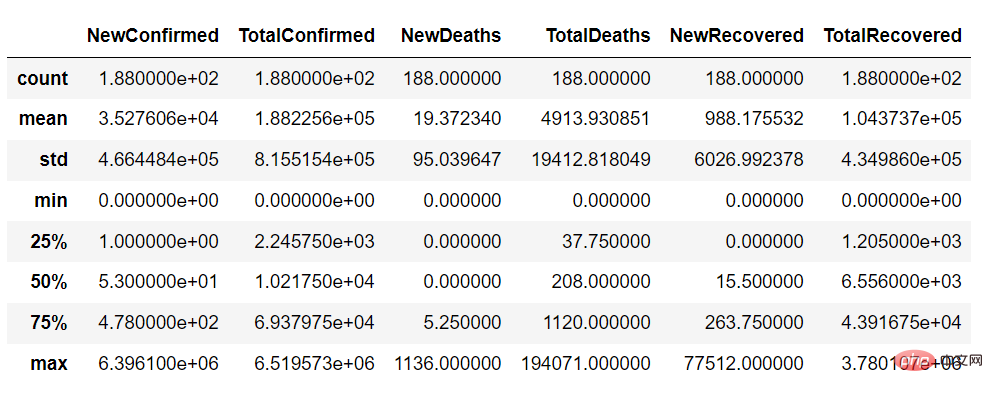
次のステップは、Newconfirmed や Totalconfirmed などの数値列の数、平均、標準偏差、分位数、頻度と最高値などのデータ概要を確認してデータを理解することです。国コードなどのカテゴリ列の出現値
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">countries_df</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">describe</span>()
describe 関数を使用すると、次のようにデータ セットの連続変数の概要を取得できます。
describe() 関数で、パラメータ「include = 'all'」を設定すると、連続変数とカテゴリ変数の概要を取得できますcountries_df.describe(include = 'all')
 3。データの選択とフィルタリング
3。データの選択とフィルタリング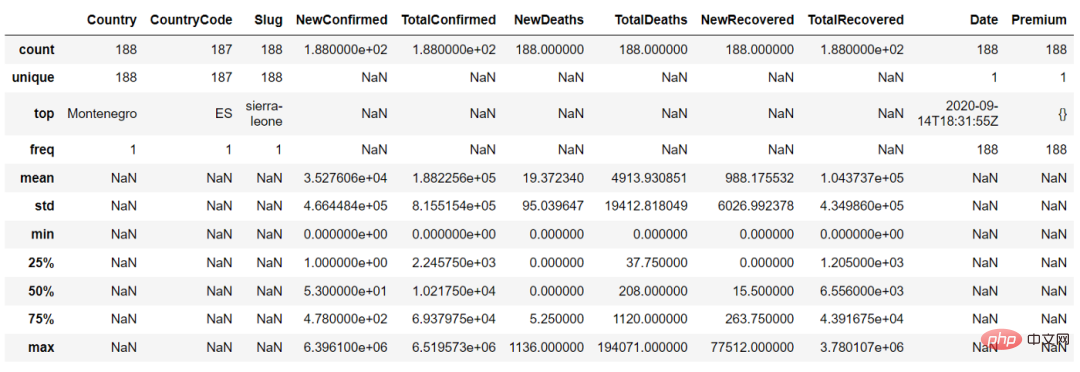 分析では実際にはすべての行とデータセット列の合計は必要ありません。関心のある列を選択し、質問に基づいて一部の行をフィルタリングするだけです。
分析では実際にはすべての行とデータセット列の合計は必要ありません。関心のある列を選択し、質問に基づいて一部の行をフィルタリングするだけです。
たとえば、次のコードを使用して Country 列と Newconfirmed 列を選択できます:
countries_df[['Country','NewConfirmed']]
データ Country をフィルターすることもできます。loc を使用すると、いくつかの値に基づいて列をフィルターできます。
countries_df.loc[countries_df['Country'] == 'United States of America']4. 集計
 カウント、合計、平均などのデータ集計は、最も一般的に実行されるタスクの 1 つです。データ分析において。
カウント、合計、平均などのデータ集計は、最も一般的に実行されるタスクの 1 つです。データ分析において。
集計を使用して、国ごとの NewConfimed ケースの合計数を見つけることができます。集計を実行するには、groupby 関数と agg 関数を使用します。
countries_df.groupby(['Country']).agg({'NewConfirmed':'sum'})5, Join
結合操作を使用して、2 つのデータ セットを 1 つのデータ セットに結合します。
例: あるデータセットにはさまざまな国の Covid-19 症例数が含まれ、別のデータセットにはさまざまな国の緯度と経度の情報が含まれる場合があります。
ここで、これら 2 つの情報を組み合わせる必要があり、次に示すように接続操作を実行できます
countries_lat_lon = pd.read_excel('C:/Users/anmol/Desktop/Courses/Python for Data Science/Code/countries_lat_lon.xlsx')
# joining the 2 dataframe : countries_df and countries_lat_lon
# syntax : pd.merge(left_df, right_df, on = 'on_column', how = 'type_of_join')
joined_df = pd.merge(countries_df, countries_lat_lon, on = 'CountryCode', how = 'inner')
joined_df6. 組み込み関数
数学的な組み込み関数を理解するmin()、max()、mean()、sum() などの関数は、さまざまな分析を実行するのに非常に役立ちます。
これらの関数を呼び出すことで、データ フレームに直接適用できます。これらの関数は、以下に示すように、列または集計関数で独立して使用できます:
# finding sum of NewConfirmed cases of all the countries
countries_df['NewConfirmed'].sum()
# Output : 6,631,899
# finding the sum of NewConfirmed cases across different countries
countries_df.groupby(['Country']).agg({'NewConfirmed':'sum'})
# Output
#NewConfirmed
#Country
#Afghanistan75
#Albania 168
#Algeria 247
#Andorra0
#Angola537. ユーザー定義関数
私たち自身が作成する関数はユーザー定義関数です。必要に応じて関数を呼び出すことで、これらの関数のコードを実行できます。たとえば、次のように 2 つの数値を加算する関数を作成できます:
# User defined function is created using 'def' keyword, followed by function definition - 'addition()' # and 2 arguments num1 and num2 def addition(num1, num2): return num1+num2 # calling the function using function name and providing the arguments print(addition(1,2)) #output : 3
8, Pivot
Pivot は、列行内の一意の値を複数の新しい列に変換することです。優れたデータ処理技術です。
Covid-19 データセットで pivot_table() 関数を使用すると、国名を別の新しい列 (
# using pivot_table to convert values within the Country column into individual columns and # filling the values corresponding to these columns with numeric variable - NewConfimed pivot_df = pd.pivot_table(countries_df,columns = 'Country', values = 'NewConfirmed') pivot_df
9) に変換できます。データ フレームを反復処理します。
データ フレームのインデックスと行を走査する必要がある場合、関数 iterrows を使用してデータ フレームを走査できます:
# iterating over the index and row of a dataframe using iterrows() function
for index, row in countries_df.iterrows():
print('Index is ' + str(index))
print('Country is '+ str(row['Country']))
# Output :
# Index is 0
# Country is Afghanistan
# Index is 1
# Country is Albania
# .......10. 文字列操作
文字列列を処理する回数が多いデータセット内 (ここ) この場合、いくつかの基本的な文字列操作を理解することが重要です。
たとえば、文字列を大文字、小文字に変換する方法や、文字列の長さを調べる方法などです。
rree以上がPython の 10 のヒントで、データ分析のニーズの 90% がカバーされます。の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

