ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Spring Security 原則の概要 (コード付き)
Spring Security 原則の概要 (コード付き)
- 不言転載
- 2019-03-22 16:49:413579ブラウズ
この記事では Spring Security の原則を (コード付きで) 紹介します。一定の参考価値があります。困っている友人は参照してください。お役に立てれば幸いです。
敵を知り、己を知ることでのみ、あらゆる戦いで勝利を収めることができます。Spring Security をニーズに合わせて使用するには、その原則を理解し、自由に拡張できるようにすることが最善です。この記事は主に記録ですSpring Securityの基本的な動作プロセス。
フィルター
Spring Security は基本的にフィルターを使用して、設定された ID 認証、権限認証、およびログアウトを完了します。
Spring Security は、サーブレットのフィルター チェーンにフィルター FilterChainProxy を登録します。これにより、リクエストが Spring Security 自体によって維持される複数のフィルター チェーンにプロキシされます。各フィルター チェーンは、いくつかの URL と一致します。一致する場合、対応するフィルターが実行されます。フィルター チェーンは連続しており、最初に一致したフィルター チェーンのみがリクエストに対して実行されます。 Spring Security の構成は基本的にフィルターの追加、削除、変更です。
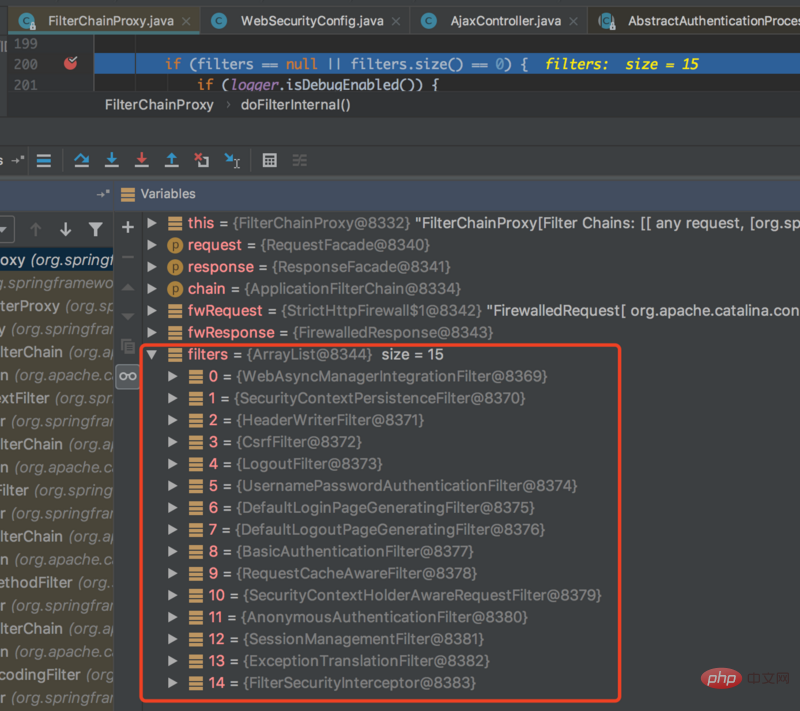
デフォルトでは、システムによって挿入される 15 個のフィルターは、さまざまな構成要件に対応します。次に、UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter フィルターの分析に焦点を当てます。これは、ユーザー名とパスワードを使用したログイン認証に使用されるフィルターです。ただし、多くの場合、ログインは単純なユーザー名とパスワードだけではなく、サードパーティの承認されたログインも使用される可能性があります。 . このとき、カスタム フィルターを使用する必要があります。もちろん、ここでは詳細な説明は省略し、カスタム フィルターを挿入する方法についてのみ説明します。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.addFilterAfter(...);
...
}
ID 認証プロセス
ID 認証プロセスを開始する前に、いくつかの基本概念を理解する必要があります
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder には SecurityContext オブジェクトが格納されます。 SecurityContextHolder は、3 つのストレージ モードを持つストレージ エージェントです。
- MODE_THREADLOCAL: SecurityContext はスレッドに格納されます。
- MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL: SecurityContext はスレッドに保存されますが、子スレッドは親スレッドの SecurityContext を取得できます。
- MODE_GLOBAL: SecurityContext はすべてのスレッドで同じです。
SecurityContextHolder はデフォルトで MODE_THREADLOCAL モードを使用し、SecurityContext は現在のスレッドに保存されます。 SecurityContextHolder を呼び出すときに明示的なパラメータを渡す必要はなく、SecurityContextHolder オブジェクトは現在のスレッドで直接取得できます。
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext(); Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
2.認証
認証とは、現在のユーザーが誰であるかを示す検証です。検証とは? 例えば、ユーザー名とパスワードのセットは検証になりますが、もちろんユーザー名とパスワードが間違っている場合も検証になりますが、Spring Security では検証に失敗します。
認証インターフェイス
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
//获取用户权限,一般情况下获取到的是用户的角色信息
Collection extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
//获取证明用户认证的信息,通常情况下获取到的是密码等信息,不过登录成功就会被移除
Object getCredentials();
//获取用户的额外信息,比如 IP 地址、经纬度等
Object getDetails();
//获取用户身份信息,在未认证的情况下获取到的是用户名,在已认证的情况下获取到的是 UserDetails (暂时理解为,当前应用用户对象的扩展)
Object getPrincipal();
//获取当前 Authentication 是否已认证
boolean isAuthenticated();
//设置当前 Authentication 是否已认证
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated);
}
3.AuthenticationManager ProviderManager AuthenticationProvider
実際、これら 3 つは簡単に区別できます。AuthenticationManager は主に ID 認証プロセスを完了するためのものです。 AuthenticationManager インターフェイスの実装。クラスの ProviderManager には、AuthenticationProvider オブジェクトを記録するコレクション属性プロバイダーがあり、AuthenticationProvider インターフェイス クラスには 2 つのメソッドがあります
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
//实现具体的身份认证逻辑,认证失败抛出对应的异常
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
//该认证类是否支持该 Authentication 的认证
boolean supports(Class> authentication);
}
次のステップは、ProviderManager のプロバイダー コレクションを走査して、適切な AuthenticationProvider を使用して ID 認証を完了します。
4.UserDetailsService UserDetails
UserDetailsService インターフェイスには単純なメソッドが 1 つだけあります
public interface UserDetailsService {
//根据用户名查到对应的 UserDetails 对象
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
5. プロセス
上記の何が間違っているのか概念を理解するには、次のプロセスでゆっくり分析します。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter フィルターを実行するときは、まずその親クラス AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter の doFilter() メソッドに入ります
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
//首先配对是不是配置的身份认证的URI,是则执行下面的认证,不是则跳过
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
...
Authentication authResult;
try {
//关键方法, 实现认证逻辑并返回 Authentication, 由其子类 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 实现, 由下面 5.3 详解
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
//认证失败调用...由下面 5.1 详解
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
//认证失败调用...由下面 5.1 详解
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
//认证成功调用...由下面 5.2 详解
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
5.1 認証失敗の処理logic
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed)
throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
...
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
//该 handler 处理失败界面跳转和响应逻辑
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}
ここで構成されているデフォルトの失敗処理ハンドラーは SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler で、カスタマイズ可能です。
public class SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler implements
AuthenticationFailureHandler {
...
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//没有配置失败跳转的URL则直接响应错误
if (defaultFailureUrl == null) {
logger.debug("No failure URL set, sending 401 Unauthorized error");
response.sendError(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(),
HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.getReasonPhrase());
}
else {
//否则
//缓存异常
saveException(request, exception);
//根据配置的异常页面是重定向还是转发进行不同方式跳转
if (forwardToDestination) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to " + defaultFailureUrl);
request.getRequestDispatcher(defaultFailureUrl)
.forward(request, response);
}
else {
logger.debug("Redirecting to " + defaultFailureUrl);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, defaultFailureUrl);
}
}
}
//缓存异常,转发则保存在request里面,重定向则保存在session里面
protected final void saveException(HttpServletRequest request,
AuthenticationException exception) {
if (forwardToDestination) {
request.setAttribute(WebAttributes.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION, exception);
}
else {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null || allowSessionCreation) {
request.getSession().setAttribute(WebAttributes.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION,
exception);
}
}
}
}
ここで小さな拡張を行いましょう: システムのエラー処理ハンドラーを使用して、認証が失敗したときにジャンプする URL を指定します。MVC の対応する URL メソッドで、リクエストからエラー情報とフィードバックを取得できます。フロントエンドの場合
5.2 認証成功処理ロジック
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
//这里要注意很重要,将认证完成返回的 Authentication 保存到线程对应的 `SecurityContext` 中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
//该 handler 就是为了完成页面跳转
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
ここで設定されているデフォルトの成功処理ハンドラーは SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler です。内部のコードは詳細には展開されません。指定された認証成功にジャンプしますインターフェイスはカスタマイズ可能です。
5.3 ID 認証の詳細
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
...
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username";
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password";
private String usernameParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY;
private String passwordParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY;
private boolean postOnly = true;
...
//开始身份认证逻辑
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
//先用前端提交过来的 username 和 password 封装一个简易的 AuthenticationToken
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
//具体的认证逻辑还是交给 AuthenticationManager 对象的 authenticate(..) 方法完成,接着往下看
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
ソース コードのブレークポイント追跡から、最終解決は AuthenticationManager インターフェイス実装クラス ProviderManager によって完了することがわかります
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,
InitializingBean {
...
private List<authenticationprovider> providers = Collections.emptyList();
...
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
....
//遍历所有的 AuthenticationProvider, 找到合适的完成身份验证
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
...
try {
//进行具体的身份验证逻辑, 这里使用到的是 DaoAuthenticationProvider, 具体逻辑记着往下看
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch
...
}
...
throw lastException;
}
}</authenticationprovider>
DaoAuthenticationProvider AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider から継承され、AuthenticationProvider インターフェイス
public abstract class AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider implements
AuthenticationProvider, InitializingBean, MessageSourceAware {
...
private UserDetailsChecker preAuthenticationChecks = new DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks();
private UserDetailsChecker postAuthenticationChecks = new DefaultPostAuthenticationChecks();
...
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
...
// 获得提交过来的用户名
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
//根据用户名从缓存中查找 UserDetails
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
//缓存中没有则通过 retrieveUser(..) 方法查找 (看下面 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的实现)
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch
...
}
try {
//比对前的检查,例如账户以一些状态信息(是否锁定, 过期...)
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
//子类实现比对规则 (看下面 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的实现)
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
//根据最终user的一些信息重新生成具体详细的 Authentication 对象并返回
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
//具体生成还是看子类实现
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
// Ensure we return the original credentials the user supplied,
// so subsequent attempts are successful even with encoded passwords.
// Also ensure we return the original getDetails(), so that future
// authentication events after cache expiry contain the details
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
principal, authentication.getCredentials(),
authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails());
return result;
}
}
接下来我们来看下 DaoAuthenticationProvider 里面的三个重要的方法,比对方式、获取需要比对的 UserDetails 对象以及生产最终返回 Authentication 的方法。
public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider {
...
//密码比对
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
//通过 PasswordEncoder 进行密码比对, 注: 可自定义
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
//通过 UserDetailsService 获取 UserDetails
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
//通过 UserDetailsService 获取 UserDetails
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
//生成身份认证通过后最终返回的 Authentication, 记录认证的身份信息
@Override
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
boolean upgradeEncoding = this.userDetailsPasswordService != null
&& this.passwordEncoder.upgradeEncoding(user.getPassword());
if (upgradeEncoding) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
String newPassword = this.passwordEncoder.encode(presentedPassword);
user = this.userDetailsPasswordService.updatePassword(user, newPassword);
}
return super.createSuccessAuthentication(principal, authentication, user);
}
}
本篇文章到这里就已经全部结束了,更多其他精彩内容可以关注PHP中文网的Java教程视频栏目!
以上がSpring Security 原則の概要 (コード付き)の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

