ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Mybatisのセッション機構をソースコードから分析(詳細)
Mybatisのセッション機構をソースコードから分析(詳細)
- 不言転載
- 2019-03-21 16:30:123193ブラウズ
この記事の内容は、Mybatis のセッションの仕組みをソースコードの観点から分析したもの(詳細)であり、一定の参考価値がありますので、困っている方は参考にしていただければ幸いです。お役に立ちます。役に立ちます。
私の隣に座っていたZhongは、私がMybatisのソースコードに精通していることを聞き(誰がニュースをリークしたのか分かりませんでした)、ところで彼は私に質問をしました: 同じメソッドで、Mybatis データベースを複数回リクエストするときに複数の SqlSession セッションを作成しますか?
最近自慰行為をしすぎたのかもしれません。その時、頭がぼんやりして目がかすみました。その時はこう答えましたが: 複数のリクエストが同じトランザクション内にある場合、複数のリクエストが同じトランザクション SqlSession を共有している場合、それ以外の場合、各リクエストは SqlSession を作成します。これは日々の開発においては当たり前のことですが、私が鍾氏に対して原則的な観点から分析していなかったため、鍾氏は飲食のことを考えていなかったのです。私は深く自責の念にかられ、密かに決意を固め、同級生の鍾さんに説明しようと決心した。
# 同意できない場合は、デモを実行してください。
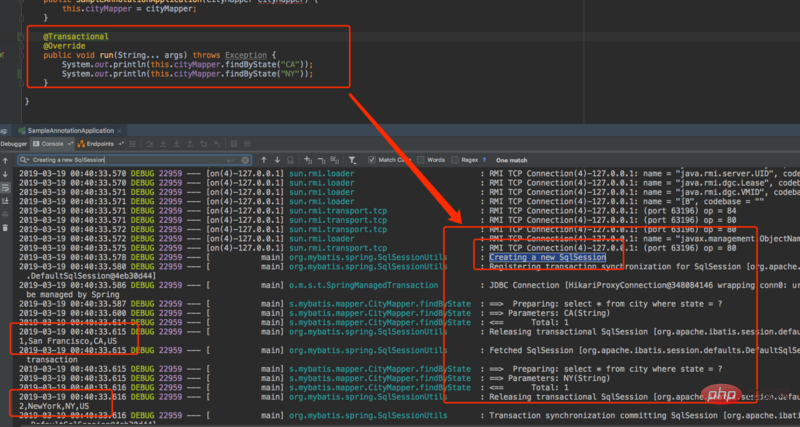
メソッドにトランザクションが追加されていない場合に、各リクエストで SqlSession が作成されるかどうかをテストします。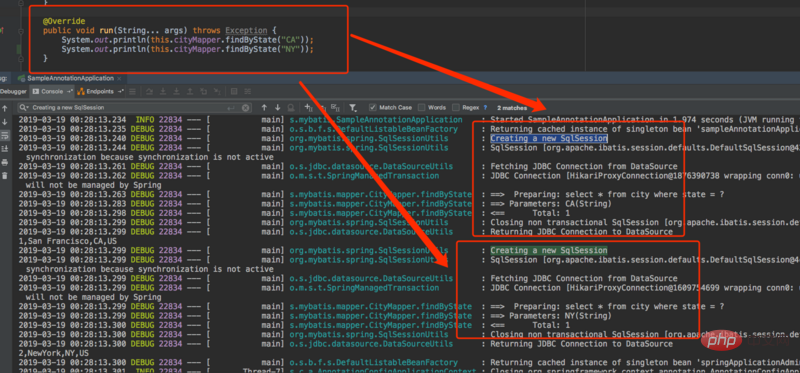
SqlSession とは
始める前に、まず SqlSession とは何なのかを理解する必要があります。 簡単に言うと、SqlSession は Mybatis の作業用のトップレベル API セッション インターフェイスです。すべてのデータベース操作はそれを通じて実装されます。これはセッションであるため、つまり、SqlSession は 1 つのビジネス リクエスト内でのみ存続する必要があります。 SqlSession はこのデータベース セッションに対応すると言えますが、永続的に存在するわけではなく、データベースにアクセスするたびに作成する必要があります。 したがって、SqlSession はスレッドセーフではありません。各スレッドには独自の SqlSession インスタンスが必要です。SqlSession をシングルトン フォームにしてはなりません。そうしないと、静的フィールドとインスタンス変数の形式によって SqlSession が表示されます。トランザクションの問題。複数のリクエストが同じトランザクション内で SqlSession セッションを共有する理由です。これを SqlSession の作成プロセスから説明します。- Configuration 構成クラス データ ソースから環境を取得します。
- データ ソースから TransactionFactory と DataSource を取得し、トランザクション接続管理オブジェクトを作成します。
- Executor オブジェクトを作成します (SqlSession はすべての操作の表面にすぎず、実際の作業は Executor であり、これをカプセル化します)基礎となる JDBC のすべての操作の詳細);
- SqlSession セッションを作成します。
ソース コードの観点からの分析
ソース コード分析のエントリ ポイントはどのステップですか?以前に書いた mybatis のソースコード解析を読んだことがある方なら、Mybatis のソースコードの前でいつまでも入り口が見つからずに長居することはないと思います。 前回の記事でも述べましたが、Mapperの実装クラスはプロキシであり、実際にロジックを実行するのはMapperProxy.invoke()であり、最終的にsqlSessionTemplateを実行するメソッドです。 org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate:private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}これは、SqlSessionTemplate を作成するための最後の構築メソッドです。SqlSession が sqlSessionTemplate で使用されていることがわかります。これは、によって実装された動的プロキシ クラスです。 SqlSessionInterceptor, so we Go direct into the fortress:
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
} All Methods of Mapper will become this method to handle all database jobs. 食べ物や米のことを考えていないクラスメートの鐘の目は曇っています。彼は自分自身を諦めて自慰行為をしすぎたかどうか知りません。彼の目は虚ろです。スプリングを統合したマイバティスとマイバティスを単独で使用することに違いがあるかどうか尋ねてください。実際、違いはありません。違いは次のとおりです。 Spring はすべての処理の詳細をカプセル化するため、多くの冗長なコードを記述する必要がなく、ビジネス開発に集中できます。 この動的プロキシメソッドは主に次の処理を実行します:
- 根据当前条件获取一个SqlSession,此时SqlSession可能是新创建的也有可能是获取到上一次请求的SqlSession;
- 反射执行SqlSession方法,再判断当前会话是否是一个事务,如果是一个事务,则不commit;
- 如果此时抛出异常,判断如果是PersistenceExceptionTranslator且不为空,那么就关闭当前会话,并且将sqlSession置为空防止finally重复关闭,PersistenceExceptionTranslator是spring定义的数据访问集成层的异常接口;
- finally无论怎么执行结果如何,只要当前会话不为空,那么就会执行关闭当前会话操作,关闭当前会话操作又会根据当前会话是否有事务来决定会话是释放还是直接关闭。
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#getSqlSession:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
是不是看到了不服跑个demo时看到的日志“Creating a new SqlSession”了,那么证明我直接深入的地方挺准确的,没有丝毫误差。在这个方法当中,首先是从TransactionSynchronizationManager(以下称当前线程事务管理器)获取当前线程threadLocal是否有SqlSessionHolder,如果有就从SqlSessionHolder取出当前SqlSession,如果当前线程threadLocal没有SqlSessionHolder,就从sessionFactory中创建一个SqlSession,具体的创建步骤上面已经说过了,接着注册会话到当前线程threadLocal中。
先来看看当前线程事务管理器的结构:
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
// ...
// 存储当前线程事务资源,比如Connection、session等
private static final ThreadLocal<map>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal("Transactional resources");
// 存储当前线程事务同步回调器
// 当有事务,该字段会被初始化,即激活当前线程事务管理器
private static final ThreadLocal<set>> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal("Transaction synchronizations");
// ...
}</set></map>
这是spring的一个当前线程事务管理器,它允许将当前资源存储到当前线程ThreadLocal中,从前面也可看出SqlSessionHolder是保存在resources中。
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#registerSessionHolder:
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
// 判断当前是否有事务
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
// 判断当前环境配置的事务管理工厂是否是SpringManagedTransactionFactory(默认)
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
// 绑定当前SqlSessionHolder到线程ThreadLocal中
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
// 注册SqlSession同步回调器
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
// 会话使用次数+1
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
}
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
}
}
注册SqlSession到当前线程事务管理器的条件首先是当前环境中有事务,否则不注册,判断是否有事务的条件是synchronizations的ThreadLocal是否为空:
public static boolean isSynchronizationActive() {
return (synchronizations.get() != null);
}
每当我们开启一个事务,会调用initSynchronization()方法进行初始化synchronizations,以激活当前线程事务管理器。
public static void initSynchronization() throws IllegalStateException {
if (isSynchronizationActive()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot activate transaction synchronization - already active");
}
logger.trace("Initializing transaction synchronization");
synchronizations.set(new LinkedHashSet<transactionsynchronization>());
}</transactionsynchronization>
所以当前有事务时,会注册SqlSession到当前线程ThreadLocal中。
Mybatis自己也实现了一个自定义的事务同步回调器SqlSessionSynchronization,在注册SqlSession的同时,也会将SqlSessionSynchronization注册到当前线程事务管理器中,它的作用是根据事务的完成状态回调来处理线程资源,即当前如果有事务,那么当每次状态发生时就会回调事务同步器,具体细节可移步至Spring的org.springframework.transaction.support包。
回到SqlSessionInterceptor代理类的逻辑,发现判断会话是否需要提交要调用以下方法:
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#isSqlSessionTransactional:
public static boolean isSqlSessionTransactional(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
notNull(session, NO_SQL_SESSION_SPECIFIED);
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
return (holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session);
}
取决于当前SqlSession是否为空并且判断当前SqlSession是否与ThreadLocal中的SqlSession相等,前面也分析了,如果当前没有事务,SqlSession是不会保存到事务同步管理器的,即没有事务,会话提交。
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#closeSqlSession:
public static void closeSqlSession(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
notNull(session, NO_SQL_SESSION_SPECIFIED);
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
if ((holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session)) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Releasing transactional SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
holder.released();
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Closing non transactional SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
session.close();
}
}
方法无论执行结果如何都需要执行关闭会话逻辑,这里的判断也是判断当前是否有事务,如果SqlSession在事务当中,则减少引用次数,没有真实关闭会话。如果当前会话不存在事务,则直接关闭会话。
写在最后
虽说钟同学问了我一个Mybatis的问题,我却中了Spring的圈套,猛然发现整个事务链路都处在Spring的管控当中,这里涉及到了Spring的自定义事务的一些机制,其中当前线程事务管理器是整个事务的核心与中轴,当前有事务时,会初始化当前线程事务管理器的synchronizations,即激活了当前线程同步管理器,当Mybatis访问数据库会首先从当前线程事务管理器获取SqlSession,如果不存在就会创建一个会话,接着注册会话到当前线程事务管理器中,如果当前有事务,则会话不关闭也不commit,Mybatis还自定义了一个TransactionSynchronization,用于事务每次状态发生时回调处理。
本篇文章到这里就已经全部结束了,更多其他精彩内容可以关注PHP中文网的Java教程视频栏目!
以上がMybatisのセッション機構をソースコードから分析(詳細)の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

