ホームページ >ウェブフロントエンド >CSSチュートリアル >CSSを使用してHTML要素を配置するにはどうすればよいですか? (例付き)
CSSを使用してHTML要素を配置するにはどうすればよいですか? (例付き)
- 不言オリジナル
- 2018-11-05 10:02:414432ブラウズ
ページ上にコンテンツを配置する場合、少数の属性を使用して要素の位置を操作できます。この記事では、CSS 位置プロパティを使用して、さまざまな位置にある要素タイプを含める例をいくつか示します。
要素で位置決めを使用するには、まずその要素に使用される位置決めメソッドのタイプを指定する位置プロパティを宣言する必要があります。 Position 属性値を使用して、top、bottom、left、right 属性を使用して要素を配置します。それらの位置は、位置の値にも依存します。 (推奨コース: css ビデオ チュートリアル )
位置決め値には static (静的)、relative (相対)、fixed (固定)、absolute (絶対) 、sticky ( Sticky)
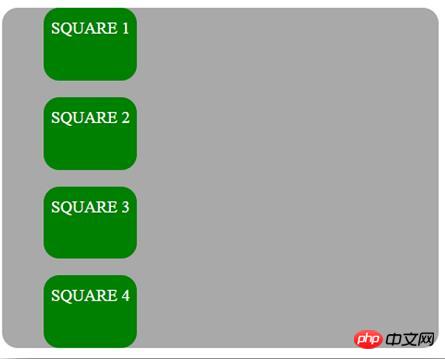
static (static)
デフォルトでは、HTML 要素は静的に配置され、要素はドキュメントの通常の静的配置に従って配置されます。上、下、左、右のプロパティの影響を受けません。 Position: static を使用して配置された要素には、他の特別な配置メソッドはありません。
位置を静的に設定するために使用される CSS は次のとおりです:
position: static;
次に、静的な位置値を使用する例を示します:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: WHITE;
font: Helvetica;
width: 420px;
}
.square-set,
.square {
border-radius: 15px;
}
.square-set {
background: darkgrey;
}
.square {
position: static;
background: Green;
height: 70px;
line-height: 40px;
text-align: center;
width: 90px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square-set">
<figure class="square square-1">SQUARE 1</figure>
<figure class="square square-2">SQUARE 2</figure>
<figure class="square square-3">SQUARE 3</figure>
<figure class="square square-4">SQUARE 4</figure>
</div>
</body>
</html>効果は次のとおりです:
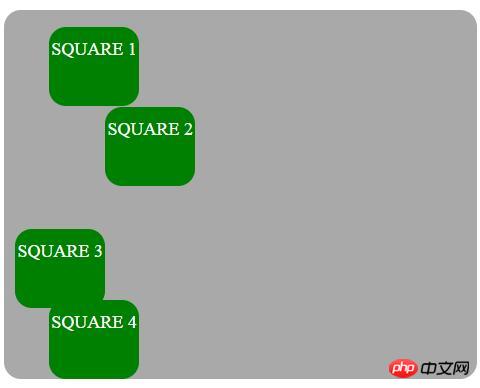
relative
要素は、ドキュメントの通常の流れに従って通常の位置を基準にして配置され、オフセットされます。上、右、下、左の値に基づいてそれ自体に相対します。オフセットは他の要素の位置に影響を与えないため、ページ レイアウト内で要素に与えられるスペースは、位置が静的である場合と同じになります。相対的に配置された要素の top、right、bottom、left プロパティを設定すると、通常の位置からさらに離れた位置に調整されます。他のコンテンツは、要素によって残された空白に合わせて調整されません。
位置を相対に設定するために使用される CSS は次のとおりです:
position: relative;
次の例では相対位置の値を使用しています:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: white;
font: Helvetica ;
width: 420px;
}
.square-set,
.square {
border-radius: 15px;
}
.square-set {
background: darkgrey;
}
.square {
background: green;
height: 70px;
line-height: 40px;
position: relative;
text-align: center;
width: 80px;
}
.square-1 {
top: 15px;
}
.square-2 {
left: 50px;
}
.square-3 {
bottom: -23px;
right: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square-set">
<figure class="square square-1">SQUARE 1</figure>
<figure class="square square-2">SQUARE 2</figure>
<figure class="square square-3">SQUARE 3</figure>
<figure class="square square-4">SQUARE 4</figure>
</div>
</body>
</html>効果は次のとおりです:
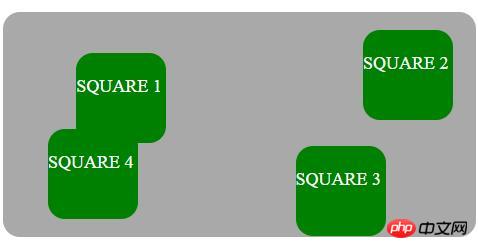
絶対
要素は通常のドキュメント フローから削除され、ページ内に要素用のスペースは作成されません。レイアウト。要素は、最後に配置された祖先を基準にして配置されます。そうでない場合は、最初の包含ブロックを基準にして配置され、最終的な位置は、top、right、bottom、および left の値によって決まります。
位置を絶対に設定するための CSS は次のとおりです。
position: absolute;
Have Position:Absolute; 最も近い祖先に相対的に配置される要素。絶対位置の要素に位置位置の祖先がない場合、その要素はドキュメント本文を使用し、ページのスクロールとともに移動します。 「位置決めされた」要素は、静的な位置を持つ要素です。
次の例は、要素の絶対位置を強調しています:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.square-set {
color: WHITE;
background: darkgrey;
height: 200px;
position: relative;
border-radius: 15px;
font: Helvetica ;
width: 420px;
}
.square {
background: green;
height: 80px;
position: absolute;
width: 80px;
border-radius: 15px;
line-height: 60px;
}
.square-1 {
top: 10%;
left: 6%;
}
.square-2 {
top: 5;
right: -20px;
}
.square-3 {
bottom: -15px;
right: 40px;
}
.square-4 {
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square-set">
<figure class="square square-1">SQUARE 1</figure>
<figure class="square square-2">SQUARE 2</figure>
<figure class="square square-3">SQUARE 3</figure>
<figure class="square square-4">SQUARE 4</figure>
</div>
</body>
</html>効果は次のとおりです:
#修正済み #通常のドキュメント フローから要素が削除され、ページ レイアウトに要素用のスペースが作成されません。要素は、ビューポートによって確立された最初の包含ブロックを基準にして配置され、最終的な位置は、top、right、bottom、left の値によって決まります。この値は常に新しいスタッキング コンテキストを作成します。
位置を固定に設定するために使用される CSS は次のようになります。
position: fixed;
要素の位置: 固定; つまり、ビューポートに対して相対的に配置されます。ページがスクロールする場所。 top、right、bottom、left 属性は要素を配置するために使用されます。
sticky要素は、ドキュメントの通常のフローに対応して配置され、上、右、下、左のオフセット値に基づいてその値に相対的に配置されます。最も近い昇順のブロック レベル (テーブル関連の要素を含む)。オフセットは他の要素の位置には影響しません。
この値は常に新しいスタッキング コンテキストを作成します。スティッキー要素は、その祖先が実際に最も近いスクロール祖先でなくても、「スクロール メカニズム」を備えた最も近い祖先に「くっつく」ことに注意してください。
位置をスティッキーに設定するための CSS は次のとおりです。
position: sticky;
position:sticky; ユーザーのスクロール位置に基づいて要素を配置し、スクロール位置に基づいて相対位置と固定位置を切り替えます。
重複する要素网页上的重叠元素非常有用,可以突出显示,推广和关注我们网页上的重要内容。在您的网站上制作元素叠加是非常有用且非常有价值的功能设计实践。当元素被定位时,它们可以与其他元素重叠,因此为了指定顺序(应该在其他元素的前面或后面放置哪个元素),我们应该使用z-index属性。堆栈顺序较大的元素始终位于堆栈顺序较低的元素前面。作为通知,z-index属性仅适用于定位元素(position:absolute,position:relative或position:fixed)。 以下示例显示了z-index属性如何在不同的方块上工作: 效果如下: 在图像上定位文本 下面的示例使用上述CSS定位值在图像上覆盖一些文本: 效果如下: 最后 在本文中,我们已经描述并给出了CSS定位类型的示例,并描述了如何重叠元素并在图像上添加一些文本。<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.square-set {
color: white;
background: purple;
height: 170px;
position: relative;
border-radius: 15px;
font: Helvetica;
width: 400px;
}
.square {
background: orange;
border: 4px solid goldenrod;
position: absolute;
border-radius: 15px;
height: 80px;
width: 80px;
}
.square-1 {
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
border: dashed;
height: 8em;
margin-bottom: 1em;
margin-top: 2em;
}
.square-2 {
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
background: black;
width: 65%;
left: 60px;
top: 3em;
}
.square-3 {
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
background: lightgreen;
width: 20%;
left: 65%;
top: -25px;
height: 7em;
opacity: 0.9;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="square-set">
<figure class="square square-1">SQUARE 1</figure>
<figure class="square square-2">SQUARE 2</figure>
<figure class="square square-3">SQUARE 3</figure>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.module{
background:
linear-gradient{
rgba(0, 4, 5, 0.6),
rgba(2, 0, 3, 0.6)
),
url(http://www.holtz.org/Library/Images/Slideshows/Gallery/Landscapes/43098-DSC_64xx_landscape-keltern-1_wall.jpg);
background-size: cover;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
margin: 10px 0 0 10px;
position: relative;
float: left;
}
.mid h3 {
font-family: Helvetica;
font-weight: 900;
color: white;
text-transform: uppercase;
margin: 0;
position: absolute;
top: 30%;
left: 50%;
font-size: 3rem;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="module mid">
<h3>Wild nature</h3>
</div>
</body>
</html>
以上がCSSを使用してHTML要素を配置するにはどうすればよいですか? (例付き)の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

