ホームページ >ウェブフロントエンド >jsチュートリアル >新規構築不要のjQueryの使い方を詳しく解説
新規構築不要のjQueryの使い方を詳しく解説
- php中世界最好的语言オリジナル
- 2018-04-23 11:24:401732ブラウズ
今回は、新規構築なしで jQuery を使用する場合の注意事項について詳しく説明します。実際の事例を見てみましょう。
jQuery の新しい無料の構築
jQuery フレームワークの核心は、HTML ドキュメントの要素を照合し、それらに対して操作を実行することです。
jQuery オブジェクトをインスタンス化するメソッドである jQuery を思い出してください。 jQuery を使用するときは、新しい構築を行わずに最初の構築メソッドを常に使用し、直接 $('') を構築します。これは jQuery にとって非常に便利な場所でもあります。
最初の new-less 構築メソッドを使用すると、本質的には new jQuery() と同等になります。では、これは jQuery 内でどのように実装されるのでしょうか?見てみましょう: $('') 进行构造,这也是 jQuery 十分便捷的一个地方。
当我们使用第一种无 new 构造方式的时候,其本质就是相当于 new jQuery(),那么在 jQuery 内部是如何实现的呢?看看:
// 无 new 构造
$('#test').text('Test');
// 当然也可以使用 new
var test = new $('#test');
test.text('Test');
没看懂?没关系,我们一步一步分析。
函数表达式和函数声明
在ECMAScript中,创建函数的最常用的两个方法是函数表达式和函数声明,两者期间的区别是有点晕,因为ECMA规范只明确了一点:函数声明必须带有标示符(Identifier)(就是大家常说的函数名称),而函数表达式则可以省略这个标示符:
(function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window);
所以,可以看出,如果不声明函数名称,它肯定是表达式,可如果声明了函数名称的话,如何判断是函数声明还是函数表达式呢?
ECMAScript是通过上下文来区分的,如果function foo(){}是作为赋值表达式的一部分的话,那它就是一个函数表达式,
如果function foo(){}被包含在一个函数体内,或者位于程序的最顶部的话,那它就是一个函数声明。
//函数声明:
function 函数名称 (参数:可选){ 函数体 }
//函数表达式:
function 函数名称(可选)(参数:可选){ 函数体 }
还有一种函数表达式不太常见,就是被括号括住的(function foo(){}),他是表达式的原因是因为括号 ()是一个分组操作符,它的内部只能包含表达式
再来看jQuery源码:
function foo(){} // 声明,因为它是程序的一部分
var bar = function foo(){}; // 表达式,因为它是赋值表达式的一部分
new function bar(){}; // 表达式,因为它是new表达式
(function(){
function bar(){} // 声明,因为它是函数体的一部分
})();
可以将上面的代码结构分成两部分:(function(){window, undefined}) 和 (window) ,
第1个()是一个表达式,而这个表达式本身是一个匿名函数,
所以在这个表达式后面加(window)就表示执行这个匿名函数并传入参数window。
原型 prototype
认识一下什么是原型?
在JavaScript中,原型也是一个对象,通过原型可以实现对象的属性继承,JavaScript的对象中都包含了一个" [[Prototype]]"
(function(window, undefined) {
/...
})(window) 理解できないですか?問題はありません。段階的に分析していきます。
と関数宣言
ECMAScript では、関数を作成する最も一般的な方法2 つのメソッドは、関数式と関数宣言です。ECMA 仕様では、関数宣言には識別子 (Identifier) が必要であるという 1 つの点だけが明確になっているため、この 2 つの違いは少しわかりにくいです。関数名を言います)、関数式はこの識別子を省略できます: function Person(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.getInfo = function(){
console.log(this.name + " is " + this.age + " years old");
};
//调用
var will = new Person("Will", 28);
will.getInfo();//"Will is 28 years old"
したがって、そうでない場合は 関数名を宣言する場合、それは式である必要があります。しかし、関数名が宣言されている場合、それが関数宣言であるか関数式であるかをどのように判断するのでしょうか? ECMAScript はコンテキストによって区別されます。function foo(){} が代入式の一部として使用される場合、それは
If function foo( ){} です。 が関数本体またはプログラムの先頭に含まれる場合、関数宣言になります。 function A(){
var count = 0;
function B(){
count ++;
console.log(count);
}
return B;
}
var c = A();
c();// 1
c();// 2
c();// 3 括弧で囲まれた (function foo(){}) というあまり一般的ではない関数式もあります。これが式である理由は、括弧 () がグループ化演算であるためです。 、式は内部にのみ含めることができます
jQuery ソース コードをもう一度見てみましょう: (function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window); 上記のコード構造は、: (function(){window, unknown}) と 2 つの部分に分割できます。 (window) ,
したがって、この式の後に (window) を追加すると、この匿名関数とパスを実行することになります。パラメータウィンドウで。
プロトタイププロトタイププロトタイプとは何か理解していますか?
🎜 JavaScript では、🎜 プロトタイプもオブジェクトです。プロトタイプを通じて、オブジェクトのプロパティの継承を実現できます。🎜 JavaScript オブジェクトにはすべて、"[[Prototype]]" という内部プロパティが含まれています。対応するものはオブジェクトのプロトタイプです。 🎜🎜「prototype」と「proto」という 2 つの属性は、「person.prototype」と「person.proto」はまったく異なるものであるため、混同されることがあります。 🎜🎜「プロトタイプ」と「プロト」について簡単に説明します: 🎜🎜 1. すべてのオブジェクトには、オブジェクトのプロトタイプに対応する proto 属性があります 🎜🎜 2. 関数オブジェクトの場合、 proto 属性 さらに、prototype 属性もあります。🎜コンストラクター🎜として関数を使用してインスタンスを作成すると、その関数のprototype属性値がプロトタイプ(つまり設定)としてすべてのオブジェクトインスタンスに割り当てられます。インスタンスの proto 属性) 🎜🎜// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
}, 🎜🎜Closure🎜🎜🎜🎜 クロージャの定義: 🎜🎜🎜 🎜内部関数🎜がその外部関数の外側の変数によって参照されると、クロージャが形成されます。 🎜🎜🎜クロージャの役割: 🎜🎜🎜クロージャの役割を理解する前に、まずJavaScriptのGCメカニズムを理解しましょう: 🎜🎜JavaScriptでは、🎜オブジェクトが参照されなくなった場合、オブジェクトはGCリサイクルされ、そうでない場合はGCリサイクルされます。このオブジェクトは常にメモリに保存されます。 🎜🎜在上述例子中,B定义在A中,因此B依赖于A,而外部变量 c 又引用了B, 所以A间接的被 c 引用,
也就是说,A不会被GC回收,会一直保存在内存中。为了证明我们的推理,看如下例子:
function A(){
var count = 0;
function B(){
count ++;
console.log(count);
}
return B;
}
var c = A();
c();// 1
c();// 2
c();// 3
count是A中的一个变量,它的值在B中被改变,函数B每执行一次,count的值就在原来的基础上累加1。因此,A中的count一直保存在内存中。
这就是闭包的作用,有时候我们需要一个模块中定义这样一个变量:希望这个变量一直保存在内存中但又不会“污染”全局的变量,这个时候,我们就可以用闭包来定义这个模块
在看jQuery源码:
(function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window);
我们知道了 什么是闭包:当一个内部函数被其外部函数之外的变量引用时,就形成了一个闭包。
jQuery.fn的init 函数被jQuery 的构造函数调用了,这里形成了一个闭包。
构造函数及调用代码:
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
问题关键来了。
如何实现无new构建
JavaScript是函数式语言,函数可以实现类,类就是面向对象编程中最基本的概念
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
//构造函数
}
aQuery.prototype = {
//原型
name:function(){},
age:function(){}
}
var a = new aQuery();
a.name();
这是常规的使用方法,显而易见jQuery不是这样玩的
要实现这样,那么jQuery就要看成一个类,那么$()应该是返回类的实例才对
按照jQuery的抒写方式
$().ready() $().noConflict()
要实现这样,那么jQuery就要看成一个类,那么$()应该是返回类的实例才对
所以把代码改一下:
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return new aQuery();
}
aQuery.prototype = {
name:function(){},
age:function(){}
}
通过new aQuery(),虽然返回的是一个实例,但是也能看出很明显的问题,死循环了!
那么如何返回一个正确的实例?
在javascript中实例this只跟原型有关系
那么可以把jQuery类当作一个工厂方法来创建实例,把这个方法放到aQuery.prototye原型中
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init:function(selector){
return this;
}
name:function(){},
age:function(){}
}
当执行aQuery() 返回的实例:
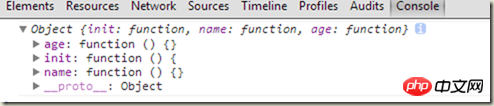
很明显aQuery()返回的是aQuery类的实例,那么在init中的this其实也是指向的aQuery类的实例
问题来了init的this指向的是aQuery类,如果把init函数也当作一个构造器,那么内部的this要如何处理?
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {},
age: 20
}
aQuery().age //18
因为this只是指向aQuery类的,所以aQuery的age属性是可以被修改的。
这样看似没有问题,其实问题很大的
为什么是new jQuery.fn.init?
看如下代码:
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
if(selector=="a")
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {},
age: 20
}
aQuery("a").age //18
aQuery("b").age //18
当我调用 传入"a"的时候,修改age=18,及aQuery("a").age 的值为18
但是当我 传入"b"的时候 并没又修改 age的值,我也希望得到默认age的值20,但是aQuery("b").age 的值为18.
因为在 调用aQuery("a").age 的时候age被修改了。
这样的情况下就出错了,所以需要设计出独立的作用域才行。
jQuery框架分隔作用域的处理
jQuery = function( selector, context ) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context, rootjQuery );
},
很明显通过实例init函数,每次都构建新的init实例对象,来分隔this,避免交互混淆
我们修改一下代码:
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return new aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
if(selector=="a")
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {},
age: 20
}
aQuery("a").age //18
aQuery("b").age //undefined
aQuery("a").name() //Uncaught TypeError: Object [object Object] has no method 'name'
又出现一个新的问题,
age :undefined,
name() :抛出错误,无法找到这个方法,所以很明显new的init跟jquery类的this分离了
怎么访问jQuery类原型上的属性与方法?
做到既能隔离作用域还能使用jQuery原型对象的作用域呢,还能在返回实例中访问jQuery的原型对象?
实现的关键点
// Give the init function the jQuery prototype for later instantiation jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
我们再改一下:
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return new aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
if(selector=="a")
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {
return age;
},
age: 20
}
aQuery.prototype.init.prototype = aQuery.prototype;
aQuery("a").age //18
aQuery("b").age //20
aQuery("a").name() //20
最后在看一下jQuery源码:
(function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window);
是不是明白了?
哈哈哈~~~
在简单说两句:
大部分人初看 jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn 这一句都会被卡主,很是不解。但是这句真的算是 jQuery 的绝妙之处。理解这几句很重要,分点解析一下:
1)首先要明确,使用 $('xxx') 这种实例化方式,其内部调用的是 return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery) 这一句话,也就是构造实例是交给了 jQuery.fn.init() 方法取完成。
2)将 jQuery.fn.init 的 prototype 属性设置为 jQuery.fn,那么使用 new jQuery.fn.init() 生成的对象的原型对象就是 jQuery.fn ,所以挂载到 jQuery.fn 上面的函数就相当于挂载到 jQuery.fn.init() 生成的 jQuery 对象上,所有使用 new jQuery.fn.init() 生成的对象也能够访问到 jQuery.fn 上的所有原型方法。
3)也就是实例化方法存在这么一个关系链
1.jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype ;
2.new jQuery.fn.init() 相当于 new jQuery() ;
3.jQuery() 返回的是 new jQuery.fn.init(),而 var obj = new jQuery(),所以这 2 者是相当的,所以我们可以无 new 实例化 jQuery 对象。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
以上が新規構築不要のjQueryの使い方を詳しく解説の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

