まず、キューの基本的な知識を得る必要があります。前の章を参照してください。
関連チュートリアル: jQuery でのアニメーション処理の概要: http://www.jb51.net/article/42000.htm
jQuery 1.9.1 ソースコード解析シリーズ (15) アニメーション処理とアニメーションコアのイージング Tween: http://www.jb51.net/article/75821.htm
a. アニメーションエントリ jQuery.fn.animate 関数実行処理の詳細説明
----------------------------------------------- --- ----------------------------------
まず、パラメータに従って jQuery.speed を呼び出してアニメーション関連のパラメータを取得し、次のようなオブジェクトを取得して、アニメーション実行関数 doAnimation
を生成します。
optall = {
complete: fnction(){...},//动画执行完成的回调
duration: 400,//动画执行时长
easing: "swing",//动画效果
queue: "fx",//动画队列
old: false/fnction(){...},
}
var empty = jQuery.isEmptyObject( prop ),
optall = jQuery.speed( speed, easing, callback ),
doAnimation = function() {
//在特征的副本上操作,保证每个特征效果不会被丢失
var anim = Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall );
doAnimation.finish = function() {
anim.stop( true );
};
//空动画或完成需要立马解决
if ( empty || jQuery._data( this, "finish" ) ) {
anim.stop( true );
}
};
doAnimation.finish = doAnimation;
実行中のアニメーションがない場合、アニメーションはすぐに実行されます。そうでない場合、アニメーションはアニメーション キューにプッシュされて実行を待ちます
//没有动画在执行则马上执行动画,否则将动画压入动画队列等待执行 return empty || optall.queue === false ? this.each( doAnimation ) : this.queue( optall.queue, doAnimation );
実際にアニメーションが実行される場所は、Animation(this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall ) 関数であることがわかります
b. jQuery 内部関数アニメーションの詳細説明
----------------------------------------------- --- ----------------------------------
アニメーション (要素、プロパティ、オプション)。プロパティはアニメーション化する CSS 機能、オプションはアニメーション関連のオプションです。{complete: function () {…},duration: 400,easing: unfineed,old: false,queue: 「FX」}。
まず、アニメーションキューの処理に使用される遅延オブジェクトを初期化します。
deferred = jQuery.Deferred().always( function() {
// don't match elem in the :animated selector
delete tick.elem;
}),
次に、各時点で実行される関数ティックを生成します (隣接する 2 つの時点間のイベント間隔はデフォルトで 13 ミリ秒です)。このティック関数は jQuery.timers に保存され、その後は毎回実行されます。 time jQuery.fx.tick実行時に取り出して実行されます。
tick = function() {
if ( stopped ) {
return false;
}
var currentTime = fxNow || createFxNow(),
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime ),
// archaic crash bug won't allow us to use 1 - ( 0.5 || 0 ) (#12497)
temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,
percent = 1 - temp,
index = 0,
length = animation.tweens.length;
//执行动画效果
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
animation.tweens[ index ].run( percent );
}
//生成进度报告
deferred.notifyWith( elem, [ animation, percent, remaining ]);
if ( percent < 1 && length ) {
return remaining;
} else {
//动画执行完毕,执行所有延时队列中的函数(包括清除动画相关的数据)
deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation ] );
return false;
}
}
jQuery によるアニメーションの進行状況の処理がわかります:
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime )temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,percent = 1 - temp,
進行状況のパーセンテージ = 1 - 残り時間のパーセンテージ。
通常、次のように処理します。アニメーションは 13 ミリ秒ごとに 1 回実行され、現在の実行は n 回目で、アニメーションの合計期間は T であると仮定します。それでは
進捗率 = (n*13)/T
実際、このアルゴリズムで得られる時間 n*13 は不正確です。これは、CPU がプログラムを実行しているだけではなく、割り当てられたタイム スライスが n*13 よりも大きいことがよくあるためです。さらに、これは非常に不正確な値であるため、アニメーションが速くなったり遅くなったり、一貫性がなくなったりする原因になります。 jQuery メソッドは、現在のイベント ポイントでのアニメーションの実行結果の精度を保証します。結局のところ、イベントは最新の計算結果です。
第三に、アニメーションに使用されるすべての機能で構成されるオブジェクト アニメーションを生成します (このオブジェクトの構造はソース コードに示されているとおりです)。animation.props に保存されるのは、ユーザーによって渡された機能です。 (アニメーションの最終目標)。
animation = deferred.promise({
elem: elem,
props: jQuery.extend( {}, properties ),
opts: jQuery.extend( true, { specialEasing: {} }, options ),
originalProperties: properties,
originalOptions: options,
startTime: fxNow || createFxNow(),
duration: options.duration,
tweens: [],
createTween: function( prop, end ) {
var tween = jQuery.Tween( elem, animation.opts, prop, end,
animation.opts.specialEasing[ prop ] || animation.opts.easing );
animation.tweens.push( tween );
return tween;
},
stop: function( gotoEnd ) {
var index = 0,
// if we are going to the end, we want to run all the tweens
// otherwise we skip this part
length = gotoEnd ? animation.tweens.length : 0;
if ( stopped ) {
return this;
}
stopped = true;
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
animation.tweens[ index ].run( 1 );
}
// resolve when we played the last frame
// otherwise, reject
if ( gotoEnd ) {
deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] );
} else {
deferred.rejectWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] );
}
return this;
}
})
4 番目に、propFilter を呼び出して CSS 機能名を修正し、ブラウザーで認識できるようにします。borderWidth/padding/margin は 1 つの CSS 機能を参照するのではなく、4 つの CSS 機能 (上部、下部) を参照することに注意してください。 、左、右)
//经过propFilter,animation.opts.specialEasing添加了相应的特征 propFilter( props, animation.opts.specialEasing );
propFilter の補正結果の例を示します。
例 1、CSS 機能 {height: 200} の変更結果は次のとおりです:
props = { height: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = {height: undefined}
例 2: CSS フィーチャー {margin:200} の修正結果は次のようになります:
props = { marginBottom: 200,marginLeft: 200,marginRight: 200,marginTop: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = { marginBottom: undefined,marginLeft: undefined,marginRight: undefined,marginTop: undefined }
5 番目に、適応処理のために defaultPrefilter を呼び出します。たとえば、高さ/幅のアニメーションには、効果を発揮するために表示とオーバーフローが特定の値である必要があります。たとえば、表示/非表示のアニメーションには大量の CSS が必要です。特徴値を指定し、関数内で createTweens を呼び出してイージング アニメーションを生成します。
// animationPrefilters[0] = defaultPrefilter
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
result = animationPrefilters[ index ].call( animation, elem, props, animation.opts );
if ( result ) {
return result;
}
}
animePrefilters[index] の値関数は、defaultPrefilter です。defaultPrefilter 関数の処理には、いくつかの重要な側面があります。
DefaultPrefilter キー ポイント 1: インライン要素内の高さ/幅に関連するアニメーションでは、表示機能の値を inline-block に設定する必要があります
// height/width overflow pass
if ( elem.nodeType === 1 && ( "height" in props || "width" in props ) ) {
//确保没有什么偷偷出来
//记录3个overflow相关特征,因为IE不能改变overflow特征值,
//当overflowX和overflowY设置了相同的值
opts.overflow = [ style.overflow, style.overflowX, style.overflowY ];
// 内联元素中height/width相关动画需要设置display特征值为inline-block
if ( jQuery.css( elem, "display" ) === "inline" &&
jQuery.css( elem, "float" ) === "none" ) {
// 内联元素接受inline-block;
// 块级元素必须内嵌在布局上
if ( !jQuery.support.inlineBlockNeedsLayout || css_defaultDisplay( elem.nodeName ) === "inline" ) {
style.display = "inline-block";
} else {
style.zoom = 1;
}
}
}
defaultPrefilterのポイント2: 高さ/幅アニメーションのオーバーフローについては、「非表示」に設定し、アニメーションが完了したら元に戻します。これにより、レンダリング速度が向上します。
//对于height/width动画overflow都要设置为"hidden",动画完成后恢复
if ( opts.overflow ) {
style.overflow = "hidden";
//收缩包装块
if ( !jQuery.support.shrinkWrapBlocks ) {
anim.always(function() {
style.overflow = opts.overflow[ 0 ];
style.overflowX = opts.overflow[ 1 ];
style.overflowY = opts.overflow[ 2 ];
});
}
}
DefaultPrefilter フォーカス 3: アニメーションの表示/非表示の特別な処理: アニメーションの表示/非表示は genFx を呼び出して形状を取得します
props = {
height: "hide"
marginBottom: "hide"
marginLeft: "hide"
marginRight: "hide"
marginTop: "hide"
opacity: "hide"
paddingBottom: "hide"
paddingLeft: "hide"
paddingRight: "hide"
paddingTop: "hide"
width: "hide"
}
アニメーション化する必要があるフィーチャをハンドル リストにプッシュし、対応するフィーチャを削除して、対応するイージング アニメーションを生成します。
for ( index in props ) {
value = props[ index ];
//rfxtypes = /^(?:toggle|show|hide)$/。可以看到最终只有和show/hide的动画才会被饶茹handled中
if ( rfxtypes.exec( value ) ) {
delete props[ index ];
toggle = toggle || value === "toggle";
//如果当前节点的状态和指定的状态相同则不需要处理直接进行下一个状态判断
if ( value === ( hidden ? "hide" : "show" ) ) {
continue;
}
handled.push( index );
}
}
//有需要执行的动画处理则进入分支,里面会对各个特征动画生成缓动动画
length = handled.length;
if ( length ) {
dataShow = jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow" ) || jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow", {} );
if ( "hidden" in dataShow ) {
hidden = dataShow.hidden;
}
// toggle需要保存状态 - enables .stop().toggle() to "reverse"
if ( toggle ) {
dataShow.hidden = !hidden;
}
if ( hidden ) {
jQuery( elem ).show();
} else {
anim.done(function() {
jQuery( elem ).hide();
});
}
anim.done(function() {
var prop;
jQuery._removeData( elem, "fxshow" );
for ( prop in orig ) {
jQuery.style( elem, prop, orig[ prop ] );
}
});
for ( index = 0 ; index < length ; index++ ) {
prop = handled[ index ];
//生成缓动动画
tween = anim.createTween( prop, hidden ? dataShow[ prop ] : 0 );
orig[ prop ] = dataShow[ prop ] || jQuery.style( elem, prop );
if ( !( prop in dataShow ) ) {
dataShow[ prop ] = tween.start;
if ( hidden ) {
tween.end = tween.start;
tween.start = prop === "width" || prop === "height" ? 1 : 0;
}
}
}
}
六番目、イージングアニメーションの生成、表示/非表示はdefaultPrefilter関数で処理されています(上記ソースコード)。
createTweens( animation, props );
我们来看一看createTweens中具体做了什么,先看一下createTweens之前的animation对象

然后看一下经过createTweens之后的animation对象的tweens数组变成了
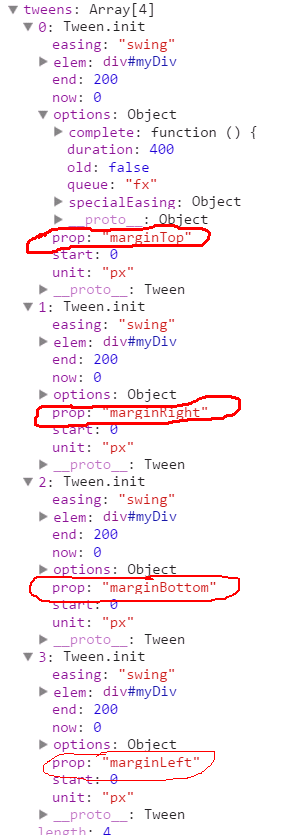
将margin分解成了四个属性(marginTop/Right/Bottom/Left)并且每个属性都有自己的动画特征。
第七,启动动画计时,定时执行tick
//启动动画计时
jQuery.fx.timer(
jQuery.extend( tick, {
elem: elem,
anim: animation,
queue: animation.opts.queue
})
);
最后,将传入的动画结束回调加入延时队列
//从options中获取回调函数添加到延时队列中 return animation.progress( animation.opts.progress ) .done( animation.opts.done, animation.opts.complete ) .fail( animation.opts.fail ) .always( animation.opts.always );
Animation函数流程到此为止
拓展:
前面提到的genFx函数是专门用在toggle、hide、show时获取相关的需要动画的特征的
最终生成的attrs = {
height: "show",
marginTop: "show",
marginRight: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有
marginBottom: "show",
marginLeft: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有
opacity: "show",
width: "show"
}
function genFx( type, includeWidth ) {
var which,
attrs = { height: type },
i = 0;
//如果包括宽度,步长值为1来完成所有cssExpand值,
//如果不包括宽度,步长值是2跳过左/右值
//cssExpand = [ "Top", "Right", "Bottom", "Left" ]
includeWidth = includeWidth? 1 : 0;
for( ; i < 4 ; i += 2 - includeWidth ) {
which = cssExpand[ i ];
attrs[ "margin" + which ] = attrs[ "padding" + which ] = type;
}
if ( includeWidth ) {
attrs.opacity = attrs.width = type;
}
return attrs;
}
Animation函数比较复杂,童鞋们可以随便使用例子去跟踪代码。这个是理解jQuery源码的一种比较好的方式。推荐两个例子:
第一个,有hide/show的例子:$("#id").hide(1000);
第二个,其他例子:$("#id").animate({"marginLeft":500},1000);
jQuery 1.9.1源码分析系列(十五)之动画处理 的全部内容就给大家介绍到这里,有问题随时给我留言,谢谢。!
 JavaScriptエンジンの理解:実装の詳細Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScriptエンジンの理解:実装の詳細Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMJavaScriptエンジンが内部的にどのように機能するかを理解することは、開発者にとってより効率的なコードの作成とパフォーマンスのボトルネックと最適化戦略の理解に役立つためです。 1)エンジンのワークフローには、3つの段階が含まれます。解析、コンパイル、実行。 2)実行プロセス中、エンジンはインラインキャッシュや非表示クラスなどの動的最適化を実行します。 3)ベストプラクティスには、グローバル変数の避け、ループの最適化、constとletsの使用、閉鎖の過度の使用の回避が含まれます。
 Python vs. JavaScript:学習曲線と使いやすさApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:学習曲線と使いやすさApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPythonは、スムーズな学習曲線と簡潔な構文を備えた初心者により適しています。 JavaScriptは、急な学習曲線と柔軟な構文を備えたフロントエンド開発に適しています。 1。Python構文は直感的で、データサイエンスやバックエンド開発に適しています。 2。JavaScriptは柔軟で、フロントエンドおよびサーバー側のプログラミングで広く使用されています。
 Python vs. JavaScript:コミュニティ、ライブラリ、リソースApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:コミュニティ、ライブラリ、リソースApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPythonとJavaScriptには、コミュニティ、ライブラリ、リソースの観点から、独自の利点と短所があります。 1)Pythonコミュニティはフレンドリーで初心者に適していますが、フロントエンドの開発リソースはJavaScriptほど豊富ではありません。 2)Pythonはデータサイエンスおよび機械学習ライブラリで強力ですが、JavaScriptはフロントエンド開発ライブラリとフレームワークで優れています。 3)どちらも豊富な学習リソースを持っていますが、Pythonは公式文書から始めるのに適していますが、JavaScriptはMDNWebDocsにより優れています。選択は、プロジェクトのニーズと個人的な関心に基づいている必要があります。
 C/CからJavaScriptへ:すべてがどのように機能するかApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
C/CからJavaScriptへ:すべてがどのように機能するかApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMC/CからJavaScriptへのシフトには、動的なタイピング、ゴミ収集、非同期プログラミングへの適応が必要です。 1)C/Cは、手動メモリ管理を必要とする静的に型付けられた言語であり、JavaScriptは動的に型付けされ、ごみ収集が自動的に処理されます。 2)C/Cはマシンコードにコンパイルする必要がありますが、JavaScriptは解釈言語です。 3)JavaScriptは、閉鎖、プロトタイプチェーン、約束などの概念を導入します。これにより、柔軟性と非同期プログラミング機能が向上します。
 JavaScriptエンジン:実装の比較Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScriptエンジン:実装の比較Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMさまざまなJavaScriptエンジンは、各エンジンの実装原則と最適化戦略が異なるため、JavaScriptコードを解析および実行するときに異なる効果をもたらします。 1。語彙分析:ソースコードを語彙ユニットに変換します。 2。文法分析:抽象的な構文ツリーを生成します。 3。最適化とコンパイル:JITコンパイラを介してマシンコードを生成します。 4。実行:マシンコードを実行します。 V8エンジンはインスタントコンピレーションと非表示クラスを通じて最適化され、Spidermonkeyはタイプ推論システムを使用して、同じコードで異なるパフォーマンスパフォーマンスをもたらします。
 ブラウザを超えて:現実世界のJavaScriptApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
ブラウザを超えて:現実世界のJavaScriptApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM現実世界におけるJavaScriptのアプリケーションには、サーバー側のプログラミング、モバイルアプリケーション開発、モノのインターネット制御が含まれます。 2。モバイルアプリケーションの開発は、ReactNativeを通じて実行され、クロスプラットフォームの展開をサポートします。 3.ハードウェアの相互作用に適したJohnny-Fiveライブラリを介したIoTデバイス制御に使用されます。
 next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する(バックエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する(バックエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM私はあなたの日常的な技術ツールを使用して機能的なマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーション(EDTECHアプリ)を作成しましたが、あなたは同じことをすることができます。 まず、マルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションとは何ですか? マルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを使用すると、Singの複数の顧客にサービスを提供できます
 next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する方法(フロントエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する方法(フロントエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMこの記事では、許可によって保護されたバックエンドとのフロントエンド統合を示し、next.jsを使用して機能的なedtech SaaSアプリケーションを構築します。 FrontEndはユーザーのアクセス許可を取得してUIの可視性を制御し、APIリクエストがロールベースに付着することを保証します


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

PhpStorm Mac バージョン
最新(2018.2.1)のプロフェッショナル向けPHP統合開発ツール

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

EditPlus 中国語クラック版
サイズが小さく、構文の強調表示、コード プロンプト機能はサポートされていません

SublimeText3 英語版
推奨: Win バージョン、コードプロンプトをサポート!

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Eclipse を SAP NetWeaver アプリケーション サーバーと統合します。






