ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >Python チュートリアル >物理学における二重バネ質量エネルギー系を解くための Python コード例
物理学における二重バネ質量エネルギー系を解くための Python コード例
- 黄舟オリジナル
- 2017-10-03 05:46:181881ブラウズ
この記事では主に、Python を使用して物理学における二重バネ質量エネルギー系を解く方法に関する関連情報をサンプル コードを通じて詳しく紹介します。この記事は、あらゆる人の学習や仕事に役立つ特定の学習価値があります。友達が必要なので、編集者をフォローして一緒に学びましょう。
前書き
この記事では主に、物理学における二重バネ質量エネルギー系を解くための Python の使用に関する関連コンテンツを紹介し、参考と学習のために共有します。以下では多くは述べません。 、詳しく紹介していきましょう。
物理モデルは次のとおりです:
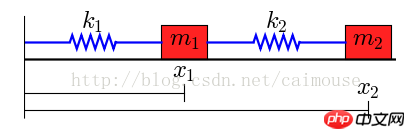
このシステムには 2 つのオブジェクトがあり、それらの質量はそれぞれ m1 と m2 で、2 つのバネで接続されています。伸縮システムは k1 と k2 (左端) です。修理済み。外力がないと仮定すると、2つのバネの長さはL1、L2となります。
2つの物体には重力があるため、平面上では摩擦が生じ、摩擦係数はそれぞれb1、b2となります。したがって、次のように微分方程式を書くことができます:
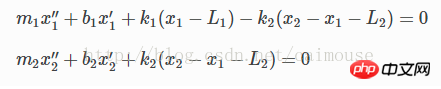
これは 2 階の微分方程式です。Python を使用して解くには、1 階の微分方程式に変換する必要があります。したがって、次の 2 つの変数が導入されます:

これら 2 つは移動速度に相当します。
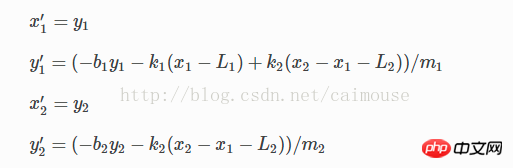
という操作でこれに変更できます。このとき、一次方程式はベクトル配列に変更でき、Pythonを使用して定義できます。コードは次のとおりです。
# Use ODEINT to solve the differential equations defined by the vector field
from scipy.integrate import odeint
def vectorfield(w, t, p):
"""
Defines the differential equations for the coupled spring-mass system.
Arguments:
w : vector of the state variables:
w = [x1,y1,x2,y2]
t : time
p : vector of the parameters:
p = [m1,m2,k1,k2,L1,L2,b1,b2]
"""
x1, y1, x2, y2 = w
m1, m2, k1, k2, L1, L2, b1, b2 = p
# Create f = (x1',y1',x2',y2'):
f = [y1,
(-b1 * y1 - k1 * (x1 - L1) + k2 * (x2 - x1 - L2)) / m1,
y2,
(-b2 * y2 - k2 * (x2 - x1 - L2)) / m2]
return f
# Parameter values
# Masses:
m1 = 1.0
m2 = 1.5
# Spring constants
k1 = 8.0
k2 = 40.0
# Natural lengths
L1 = 0.5
L2 = 1.0
# Friction coefficients
b1 = 0.8
b2 = 0.5
# Initial conditions
# x1 and x2 are the initial displacements; y1 and y2 are the initial velocities
x1 = 0.5
y1 = 0.0
x2 = 2.25
y2 = 0.0
# ODE solver parameters
abserr = 1.0e-8
relerr = 1.0e-6
stoptime = 10.0
numpoints = 250
# Create the time samples for the output of the ODE solver.
# I use a large number of points, only because I want to make
# a plot of the solution that looks nice.
t = [stoptime * float(i) / (numpoints - 1) for i in range(numpoints)]
# Pack up the parameters and initial conditions:
p = [m1, m2, k1, k2, L1, L2, b1, b2]
w0 = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# Call the ODE solver.
wsol = odeint(vectorfield, w0, t, args=(p,),
atol=abserr, rtol=relerr)
with open('two_springs.dat', 'w') as f:
# Print & save the solution.
for t1, w1 in zip(t, wsol):
out = '{0} {1} {2} {3} {4}\n'.format(t1, w1[0], w1[1], w1[2], w1[3]);
print(out)
f.write(out); ここに結果を出力します ファイル two_springs.dat に移動し、データを画像として表示するプログラムを作成すると、論文を公開できます。 コードは次のとおりです。
# Plot the solution that was generated from numpy import loadtxt from pylab import figure, plot, xlabel, grid, hold, legend, title, savefig from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties t, x1, xy, x2, y2 = loadtxt('two_springs.dat', unpack=True) figure(1, figsize=(6, 4.5)) xlabel('t') grid(True) lw = 1 plot(t, x1, 'b', linewidth=lw) plot(t, x2, 'g', linewidth=lw) legend((r'$x_1$', r'$x_2$'), prop=FontProperties(size=16)) title('Mass Displacements for the\nCoupled Spring-Mass System') savefig('two_springs.png', dpi=100)
最後に、次のように出力された PNG 画像を確認してみましょう:
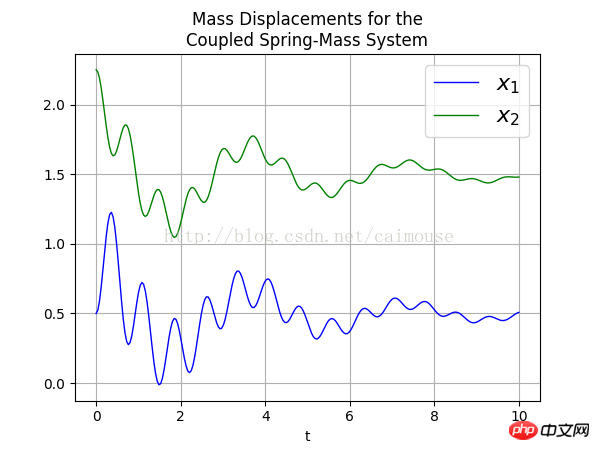
以上が物理学における二重バネ質量エネルギー系を解くための Python コード例の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

