ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >C#.Net チュートリアル >史上最も包括的な ASP.NET MVC ルーティング構成
史上最も包括的な ASP.NET MVC ルーティング構成
- 巴扎黑オリジナル
- 2017-04-09 11:15:115517ブラウズ
まず、ルーティング ルールの基本原則について説明します。基本的なルーティング ルールは特別なものから一般的なものへと配置されています。つまり、最も特殊な (非主流の) ルールが先頭にあり、最も一般的な (万能の) ルールが最後にあります。これは、一致するルーティング ルールもこの順序に従うためです。逆に書くと、ルーティングルールを正しく書いたとしても、404を待つことになります
XD まず、URL の構造について話しましょう。 実際、これは構造ではなく、単なる文法上の特徴です。
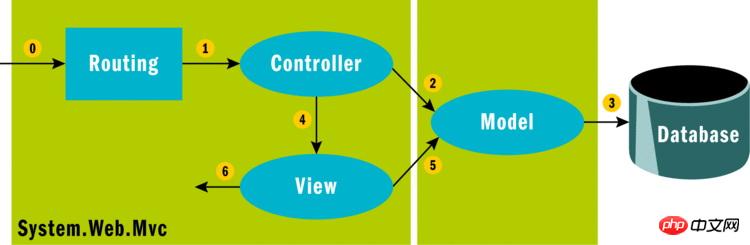
URL構築
名前付きパラメータ仕様 + 匿名オブジェクト
routes.MapRoute(name: "Default",url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } );ルートを構築し、
Route myRoute = new Route("{controller}/{action}", new MvcRouteHandler());
routes.Add("MyRoute", myRoute);を追加します ダイレクトメソッドのオーバーロード + 匿名オブジェクト
routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema", "Shop/{action}", new { controller = "Home" });個人的には、1 番目の方が理解しやすく、2 番目の方がデバッグしやすく、3 番目の方が書くのが効率的だと思います。あなたが必要なものを取る。この記事の執筆は 3 番目のタイプに偏っています。
ルーティングルール
1.デフォルトのルーティング (MVC に付属)
routes.MapRoute(
"Default", // 路由名称
"{controller}/{action}/{id}", // 带有参数的 URL
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } // 参数默认值 (UrlParameter.Optional-可选的意思) );2. 静的 URL セグメント
routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema2", "Shop/OldAction", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" });
routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema", "Shop/{action}", new { controller = "Home" });
routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema2", "Shop/OldAction.js",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" });プレースホルダー ルーティングがなければ、既成のハードコーディングされたものになります。
たとえば、次のように書いて http://localhost:XXX/Shop/OldAction.js にアクセスすると、問題なく応答されます。コントローラー、アクション、エリアという 3 つの予約語は、静的変数に配置しないでください。
3. 通常の変数 URL セグメントをカスタマイズします (この翻訳により、あなたの IQ が明らかになります)
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute2", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "DefaultId" });この場合、/Home/Index にアクセスすると、3 番目のセグメント (id) には値がないため、このパラメーターはルーティング ルールに従って DefaultId に設定されます
これは、viewbag を使用してタイトルに値を割り当てるとはっきりとわかります
ViewBag.Title = RouteData.Values["id"];
画像は投稿されなくなり、タイトルが DefaultId として表示されるようになりました。 コントローラーに値を割り当てる必要があることに注意してください。ビューに値を割り当てるとコンパイルされません。
4. デフォルトルートについて話しましょう
その後、デフォルトのルートに戻ります。 UrlParameter.Optional は、オプションの URL セグメントと呼ばれます。ルートにそのようなパラメーターがない場合、ID は null になります。 元の記事によると、このオプションの URL セグメントを使用して懸念事項の分離を実現できます。先ほどルートにパラメータのデフォルト値を直接設定するのは、実はあまり良い方法ではありません。私の理解によれば、実際のパラメータはユーザーによって送信され、私たちが行うのは正式なパラメータ名を定義することだけです。ただし、パラメータにデフォルト値を割り当てることを主張する場合は、構文シュガーを使用してそれらをアクションパラメータに書き込むことをお勧めします。例:
public ActionResult Index(string id = "abcd"){ViewBag.Title = RouteData.Values["id"];return View();}5. 可変長ルーティング。
りーここで、ID と最後のセグメントは両方とも変数であるため、/Home/Index/dabdafdaf は /Home/Index//abcdefdjldfiaeahfoeiho と同等であり、/Home/Index/All/Delete/Perm/… と同等です
6. クロスネームスペースルーティング
これは、名前空間を引用符で囲んで IIS Web サイトを開くことを忘れないよう注意するものです。そうしないと 404 が発生します。これは非常に非主流なので、いじることはお勧めできません。
りーただし、このように記述すると、配列のランキングは順不同となり、一致するルートが複数ある場合はエラーが報告されます。 そこで著者は改良された書き方を提案した。
りーこのようにして、最初の URL セグメントが Home でない場合は、処理のために 2 番目の URL セグメントに渡されます。最後に、このルートが見つからない場合は、後続のルートに道を残さないように設定することもできます。もう見下すことはありません。
りー7. ルーティングに一致する正規表現
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional });複数の URL を制限する
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute","{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers", "UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers" });8. リクエストメソッドを指定します
routes.MapRoute("AddContollerRoute","Home/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers" });
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers" });9. Webフォームのサポート
Route myRoute = routes.MapRoute("AddContollerRoute",
"Home/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers" }); myRoute.DataTokens["UseNamespaceFallback"] = false;詳細が見れます
Asp.Net4 の新機能ルーティングを使用して WebForm アプリケーションを作成します
または公式 msdn
10.MVC5のRouteAttribute
まずはルート登録方法へ
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
new { controller = "^H.*"},
new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers"});こっちだよ
れぇルート機能はのみ有効です。この機能には、ルーティング制約、順序、ルート名などもあります。
其他的还有路由前缀,路由默认值
[RoutePrefix("reviews")]<br>[Route("{action=index}")]<br>public class ReviewsController : Controller<br>{<br>}路由构造
// eg: /users/5
[Route("users/{id:int}"]
public ActionResult GetUserById(int id) { ... }
// eg: users/ken
[Route("users/{name}"]
public ActionResult GetUserByName(string name) { ... }参数限制
// eg: /users/5
// but not /users/10000000000 because it is larger than int.MaxValue,
// and not /users/0 because of the min(1) constraint.
[Route("users/{id:int:min(1)}")]
public ActionResult GetUserById(int id) { ... }| Constraint | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| alpha | Matches uppercase or lowercase Latin alphabet characters (a-z, A-Z) | {x:alpha} |
| bool | Matches a Boolean value. | {x:bool} |
| datetime | Matches a DateTime value. | {x:datetime} |
| decimal | Matches a decimal value. | {x:decimal} |
| double | Matches a 64-bit floating-point value. | {x:double} |
| float | Matches a 32-bit floating-point value. | {x:float} |
| guid | Matches a GUID value. | {x:guid} |
| int | Matches a 32-bit integer value. | {x:int} |
| length | Matches a string with the specified length or within a specified range of lengths. | {x:length(6)} {x:length(1,20)} |
| long | Matches a 64-bit integer value. | {x:long} |
| max | Matches an integer with a maximum value. | {x:max(10)} |
| maxlength | Matches a string with a maximum length. | {x:maxlength(10)} |
| min | Matches an integer with a minimum value. | {x:min(10)} |
| minlength | Matches a string with a minimum length. | {x:minlength(10)} |
| range | Matches an integer within a range of values. | {x:range(10,50)} |
| regex | Matches a regular expression. | {x:regex(^\d{3}-\d{3}-\d{4}$)} |
具体的可以参考
Attribute Routing in ASP.NET MVC 5
对我来说,这样的好处是分散了路由规则的定义.有人喜欢集中,我个人比较喜欢这种灵活的处理.因为这个action定义好后,我不需要跑到配置那里定义对应的路由规则
11.最后还是不爽的话自己写个类实现 IRouteConstraint的匹配方法。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Routing;
/// <summary>
/// If the standard constraints are not sufficient for your needs, you can define your own custom constraints by implementing the IRouteConstraint interface.
/// </summary>
public class UserAgentConstraint : IRouteConstraint
{
private string requiredUserAgent;
public UserAgentConstraint(string agentParam)
{
requiredUserAgent = agentParam;
}
public bool Match(HttpContextBase httpContext, Route route, string parameterName,
RouteValueDictionary values, RouteDirection routeDirection)
{
return httpContext.Request.UserAgent != null &&
httpContext.Request.UserAgent.Contains(requiredUserAgent);
}
}routes.MapRoute("ChromeRoute", "{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" },
new { customConstraint = new UserAgentConstraint("Chrome") },
new[] { "UrlsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers" });比如这个就用来匹配是否是用谷歌浏览器访问网页的。
12.访问本地文档
routes.RouteExistingFiles = true;
routes.MapRoute("DiskFile", "Content/StaticContent.html", new { controller = "Customer", action = "List", });浏览网站,以开启 IIS Express,然后点显示所有应用程序-点击网站名称-配置(applicationhost.config)-搜索UrlRoutingModule节点
<add name="UrlRoutingModule-4.0" type="System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule" preCondition="managedHandler,runtimeVersionv4.0" />
把这个节点里的preCondition删除,变成
<add name="UrlRoutingModule-4.0" type="System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule" preCondition="" />
13.直接访问本地资源,绕过了路由系统
routes.IgnoreRoute("Content/{filename}.html");文件名还可以用 {filename}占位符。
IgnoreRoute方法是RouteCollection里面StopRoutingHandler类的一个实例。路由系统通过硬-编码识别这个Handler。如果这个规则匹配的话,后面的规则都无效了。 这也就是默认的路由里面routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");写最前面的原因。
路由测试(在测试项目的基础上,要装moq)
PM> Install-Package Moq
using System;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System.Web;
using Moq;
using System.Web.Routing;
using System.Reflection;
[TestClass]
public class RoutesTest
{
private HttpContextBase CreateHttpContext(string targetUrl = null, string HttpMethod = "GET")
{
// create the mock request
Mock<HttpRequestBase> mockRequest = new Mock<HttpRequestBase>();
mockRequest.Setup(m => m.AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath)
.Returns(targetUrl);
mockRequest.Setup(m => m.HttpMethod).Returns(HttpMethod);
// create the mock response
Mock<HttpResponseBase> mockResponse = new Mock<HttpResponseBase>();
mockResponse.Setup(m => m.ApplyAppPathModifier(
It.IsAny<string>())).Returns<string>(s => s);
// create the mock context, using the request and response
Mock<HttpContextBase> mockContext = new Mock<HttpContextBase>();
mockContext.Setup(m => m.Request).Returns(mockRequest.Object);
mockContext.Setup(m => m.Response).Returns(mockResponse.Object);
// return the mocked context
return mockContext.Object;
}
private void TestRouteMatch(string url, string controller, string action, object routeProperties = null, string httpMethod = "GET")
{
// Arrange
RouteCollection routes = new RouteCollection();
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(routes);
// Act - process the route
RouteData result = routes.GetRouteData(CreateHttpContext(url, httpMethod));
// Assert
Assert.IsNotNull(result);
Assert.IsTrue(TestIncomingRouteResult(result, controller, action, routeProperties));
}
private bool TestIncomingRouteResult(RouteData routeResult, string controller, string action, object propertySet = null)
{
Func<object, object, bool> valCompare = (v1, v2) =>
{
return StringComparer.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase
.Compare(v1, v2) == 0;
};
bool result = valCompare(routeResult.Values["controller"], controller)
&& valCompare(routeResult.Values["action"], action);
if (propertySet != null)
{
PropertyInfo[] propInfo = propertySet.GetType().GetProperties();
foreach (PropertyInfo pi in propInfo)
{
if (!(routeResult.Values.ContainsKey(pi.Name)
&& valCompare(routeResult.Values[pi.Name],
pi.GetValue(propertySet, null))))
{
result = false;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
private void TestRouteFail(string url)
{
// Arrange
RouteCollection routes = new RouteCollection();
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(routes);
// Act - process the route
RouteData result = routes.GetRouteData(CreateHttpContext(url));
// Assert
Assert.IsTrue(result == null || result.Route == null);
}
[TestMethod]
public void TestIncomingRoutes()
{
// check for the URL that we hope to receive
TestRouteMatch("~/Admin/Index", "Admin", "Index");
// check that the values are being obtained from the segments
TestRouteMatch("~/One/Two", "One", "Two");
// ensure that too many or too few segments fails to match
TestRouteFail("~/Admin/Index/Segment");//失败
TestRouteFail("~/Admin");//失败
TestRouteMatch("~/", "Home", "Index");
TestRouteMatch("~/Customer", "Customer", "Index");
TestRouteMatch("~/Customer/List", "Customer", "List");
TestRouteFail("~/Customer/List/All");//失败
TestRouteMatch("~/Customer/List/All", "Customer", "List", new { id = "All" });
TestRouteMatch("~/Customer/List/All/Delete", "Customer", "List", new { id = "All", catchall = "Delete" });
TestRouteMatch("~/Customer/List/All/Delete/Perm", "Customer", "List", new { id = "All", catchall = "Delete/Perm" });
}
}最后还是再推荐一下Adam Freeman写的apress.pro.asp.net.mvc.4这本书。稍微熟悉MVC的从第二部分开始读好了。前面都是入门(对我来说是扯淡)。但总比国内某些写书的人好吧——把个开源项目的源代码下载下来帖到书上面来,然后标题起个深入解析XXXX,然后净瞎扯淡。最后一千多页的巨著又诞生了。Adam Freeman的风格我就很喜欢,都是实例写作,然后还在那边书里面专门写了大量的测试。
哎没办法啊,技术差距就是这样了。
以上が史上最も包括的な ASP.NET MVC ルーティング構成の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

