.NETフレームワークのLinkListは双方向リンクリストを実装しています。その実装ソースコードを要約してみましょう。
まず、LinkedList によって提供されるパブリック プロパティとメソッドのマップを確認します:
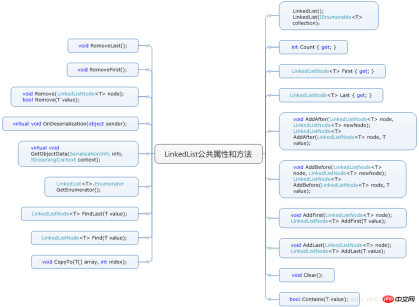
1 LinkedList によって実装される インターフェイス:
public class LinkedList<T> : ICollection<T>, ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback
2 LinkedList のグローバル 変数 には、以下が含まれます。
head はカプセル化されたクラスの head ノード です。
// This LinkedList is a doubly-Linked circular list.
internal LinkedListNode<T> head;
internal int count;
internal int version;
private object _syncRoot;
//A temporary variable which we need during deserialization.
private SerializationInfo _siInfo;
// names for serialization
private const string VersionName = "Version";
private const string CountName = "Count";
private const string ValuesName = "Data";によってカプセル化された各ノードのデータ構造は次のとおりです:
public sealed class LinkedListNode<T>
{ public LinkedListNode(T value);
//获取LinkedListNode所属的LinkedList
public LinkedList<T> List { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Next { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Previous { get; }
//获取节点中包含的值。
public T Value { get; set; }
}3 Constructor:
public LinkedList() //默认的构造函数
{
} //带有参数的
public LinkedList(IEnumerable<T> collection)
{ if (collection == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(collection));
} foreach (T item in collection)
{
AddLast(item);
}
}IEnumerable 型のコレクションを構築する場合、AddLast ( T) メソッドには、オーバーロードもあり、動作の詳細は次のとおりです:
public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
} return result;
}
public void AddLast(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
}
node.list = this; //结合LinkedListNode看
}上記の 2 つのメソッド、セマンティクスは、特定のノードを挿入し、
空のリストに新しいノードを挿入し、InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList
new を挿入します。空のリスト InternalInsertNodeBefore にノードを追加し、newNode が挿入される前にノードを指定し、新しく挿入されたノードが有効な新しいノードであるかどうかも判断します。
internal void ValidateNewNode(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{ if (node == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(node));
} if (node.list != null)
{ throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.LinkedListNodeIsAttached);
}
}同時に、ノードが有効なノードであるかどうかを判断する方法も提供します:
internal void ValidateNode(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{ if (node == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(node));
} if (node.list != this)
{ throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.ExternalLinkedListNode);
}
}これは二重リンクリストの重要な内部メソッドです。
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList 実装の詳細:
private void InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
Debug.Assert(head == null && count == 0, "LinkedList must be empty when this method is called!");
newNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}InternalInsertNodeBefore 実装の詳細:
private void InternalInsertNodeBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
newNode.next = node;
newNode.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = newNode;
node.prev = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}4 リンク リストは当然のことです。これはノードを挿入するパブリック メソッドと切り離すことができません。
public LinkedListNode<T> AddAfter(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value)
{
ValidateNode(node);
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(node.list, value);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node.next, result); return result;
} public void AddAfter(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
ValidateNode(node);
ValidateNewNode(newNode);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node.next, newNode);
newNode.list = this;
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value)
{
ValidateNode(node);
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(node.list, value);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node, result); if (node == head)
{
head = result;
} return result;
} public void AddBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
ValidateNode(node);
ValidateNewNode(newNode);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node, newNode);
newNode.list = this; if (node == head)
{
head = newNode;
}
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddFirst(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
head = result;
} return result;
} public void AddFirst(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node); if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
head = node;
}
node.list = this;
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
} return result;
} public void AddLast(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node); if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
}
node.list = this;
}5 もう一度見てみましょう。リンク リスト内のすべてのノードをクリアします。ここでは、すべてのノードがメモリをポイントしないように設定します。ヒープを作成し、GC リサイクルを待ちます。
public void Clear()
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while (current != null)
{
LinkedListNode<T> temp = current;
current = current.Next;
// use Next the instead of "next", otherwise it will loop forever
temp.Invalidate();
}
head = null;
count = 0;
version++;
}6 にのみ対応します。ノードの一連のインターフェイスの削除は追加と同様なので、詳細は説明しません。
Clear で呼び出されます。は非常に単純です:
internal void Invalidate()
{
list = null;
next = null;
prev = null;
}7 ノード値が値として存在するかどうかを判断するには、 Find メソッド、
public bool Contains(T value)
{ return Find(value) != null;
}Find メソッド実装の詳細を呼び出します。これは、 API と FindLast に似ています。これは二重リンクリストであるため、リンクされたリストを端からたどるだけです、
public LinkedListNode<T> Find(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
//调用默认相等比较器
EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default;
if (node != null)//链表为null
{
if (value != null)
{
do
{
if (c.Equals(node.item, value)) //Equals:某个节点node的item与value相等
{
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
else
{
do
{
if (node.item == null)
{
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
} return null; //链表为null,直接返回null
}8 データを array にコピーする実装を見てみましょう :
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index)
{
if (array == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(array));
}
if (index < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), index, SR.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum);
}
if (index > array.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), index, SR.ArgumentOutOfRange_BiggerThanCollection);
}
if (array.Length - index < Count)
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Arg_InsufficientSpace);
}
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
if (node != null)
{
do
{
array[index++] = node.item;
node = node.next;
} while (node != head); //双向链表,再次遍历到头结点时
}
}以上が.NET Framework - 二重リンク リスト (LinkedList) コード分析 (図)の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
 C#.NETで開発:実用的なガイドと例May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AM
C#.NETで開発:実用的なガイドと例May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AMC#と.NETは、強力な機能と効率的な開発環境を提供します。 1)C#は、CのパワーとJavaのシンプルさを組み合わせた最新のオブジェクト指向プログラミング言語です。 2).NETフレームワークは、複数のプログラミング言語をサポートするアプリケーションを構築および実行するためのプラットフォームです。 3)C#のクラスとオブジェクトは、オブジェクト指向プログラミングの中核です。クラスはデータと動作を定義し、オブジェクトはクラスのインスタンスです。 4).NETのゴミ収集メカニズムは、開発者の作業を簡素化するためにメモリを自動的に管理します。 5)C#および.NETは、同期および非同期プログラミングをサポートする強力なファイル操作関数を提供します。 6)一般的なエラーは、デバッガー、ロギング、例外処理を通じて解決できます。 7)パフォーマンスの最適化とベストプラクティスには、StringBuildの使用が含まれます
 C#.NET:Microsoft .NETフレームワークの理解May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM
C#.NET:Microsoft .NETフレームワークの理解May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM.NetFrameworkは、一貫したプログラミングモデルと強力なランタイム環境を提供する、クロス言語のクロスプラットフォーム開発プラットフォームです。 1)メモリとスレッドを管理するCLRとFCLで構成され、FCLは事前に構築された機能を提供します。 2)使用の例には、読み取りファイルとLINQクエリが含まれます。 3)一般的なエラーには、未処理の例外とメモリリークが含まれ、デバッグツールを使用して解決する必要があります。 4)パフォーマンスの最適化は、非同期プログラミングとキャッシュを通じて実現でき、コードの読みやすさと保守性を維持することが重要です。
 c#.netの寿命:その永続的な人気の理由May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AM
c#.netの寿命:その永続的な人気の理由May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AMC#.NETが永続的に魅力的なままである理由には、その優れたパフォーマンス、リッチエコシステム、強力なコミュニティサポート、クロスプラットフォーム開発機能が含まれます。 1)優れたパフォーマンスであり、エンタープライズレベルのアプリケーションとゲーム開発に適しています。 2).NETフレームワークは、さまざまな開発分野をサポートするための幅広いクラスライブラリとツールを提供します。 3)アクティブな開発者コミュニティと豊富な学習リソースがあります。 4).NetCoreは、クロスプラットフォーム開発を実現し、アプリケーションシナリオを拡張します。
 マスターC#.NETデザインパターン:シングルトンから依存関係への注入までMay 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
マスターC#.NETデザインパターン:シングルトンから依存関係への注入までMay 09, 2025 am 12:15 AMC#.NETの設計パターンには、Singletonパターンと依存関係の注入が含まれます。 1.シングルトンモードは、クラスに1つのインスタンスしかないことを保証します。これは、グローバルアクセスポイントが必要なシナリオに適していますが、安全性と虐待の問題をスレッドすることに注意する必要があります。 2。依存関係の噴射により、依存関係を注入することにより、コードの柔軟性とテスト可能性が向上します。多くの場合、コンストラクターの注入に使用されますが、複雑さを高めるために過度の使用を避ける必要があります。
 C#.NET現代世界:アプリケーションと産業May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AM
C#.NET現代世界:アプリケーションと産業May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AMC#.NETは、ゲーム開発、金融サービス、モノのインターネット、クラウドコンピューティングの分野で現代世界で広く使用されています。 1)ゲーム開発では、C#を使用してUnityエンジンを介してプログラムします。 2)金融サービスの分野では、C#.NETが高性能取引システムとデータ分析ツールの開発に使用されます。 3)IoTおよびクラウドコンピューティングに関して、C#.NETはAzure Servicesを通じてサポートを提供して、デバイス制御ロジックとデータ処理を開発します。
 C#.NETフレームワークvs.Net Core/5/6:違いは何ですか?May 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C#.NETフレームワークvs.Net Core/5/6:違いは何ですか?May 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM.NETFRAMEWORKISWINDOWS-CENTRIC、while.netcore/5/6supportscross-platformdevelopment.1).netframework、2002年以来、isidealforwindowsprimitedincross-platformcapabilities.2).netcore、andtseverutions(andtseverutions(andtseverution)
 C#.NET開発者のコミュニティ:リソースとサポートMay 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
C#.NET開発者のコミュニティ:リソースとサポートMay 06, 2025 am 12:11 AMC#.NET開発者コミュニティは、次のような豊富なリソースとサポートを提供します。1。Microsoftの公式文書、2。StackoverflowやRedditなどのコミュニティフォーラム、3。Githubのオープンソースプロジェクト。これらのリソースは、開発者が基本的な学習から高度なアプリケーションまでプログラミングスキルを向上させるのに役立ちます。
 C#.NETアドバンテージ:機能、利点、およびユースケースMay 05, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C#.NETアドバンテージ:機能、利点、およびユースケースMay 05, 2025 am 12:01 AMC#.NETの利点には以下が含まれます。1)非同期プログラミングなどの言語機能により、開発が簡素化されます。 2)パフォーマンスと信頼性、JITコンピレーションとゴミ収集メカニズムによる効率の向上。 3)クロスプラットフォームサポート、.NetCoreはアプリケーションシナリオを拡張します。 4)Webからデスクトップ、ゲーム開発までの優れたパフォーマンスを備えた幅広い実用的なアプリケーション。


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

MantisBT
Mantis は、製品の欠陥追跡を支援するために設計された、導入が簡単な Web ベースの欠陥追跡ツールです。 PHP、MySQL、Web サーバーが必要です。デモおよびホスティング サービスをチェックしてください。

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい






