ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >C#.Net チュートリアル >C#の基礎知識集 基礎知識(16) IListインターフェース - 非ジェネリック
C#の基礎知識集 基礎知識(16) IListインターフェース - 非ジェネリック
- 黄舟オリジナル
- 2017-02-11 13:44:421443ブラウズ
ICollection インターフェイス、反復、および汎用コレクションを理解した後、IList インターフェイスについてさらに学びましょう。
MSDN を見ると、IList インターフェイスには 2 種類あることがわかります。 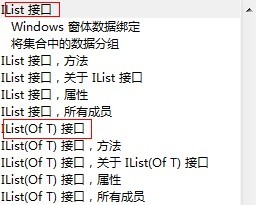
要素がオブジェクト型である IList インターフェイスは、さまざまな種類のオブジェクト参照を保持できます。
IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c のオブジェクト参照のみを保存できます。指定されたタイプ。実際、IList と IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c は、コレクションの長さを動的に変更できることが特徴です。コレクションの初期長を決定する必要はありません。保存されたデータの。
IList と IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c の間の継承関係がわかります。
[ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public interface IList : ICollection, IEnumerable public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerableここで、IList と IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c の違いを見てください。次のコードを見てください。 :
public class IListClass
{
void test()
{
TestClass1 c1 = null;
ArrayList arryList = new ArrayList();
arryList.Add(c1);
List<TestClass1> list = new List<TestClass1>();
list.Add(c1);
//取值
TestClass1 getC1Array = arryList[0] as TestClass1;//必须要一次强制转换
TestClass1 getC1List = list[0];//不需要转换,所谓泛型
}
}
public class TestClass1
{
}これで、より明確になりました。 1. IList インターフェイスの概要
ILis インターフェイスは ICollection インターフェイスを継承し、次の特性を備えています。
Count プロパティ - コレクション要素の数を取得します。
GetEnumerator メソッド - 反復可能。
CopyTo メソッド - 指定された要素をコピーします。別の配列 Medium;
Clear メソッド - コレクション全体をクリアします。
IList の新機能、
Indexer 属性 - インデックスに基づいてコレクション内の任意の要素にアクセスします。
Add メソッド - コレクションの末尾に要素を追加します。
Insert メソッド - コレクションの指定された位置に要素を挿入します。 Remove メソッド - 削除 要素を指定します。(RemoveAt を含む)
Contains メソッド - オブジェクトがコレクション内にあるかどうかを判断します。
IndexOf メソッド - コレクション内の指定されたオブジェクトのインデックス位置を検索します。
さらに、IList インターフェイス コレクションは要素を順番に保存し、要素の保存順序を変更しません。
2. アルゴリズム
ベクトル コレクションには、配列と同様にランダム アクセスの特性があります。つまり、ベクトル セットのどのユニットにアクセスする場合でも、必要なアクセス時間はまったく同じです。ベクトル クラスでは、コレクション データを記録するために実際には通常の配列が使用されます。ベクトル クラスは、クラス全体を外部的に通常の配列とは異なる動作にするために、いくつかのアルゴリズム手法を使用します。つまり、配列の長さを動的に変更できます。具体的なアルゴリズムは次のとおりです。
内部配列の長さが十分な場合は、追加および挿入操作が直接実行されます。内部配列の長さが不十分な場合は、内部配列の長さを新しい配列の長さの 2 倍にしてから実行します。データを移動します (つまり、古い配列を新しい配列に移動します)。ベクトルが要素の記憶領域を割り当てるとき、メモリ割り当ての数を最小限に抑えるために、より多くの冗長領域が割り当てられます。データを削除した場合、内部配列の長さは変更されませんが、削除されたデータは削除されたデータの次のデータで上書きされます。
ただし、ベクターがスペースを割り当てるたびに、より多くの冗長なスペースが割り当てられるため、メモリ負荷が発生するため、プログラム内で集中した多数のメモリ割り当てを避ける必要があります。
3. 実装クラス
IList と IList
ArrayList クラスは System.Collection 名前空間の下にあります。
List
IV. 実装コード (非汎用)
/// <summary>
/// 实现IList,非泛型
/// </summary>
public class ArrayList : IList
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代
/// </summary>
public struct Enumertor : IEnumerator
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代索引
/// </summary>
private int index;
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器所属的向量类对象的引用
/// </summary>
private ArrayList arrayList;
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="arrayList">迭代器所属的集合类</param>
public Enumertor(ArrayList arrayList)
{
this.arrayList = arrayList;
this.index = -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取当前对象,根据index的值返回向量对应的对象引用
/// </summary>
public object Current
{
get
{
return arrayList[index];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 将迭代器指向下一个数据位置,通过改变index的值,加1或减1
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool MoveNext()
{
if (this.index < arrayList.Count)
{
++this.index;
}
return this.index < arrayList.Count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器回到起始位置,将index置为-1
/// </summary>
public void Reset()
{
this.index = -1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 保存集合的数组
/// </summary>
private object[] array = new object[1];
/// <summary>
/// 当前集合的长度
/// </summary>
private int count;
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数
/// </summary>
public ArrayList()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 参数构造函数,通过参数指定内部数组长度,减少重新分配空间
/// </summary>
/// <param name="capacity"></param>
public ArrayList(int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
if (capacity == 0)
{
capacity = 1;
}
this.array = new object[capacity];
this.count = 0;
}
public int Count
{
get
{
return this.count;//该属性只读
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 集合实际使用长度
/// </summary>
public int Capacity
{
get
{
return this.array.Length;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否固定大小
/// </summary>
public bool IsFixedSize
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否只读集合
/// </summary>
public bool IsReadOnly
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否同步,即是否支持多线程访问
/// </summary>
public bool IsSynchronized
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 同步对象
/// </summary>
public object SyncRoot
{
get
{
return null;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 当array长度不足时,重新分配新的长度足够的数组
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private object[] GetNewArray()
{
return new object[(this.array.Length + 1) * 2];
}
public int Add(object value)
{
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (this.array.Length < newCount)//长度不足
{
object[] newArray = GetNewArray();
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, this.count);
this.array = newArray;//重新引用,指向新数组
}
//增加新元素
this.array[this.count] = value;
this.count = newCount;
//返回新元素的索引位置
return this.count - 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 索引器属性,按索引返回向量中的某一项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
return this.array[index];
}
set
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
this.array[index] = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除集合中的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <param name="count"></param>
public void RemoveRange(int index, int count)
{
if (index < 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
int removeIndex = index + count;//计算集合中最后一个被删元素的索引
if (count < 0 || removeIndex > this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//删除其实是将要删除元素之后的所有元素拷贝到要删除元素的位置覆盖掉
Array.Copy(this.array, index + 1, this.array, index + count - 1, this.count - removeIndex);
//重新设置集合长度
this.count -= count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 查找对应的数组项,实际是遍历查找
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int IndexOf(object value)
{
int index = 0;
if (value == null)
{
while (index < this.count)
{
if (this.array[index] == null)
{
return index;
}
++index;
}
}
else
{
while (index < this.count)
{
if (this.array[index].Equals(value))
{
return index;
}
++index;
}
}
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中删除指定元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void Remove(object value)
{
int index = this.IndexOf(value);
if (index >= 0)
{
this.RemoveRange(index, 1);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中删除指定位置的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
public void RemoveAt(int index)
{
RemoveRange(index, 1);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取最后一个元素的引用后删除最后一个元素
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object PopBack()
{
object obj = this.array[this.count - 1];
RemoveAt(this.count - 1);
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取第一个元素引用并删除第一个元素
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object PropFront()
{
object obj = this.array[0];
RemoveAt(0);
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 插入元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void Insert(int index, object value)
{
if (index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//插入元素当空间不足时也是声明新的2倍长度数组,并拷贝旧数据。
//插入数据原理是,将指定位置后的数据全部后移,再将新数据放在指定位置。
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (this.array.Length < newCount)
{
object[] newArray = GetNewArray();
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, index);
this.array = newArray;
}
Array.Copy(this.array, index, this.array, index + 1, this.count - index);
this.array[index] = value;
this.count = newCount;
}
/// <summary>
/// 查看当前集合是否包含指定对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(object value)
{
return this.IndexOf(value) >= 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 将集合的长度改变为实际长度
/// </summary>
public void TrimToSize()
{
//为了消除Add和Insert时增加的冗余,原理是新生成一个和实际长度相同的数组,然后将值全部移过来。
if (this.array.Length > this.count)
{
object[] newArray = null;
if (this.count > 0)
{
newArray = new object[this.count];
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, this.count);
}
else
{
newArray = new object[1];
}
this.array = newArray;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 清空集合
/// </summary>
public void Clear()
{
this.count = 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取集合的迭代器
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
Enumertor enumerator = new Enumertor(this);
return enumerator;
}
/// <summary>
/// 转移集合元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetArray"></param>
/// <param name="index"></param>
public void CopyTo(Array targetArray, int index)
{
Array.Copy(this.array, 0, targetArray, index, this.count);
}
}
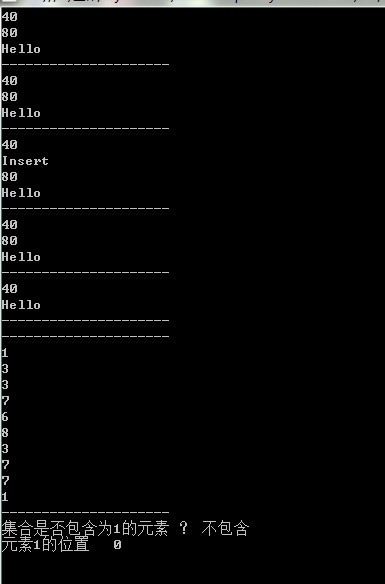
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//调用测试
ArrayList myArrayList = new ArrayList();
myArrayList.Add(40);
myArrayList.Add(80);
myArrayList.Add("Hello");
//使用for循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < myArrayList.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(myArrayList[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
//使用迭代循环
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Insert(1, "Insert");
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Remove("Insert");
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.RemoveAt(1);
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Clear();
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
myArrayList.Add(rand.Next(10));
}
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
Console.WriteLine("集合是否包含为1的元素 ? " + (myArrayList.Contains(0) ? "包含" : "不包含"));
Console.WriteLine("元素1的位置 " + myArrayList.IndexOf(1));
Console.ReadLine();
}結果:
上記の内容は、PHP 中国語 Web サイト ( www.php.cn )!

