ホームページ >データベース >mysql チュートリアル >Jdbc -- 固有のコード実装
Jdbc -- 固有のコード実装
- 黄舟オリジナル
- 2017-02-11 11:10:391570ブラウズ
1. 接続を取得します
1) jar パッケージをプロジェクト ディレクトリにコピーします現在のプロジェクトの下に次の内容の jdbc.properties ファイルを作成します。 Oracle、MySql に接続するためにデータベースに必要な 4 つの主なパラメータは次のとおりです: ドライバーのロード、データベースに接続するための IP とポートの取得、ユーザー名、パスワード)。その目的は、呼び出しと変更を容易にすることです。
2) クラスパスがビルドパスと一致するように、jar パッケージをプロジェクトのビルドパス環境変数に追加します。特定のサブクラスを簡単にロードします
3) ドライバークラスを反射的にロードし、ドライバーを自動的に登録します
#driverClass = oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver #url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl #user = scott#password = tigerdriverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/companyuser = root password = 123456
接続の取得と接続のクローズの具体的な実装は次のとおりです:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 获取连接
* 1) 把jar包复制到项目目录下
* 2) 把jar包加入项目的buildpath环境变量中, 使得classpath也和buildpath一致, 让类加载器便于加载具体子类
* 3) 反射加载驱动程序类, 会自动注册驱动程序
* 4) 通过驱动程序管理器获取连接.
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class DriverTest {
// 使用Properties类对象的getPropety方法与FileInputStream方法获取文件中的内容,从而创建Connection对象
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
}
すべての jdbc 操作は接続を確立する必要があるため、接続メソッドと接続を確立します。リソースを閉じるメソッドを、簡単に使用できるように JdbcUtil クラスに固定メソッドとして配置します。データベースと通信するには、Statement クラスを使用する必要があります。まず、Statement クラスで作成された会社データベース内のユーザー テーブルに対応する User クラスを作成する必要があります:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtil {
// 获取建立连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
// 关闭资源
public static void close(Connection connection) {
close(connection, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
close(connection, statement, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Use Statement to createユーザーテーブルに 3 行のデータを挿入します:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class User {
private String user;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String user, String password) {
super();
this.user = user;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [user=" + user + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
} ただし、Statement には 欠点があります。SQL ステートメントを詳しく記述する必要があるだけでなく、SQL インジェクションの問題も発生します。次の小さな例では、
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
// 使用Statement执行创建user表,并插入三行数据
public class StatementTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();// 获取执行体对象
// 执行SQL
// 创建user表
String sql = "create table if not exists user(user varchar(50), password varchar(100))";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 执行的DDL语句, 还可以执行DML
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('admin','admin')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user1','user1')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user2','123456')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, statement);
}
}
}
+------+---------- +
| パスワード |+------+------ ---+
| 管理者 |
| ユーザー 1 || +
しかし、SQLマスターは以下を実行することで正常にログインできます
。
SQLインジェクションの問題を防ぐために、そのサブクラスPreparedStatementを使用して実行本体をプリコンパイルする必要があります。以下のPreparedStatementを練習してみましょう。 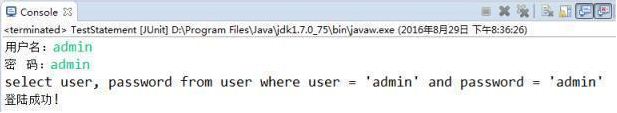 最初に作成するthe Customer クラス
最初に作成するthe Customer クラス
// 属性 name、性別、電話番号を含むクラス Customer を書き込みます
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestStatement {
// 弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题
@Test
public void testLogin() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("密 码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
String sql = "select user, password from user where user = '"
+ userName + "' and password = '" + password + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
User user = get(sql, User.class);
if(user != null){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else{
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
public <T> T get(String sql, Class<T> clazz) {// (sql, Customer.class)
T t = null;
Connection conn = null;
Statement stam = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
stam = conn.createStatement();
rs = stam.executeQuery(sql);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// //1. 获取列的名称
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 1. 获取列的别名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 注意:
// 获取结果集中(相当于数据表)列的名称(别名)
// 2. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(columnName);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 注意:反射根据Java中类的属性获取Field对象
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//JDBCUtils.close(rs, stam, conn);
}
return t;
}
} テスト クラスで PreparedStatment executor オブジェクトを使用して、対応するテーブルを作成し、2 つのデータを挿入します。
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String gender;
private String phone;
public Customer(String name, int age, String gender, String phone,) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Customer() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", phone=" + phone + "]";
}
}Customer クラスに属性 int age、double Weight を追加し、Customer テーブルに対応する列を追加し、レコードを追加します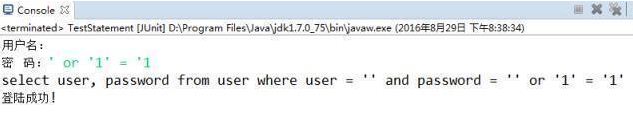
public class PreparedStatementTest {
@Test
public void exer1() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "create table if not exists customer(name varchar(30), gender enum('男','女') default '男', phone varchar(20))";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement); // 在获取新的预编译对象前,一定要先关闭原来的.
String sql2 = "insert into customer(name, gender, phone) values(?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); // 要想重新执行新的SQL,必须再次预编译
preparedStatement.setString(1, "张三");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "13343493434");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
preparedStatement.setString(1, "李四");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "1322243434");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
// 并通过客户端验证.
}
}上記と同じコードを毎回追加します。ここでは共通のものを設定します。更新操作は、ツール クラスの一般的な更新操作として CommonUtil クラスに保存されます。具体的な実装は次のとおりです。
public class PreparedStatementTest {
// 在Customer类中添加属性int age,double weight,给Customer表中添加对应的列,并添加记录
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add age int after name";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "alter table customer add weight double";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 50);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "134234234234");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 98.5);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 添加记录
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add birthdate date";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "赵六");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 60);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "13882342323");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 40);
preparedStatement.setString(6, "1960-2-3");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 再添加记录
@Test
public void test5() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "张七");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 20);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "1343434343");
preparedStatement.setObject(5, 58.8);
preparedStatement.setObject(6, "1980-3-8");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (rows == 1) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
}ResultSet クラス

