ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Android模倣淘宝網、京東省の製品詳細ページをドラッグしてグラフィックの詳細を表示し、デモの詳細な説明を表示します
Android模倣淘宝網、京東省の製品詳細ページをドラッグしてグラフィックの詳細を表示し、デモの詳細な説明を表示します
- 高洛峰オリジナル
- 2017-02-08 17:10:332200ブラウズ
この記事では、Android 模倣淘宝網と京東省の製品詳細ページの詳細なデモ説明を紹介します。2 つのスクロールビューが使用され、2 つのスクロールビューの垂直方向の配置が制御されます。 viewGroup をカスタマイズし、スライディング イベントを処理します。 Android で写真やテキストの詳細を表示するためのドラッグの知識に興味のある友人、一緒に学びましょう
1. 淘宝網の商品詳細ページの効果
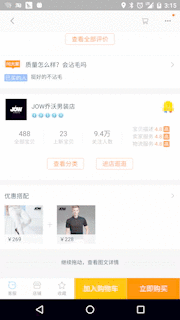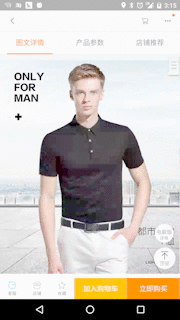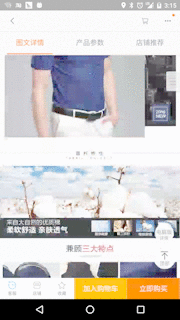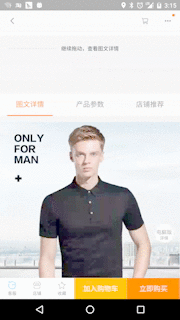
私たちの効果

2.実装アイデア
2つのscrollViewを使用し、2つのscrollViewを縦に配置し、2つのscrollViewの縦の配置はviewGroupのカスタマイズとスライドイベントの処理によって制御します。以下に示すように
3. 具体的な実装
1. viewGroup カスタム レイアウト View を継承し、onMeasure() メソッドと onLayout メソッドを書き換えて、onLayout メソッド内の 2 つのサブ ScrollView の垂直レイアウトを完成させるコードです。
レイアウトファイル:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MainActivity">
<com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.PullUpToLoadMore
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fillViewport="true">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/a1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="180dp" />
<TextView
android:text="这里是标题"
android:textSize="18dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="子标题"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:textSize="18dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
..............
<LinearLayout
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:height="50dp"
android:background="#b11"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="继续拖动查看图文详情"
android:textColor="#000" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView>
<com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fillViewport="true">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/a1" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/a3" />
.........
</LinearLayout>
</com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.MyScrollView> </com.baoyunlong.view.pulluptoloadmore.PullUpToLoadMore>
</RelativeLayout>
コード:
public class PullUpToLoadMore extends ViewGroup {
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int childTop = t;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
child.layout(l, childTop, r, childTop + child.getMeasuredHeight());
childTop += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
}
2. スライディングイベントの処理
ルールは次のとおりです:
(1) 最初のスクロールそれがいつ最初の画面上にあります。ビューがスライドしました。ビューが一番下に到達し、スライド方向が上にスライドする場合、スライド イベントは処理のために親ビューに渡される必要があります。つまり、イベントがインターセプトされ、onInterceptTouchEvent が true を返します。親ビューは、scrollBy() メソッドを介してスクロールし、2 番目のscrollView を表示します。
(2) 2番目の画面で、2番目のScrollViewが上にスライドし、スライド方向が下にスライドしています。このとき、スライドイベントは親ビューに渡されて処理され、最初のScrollViewは処理されます。スライドイベントに応じてScrollViewが表示されます。
(3) 指が画面から離れたときに、スライド速度に基づいて最初の ScrollView にリバウンドするか 2 番目の ScrollView にリバウンドするかを決定し、VelocityTracker を通じてスライド速度を取得します。
3. いくつかの詳細の処理
(1) タオバオの実装を注意深く見ると、「ドラッグを続けて画像とテキストの詳細を表示」という部分までスライドしたら、指を離します。次に、もう一度押して上にドラッグすると、2 番目のページが表示されず、「ドラッグを続けて画像とテキストの詳細を表示」の下部に留まることがわかります。JD.com での効果は同じです。このユーザー エクスペリエンスはあまり良くありません。最適化しましょう。実際、ScrollView のソース コードを見ると、ScrollView クラスの onTouchEvent メソッドのデフォルトの実装が、イベントのインターセプトを防ぐためにparent.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true) メソッドを呼び出し、onInterceptTouchEvent が発生することが原因であることがわかります。親ビューのメソッドを実行できないため、イベントを受信できない場合、またはイベントをインターセプトできない場合、onTouchEvent で作成したスクロール ロジックを実行できません。上で見たように、スクロールできない影響が生じます。解決策は、サブビューが邪魔しないようにdispatchTouchEvent()メソッドを書き換えて、スライド時に一度で完了できるようにすることです。コードは以下の通りです:
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//防止子View禁止父view拦截事件
this.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(false);
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
(2) ScrollViewのスライドイベント監視の問題
ScrollViewにはスクロールイベントの監視方法が用意されていないため、上までスクロールしたかどうかを判断する方法がありません。ここでは ScrollView を継承し、Scroll イベントをリッスンして実装します。
/**
* Created by baoyunlong on 16/6/8.
*/
public class MyScrollView extends ScrollView {
private static String TAG=MyScrollView.class.getName();
public void setScrollListener(ScrollListener scrollListener) {
this.mScrollListener = scrollListener;
}
private ScrollListener mScrollListener;
public MyScrollView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
switch (ev.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if(mScrollListener!=null){
int contentHeight=getChildAt(0).getHeight();
int scrollHeight=getHeight();
int scrollY=getScrollY();
mScrollListener.onScroll(scrollY);
if(scrollY+scrollHeight>=contentHeight||contentHeight<=scrollHeight){
mScrollListener.onScrollToBottom();
}else {
mScrollListener.notBottom();
}
if(scrollY==0){
mScrollListener.onScrollToTop();
}
}
break;
}
boolean result=super.onTouchEvent(ev);
requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(false);
return result;
}
public interface ScrollListener{
void onScrollToBottom();
void onScrollToTop();
void onScroll(int scrollY);
void notBottom();
}
4. 完全なコードは次のとおりです
/**
* Created by baoyunlong on 16/6/8.
*/
public class PullUpToLoadMore extends ViewGroup {
public static String TAG = PullUpToLoadMore.class.getName();
MyScrollView topScrollView, bottomScrollView;
VelocityTracker velocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
Scroller scroller = new Scroller(getContext());
int currPosition = 0;
int position1Y;
int lastY;
public int scaledTouchSlop;//最小滑动距离
int speed = 200;
boolean isIntercept;
public boolean bottomScrollVIewIsInTop = false;
public boolean topScrollViewIsBottom = false;
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public PullUpToLoadMore(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
topScrollView = (MyScrollView) getChildAt(0);
bottomScrollView = (MyScrollView) getChildAt(1);
topScrollView.setScrollListener(new MyScrollView.ScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollToBottom() {
topScrollViewIsBottom = true;
}
@Override
public void onScrollToTop() {
}
@Override
public void onScroll(int scrollY) {
}
@Override
public void notBottom() {
topScrollViewIsBottom = false;
}
});
bottomScrollView.setScrollListener(new MyScrollView.ScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollToBottom() {
}
@Override
public void onScrollToTop() {
}
@Override
public void onScroll(int scrollY) {
if (scrollY == 0) {
bottomScrollVIewIsInTop = true;
} else {
bottomScrollVIewIsInTop = false;
}
}
@Override
public void notBottom() {
}
});
position1Y = topScrollView.getBottom();
scaledTouchSlop = ViewConfiguration.get(getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop();
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//防止子View禁止父view拦截事件
this.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(false);
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
int y = (int) ev.getY();
switch (ev.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//判断是否已经滚动到了底部
if (topScrollViewIsBottom) {
int dy = lastY - y;
//判断是否是向上滑动和是否在第一屏
if (dy > 0 && currPosition == 0) {
if (dy >= scaledTouchSlop) {
isIntercept = true;//拦截事件
lastY=y;
}
}
}
if (bottomScrollVIewIsInTop) {
int dy = lastY - y;
//判断是否是向下滑动和是否在第二屏
if (dy < 0 && currPosition == 1) {
if (Math.abs(dy) >= scaledTouchSlop) {
isIntercept = true;
}
}
}
break;
}
return isIntercept;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int y = (int) event.getY();
velocityTracker.addMovement(event);
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int dy = lastY - y;
if (getScrollY() + dy < 0) {
dy = getScrollY() + dy + Math.abs(getScrollY() + dy);
}
if (getScrollY() + dy + getHeight() > bottomScrollView.getBottom()) {
dy = dy - (getScrollY() + dy - (bottomScrollView.getBottom() - getHeight()));
}
scrollBy(0, dy);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
isIntercept = false;
velocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float yVelocity = velocityTracker.getYVelocity();
if (currPosition == 0) {
if (yVelocity < 0 && yVelocity < -speed) {
smoothScroll(position1Y);
currPosition = 1;
} else {
smoothScroll(0);
}
} else {
if (yVelocity > 0 && yVelocity > speed) {
smoothScroll(0);
currPosition = 0;
} else {
smoothScroll(position1Y);
}
}
break;
}
lastY = y;
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int childTop = t;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
child.layout(l, childTop, r, childTop + child.getMeasuredHeight());
childTop += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
//通过Scroller实现弹性滑动
private void smoothScroll(int tartY) {
int dy = tartY - getScrollY();
scroller.startScroll(getScrollX(), getScrollY(), 0, dy);
invalidate();
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (scroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
scrollTo(scroller.getCurrX(), scroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
}
}
}
ソースコード:
githubアドレス
上記は編集者が紹介したAndroid模倣品淘宝と京東の製品詳細ページです。上にドラッグします。グラフィック詳細コントロールの詳細なデモ説明をご覧ください。ご質問があれば、メッセージを残してください。編集者がすぐに返信します。また、PHP 中国語 Web サイトをサポートしていただきありがとうございます。
その他の Android 模倣淘宝網と JD.com の製品詳細ページについては、上にドラッグしてグラフィックの詳細を表示し、デモの詳細を制御してください。 関連記事については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトに注目してください。

