ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >AndroidカスタムViewGroupの実装方法
AndroidカスタムViewGroupの実装方法
- 高洛峰オリジナル
- 2017-01-16 16:59:271450ブラウズ
LinearLayout、Relativeayout、FrameLayout など、いくつかの一般的な ViewGroup 実装が Android で提供されています。これらの ViewGroup は一般的な開発ニーズを満たすことができますが、複雑なインターフェイス要件の場合、これらのレイアウトでは不十分です。したがって、私たちがこれまで接してきたアプリケーションには、カスタム ViewGroup が数多く存在します。
カスタム ViewGroup を実装するには、最初のステップはカスタム属性を学習することです。これらのカスタム属性により、レイアウト ファイルを構成する際の柔軟性が高まります。カスタム属性は、value ディレクトリ内の attrs.xml ファイルで宣言されます。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="CascadeViewGroup"> <attr name="verticalspacing" format="dimension"/> <attr name="horizontalspacing" format="dimension"/> </declare-styleable> <declare-styleable name="CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams"> <attr name="layout_paddingleft" format="dimension"/> <attr name="layout_paddinTop" format="dimension"/> </declare-styleable> </resources>
ここでは、CascadeViewGroup のプロパティ セットをカスタム CascadeViewGroup コンポーネントに設定します。これらのプロパティは、レイアウト ファイルの
コードを記述する前に、CascadeLayout が使用するデフォルトの幅と高さも設定します。これら 2 つのプロパティは dimens.xml で定義されています。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <dimen name="default_horizontal_spacing">10dp</dimen> <dimen name="default_vertical_spacing">10dp</dimen> </resources>
カスタム コンポーネント CascadeLayout を書き始めましょう。
package com.app.CustomViewMotion;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* Created by charles on 2015/8/13.
*/
public class CascadeViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
//自定义布局中设置的宽度和高度
private int mHoriztonalSpacing;
private int mVerticalSpacing;
public CascadeViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CascadeViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CascadeViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup);
try {
//获取设置的宽度
mHoriztonalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_horizontalspacing,
this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.default_horizontal_spacing));
//获取设置的高度
mVerticalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_verticalspacing,
this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.default_vertical_spacing));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int count = this.getChildCount();
int width = this.getPaddingLeft();
int height = this.getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View currentView = this.getChildAt(i);
this.measureChild(currentView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = (CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams) currentView.getLayoutParams();
if(lp.mSettingPaddingLeft != 0){
width +=lp.mSettingPaddingLeft;
}
if(lp.mSettingPaddingTop != 0){
height +=lp.mSettingPaddingTop;
}
lp.x = width;
lp.y = height;
width += mHoriztonalSpacing;
height += mVerticalSpacing;
}
width +=getChildAt(this.getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredWidth() + this.getPaddingRight();
height += getChildAt(this.getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredHeight() + this.getPaddingBottom();
this.setMeasuredDimension(resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec), resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec));
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int l, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
final int count = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View currentView = this.getChildAt(i);
CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = (CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams) currentView.getLayoutParams();
currentView.layout(lp.x, lp.y, lp.x + currentView.getMeasuredWidth(),
lp.y + currentView.getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
int x;
int y;
int mSettingPaddingLeft;
int mSettingPaddingTop;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams);
mSettingPaddingLeft = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams_layout_paddingleft, 0);
mSettingPaddingTop = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams_layout_paddinTop, 0);
a.recycle();
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new LayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LayoutParams(this.getContext(), attrs);
}
}コードは少し長くなりますが、構造は依然として非常に明確です。
1) コンストラクターまたは XML ファイル内の構成属性の値。 TypedArray のメソッドを通じてレイアウトに設定したプロパティを取得し、メンバー変数に保存します。
2) カスタム内部クラス LayoutParams を構築します。この内部クラスを構築すると、レイアウト ステージでレイアウトのサブビューを測定するときに、その属性値を保存できるようになります。
3)generateLayoutParams()、generateDefaultParams()およびその他のメソッド。これらのメソッドでカスタムのlayoutParamsを返します。これらのメソッドをオーバーライドする必要がある理由は、ViewGroup クラスの addView() メソッドを見れば明らかです。
4) 測定段階。測定フェーズでは、独自のサイズとサブビューのサイズを測定し、サブビューの情報を LayoutParams に保存します。
5) レイアウト段階。各サブビューの情報に基づいて位置を配置します。
最後にレイアウトファイルを追加します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--添加自定义属性给viewGroup-->
<!--新添加的命名空间的后缀必须保持和.xml中声明的包名一致-->
<com.app.CustomViewMotion.CascadeViewGroup
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:ts="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.app.CustomViewMotion"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
ts:horizontalspacing="15dp"
ts:verticalspacing="15dp">
<TextView android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="text1"
android:background="#668B8B"/>
<TextView android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="text2"
android:background="#FFDAB9"/>
<TextView android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="text3"
android:background="#43CD80"/>
<!--这个子view中添加自定义子view属性-->
<TextView android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="text4"
ts:layout_paddingleft="100dp"
ts:layout_paddinTop="100dp"
android:background="#00CED1"/>
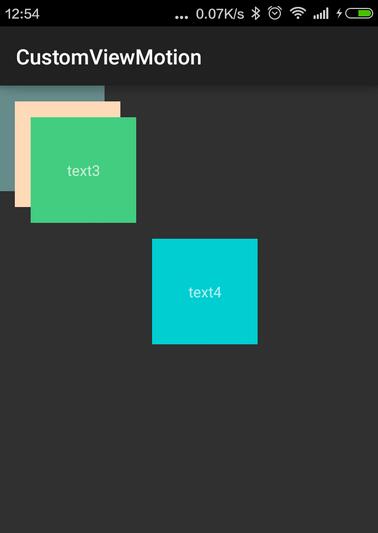
</com.app.CustomViewMotion.CascadeViewGroup>によって得られる効果は次のとおりです:
以上が皆様の参考になれば幸いです。また、皆様にも PHP 中国語 Web サイトをサポートしていただければ幸いです。
Android カスタム ViewGroup の実装方法に関連するその他の記事については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトに注目してください。

