物体の運動の原理: 物体の位置を変えることによって動きの変化が起こります。 物理学の運動公式: s (達成される) = s0 (現在のスタイル値) + vt と同様に、あらゆる動きは相対的です。
メソッド:
1. 移動オブジェクトには絶対位置を使用します
2. 配置されたオブジェクトの属性 (左、右、上、下) を変更して、オブジェクトを移動します。たとえば、右または左に移動するには、offsetLeft(offsetRight) を使用して左右の動きを制御できます。
手順:
1. 移動を開始する前に、既存のタイマーをクリアします (理由: ボタンをクリックし続けると、オブジェクトの移動がますます速くなり、移動が混乱します)
2. タイマーをオンにして速度を計算します
3. 移動と停止(if/else)を分離し、停止条件を決定し、移動を実行します
キーポイント:
1. 複数のオブジェクト
タイマーをオブジェクトにアタッチします
2. チェーンモーション
ループ内でタイマーを呼び出します: fnEnd 関数で別のタイマーを開始します
3. 多価値スポーツ
ループ属性値配列: タイマー時間、複数の属性値変更を実行します
移動が終了し、すべての属性が所定の値に達したことを判断します。最初にブール値フラグを追加します。var bStop=true; // 仮定: すべての値が到達しているかどうかをループ中に判断します。 =json[attr]) bStop=false;
1. タイマー
JavaScript には、タイマー専用の関数が 2 つあります。
1. カウントダウン タイマー: timename=setTimeout("function();",laytime);
2. ループタイマー: timename=setInterval("function();",laytime);
Function() は、タイマーがトリガーされたときに実行されるイベント関数です。これは、1 つの関数、複数の関数、または JavaScript ステートメントにすることができます。「;laytime」で区切る必要があるだけです。ミリ秒単位の間隔。
カウントダウン タイマーは指定された時間の後にイベントをトリガーしますが、ループ タイマーは間隔が到来するとイベントを繰り返しトリガーします。違いは、前者は 1 回だけ動作するのに対し、後者は継続的に動作することです。
カウントダウン タイマーは、通常、ページを 1 回だけトリガーする必要がある場合に使用されます。たとえば、特定のボタンをクリックした後、一定時間後にページが対応するサイトにジャンプするかどうかを判断するためにも使用されます。訪問者はあなたのサイトの「古い訪問者」です。そうでない場合は、5 秒または 10 秒後に対応するサイトにジャンプし、どこかのボタンを押してすぐにアクセスできるように伝えます。後で戻ってきます。
ループ タイマーは通常、JavaScript スクロール バーやステータス バーなど、サイト上で繰り返し実行する必要がある効果に使用され、ページの背景を雪の絵で表現するために使用することもできます。これらのイベントは一定の間隔で実行する必要があります。
追加されたタイマーを削除したい場合もあります。この場合、clearTimeout(timename) を使用してカウントダウン タイマーをオフにし、clearInterval(timename) を使用してループ タイマーをオフにすることができます。
2. 運動研究
1. 動き:等速運動(物体を動かす)
タイマーの使用
DIV
に絶対位置を追加します
オフセット左
解決策:条件を満たしたら判断してタイマーをオフにする(タイマーを保存する)
速度が遅くなります (通常は時間は変わりませんが、数字の速度が変わります)
変数を使用して速度を保存します
解決策:>=300 //301 で停止
理由: ボタンをクリックし、関数を実行し、タイマーを開始します (現在の関数を少なくとも 1 回実行します)
解決策: else を追加 (ターゲットに到達する前に実行)
理由: クリックするたびにタイマーが開始され、数回クリックすると複数のタイマーが同時に動作します
解決策: 一度に 1 つのタイマーだけが動作するようにするには、最初に cearlinterval ()
を実行します。
例 1、共有先:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>分享到</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:150px; height:200px; background:green; position:absolute; left:-150px;}
#div1 span {position:absolute; width:20px; height:60px; line-height:20px; background:blue; right:-20px; top:70px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(0);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(-150);
};
};
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(oDiv.offsetLeft>iTarget)
{
speed=-10;
}
else
{
speed=10;
}
if(oDiv.offsetLeft==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
}
else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<span>分享到</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>

例 2、フェードインとフェードアウト:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>淡入淡出</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:200px; height:200px; background:red; filter:alpha(opacity:30); opacity:0.3;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(100);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(30);
};
};
var alpha=30;
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(alpha<iTarget)
{
speed=10;
}
else
{
speed=-10;
}
if(alpha==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
}
else
{
alpha+=speed;
oDiv.style.filter='alpha(opacity:'+alpha+')';
oDiv.style.opacity=alpha/100;
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1"></div>
</body>
</html>
十分近い
例 3、等速運動の停止条件:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>匀速运动的停止条件</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;}
#div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;}
#div3 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:100px; top:0; background:black;}
</style>
<script>
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(oDiv.offsetLeft<iTarget)
{
speed=7;
}
else
{
speed=-7;
}
if(Math.abs(iTarget-oDiv.offsetLeft)<=7)
{
clearInterval(timer);
oDiv.style.left=iTarget+'px';
}
else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="到100" onclick="startMove(100)" />
<input type="button" value="到300" onclick="startMove(300)" />
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
<div id="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>
2.变速运动(缓冲运动)
逐渐变慢,最后停止
距离越远速度越大
速度有距离决定
速度=(目标值-当前值)/缩放系数
如果没有缩放系数t速度太大,瞬间到达终点.没有过程
问题:并没有真正到达300
原因:速度只剩0.9 //像素是屏幕能够显示的最/J库位,并不会四舍五入掉
Math.ceil ()向上取整
Math.floor ()向下取整
问题:向左走,又差一块--Math.floor ()
判断:三目 speed=speed>0 ? Math.ceil ( speed ): Math.floor ( speed )
示例,缓冲运动:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>缓冲运动</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;}
#div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;}
</style>
<script>
function startMove()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
setInterval(function (){
var speed=(300-oDiv.offsetLeft)/10;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
document.title=oDiv.offsetLeft+','+speed;
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="开始运动" onclick="startMove()" />
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:

3.多物体运动
多个div ,鼠标移入变宽
运动框架传参obj,知道让哪个物体动起来
用到缓冲一定要取整
问题:div没运动回去 //清除前一个定时器
原因:只有一个定时器
解决:加物体上的定时器,使每个物体都有一个定时器。定时器作为物体属性
多个div淡入淡出
首先关闭物体上的定时器
经验:多物体运动框架所有东西都不能共用
问题:不是因为定时器,而是因为alpha
解决:作为属性附加到物体上 /不以变量形式存在
offset 的 bug
加border变宽
offsetWith并不是真正的width ,它获取的是盒模型尺寸
解决:躲着 宽度扔到行间,parselnt ( oDiv.style.width )
进一步解决: getStyle ( obj, name ) currentStyle , getComputedStyle
加border ,只要offset就有问题 去掉offset
示例,多物体运动:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
div {width:100px; height:50px; background:red; margin:10px; border:10px solid black;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var aDiv=document.getElementsByTagName('div');
for(var i=0;i<aDiv.length;i++)
{
aDiv[i].timer=null;
aDiv[i].onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(this, 400);
};
aDiv[i].onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(this, 100);
};
}
};
function startMove(obj, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=(iTarget-obj.offsetWidth)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(obj.offsetWidth==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style.width=obj.offsetWidth+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
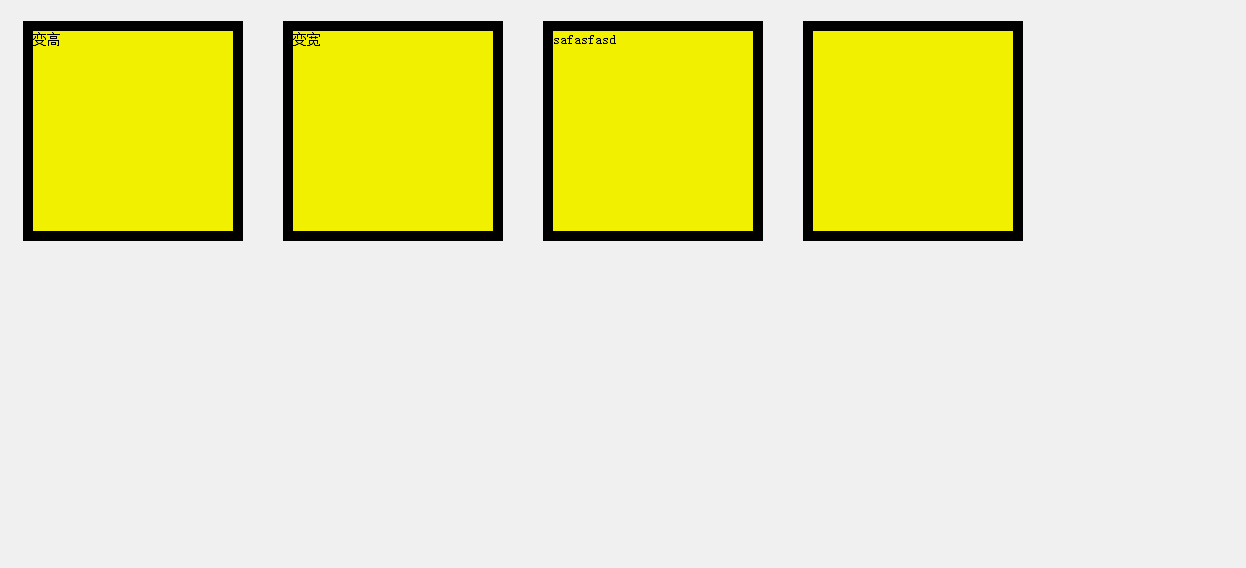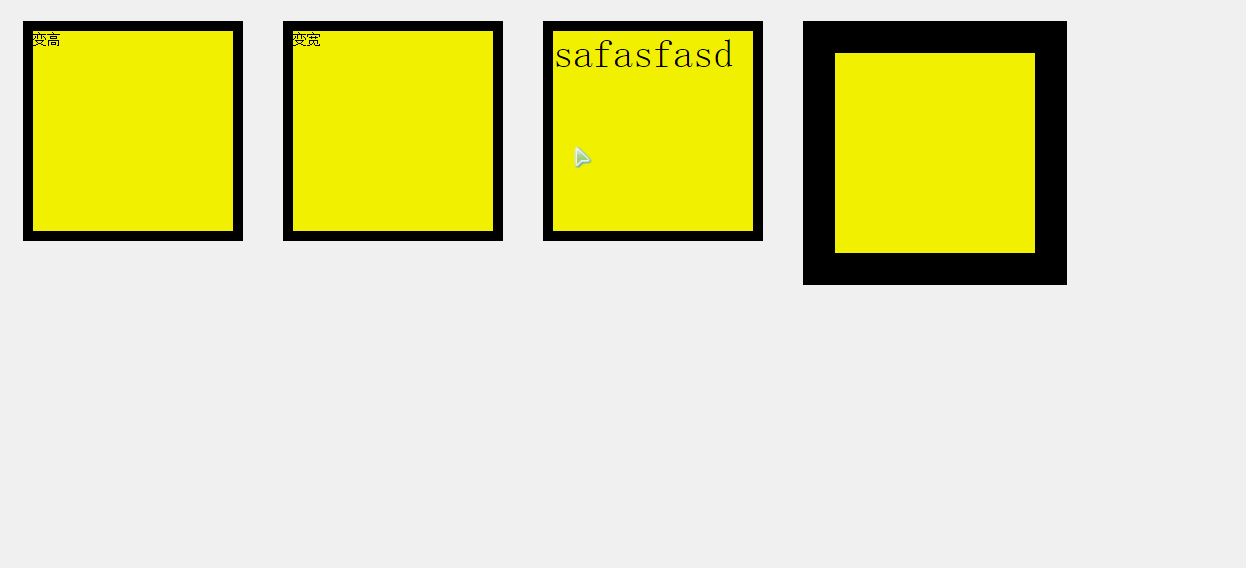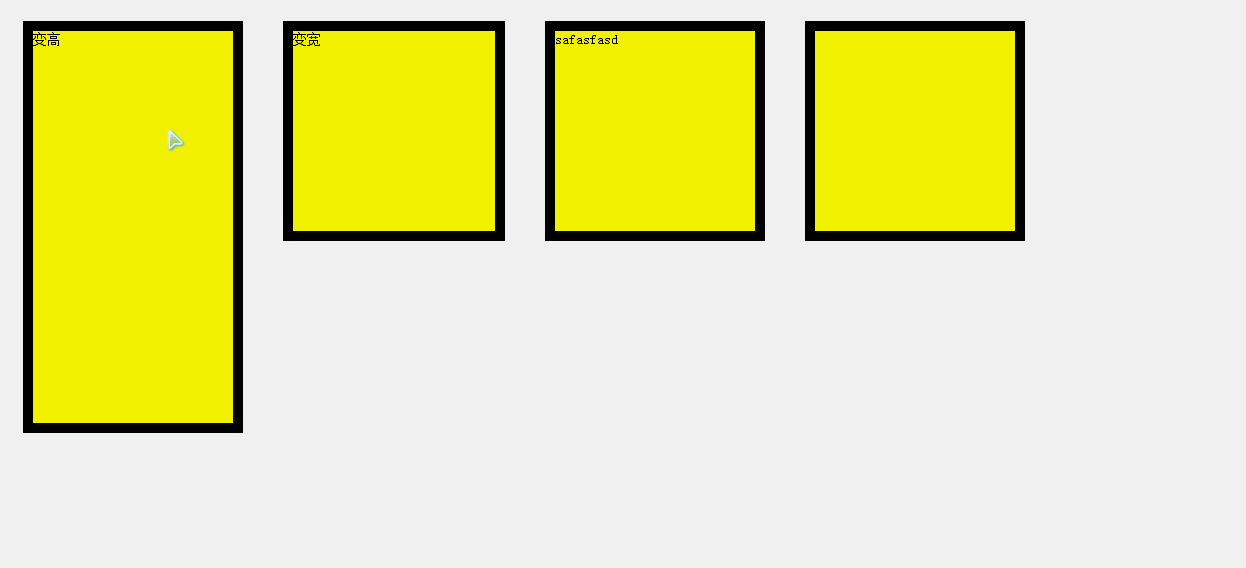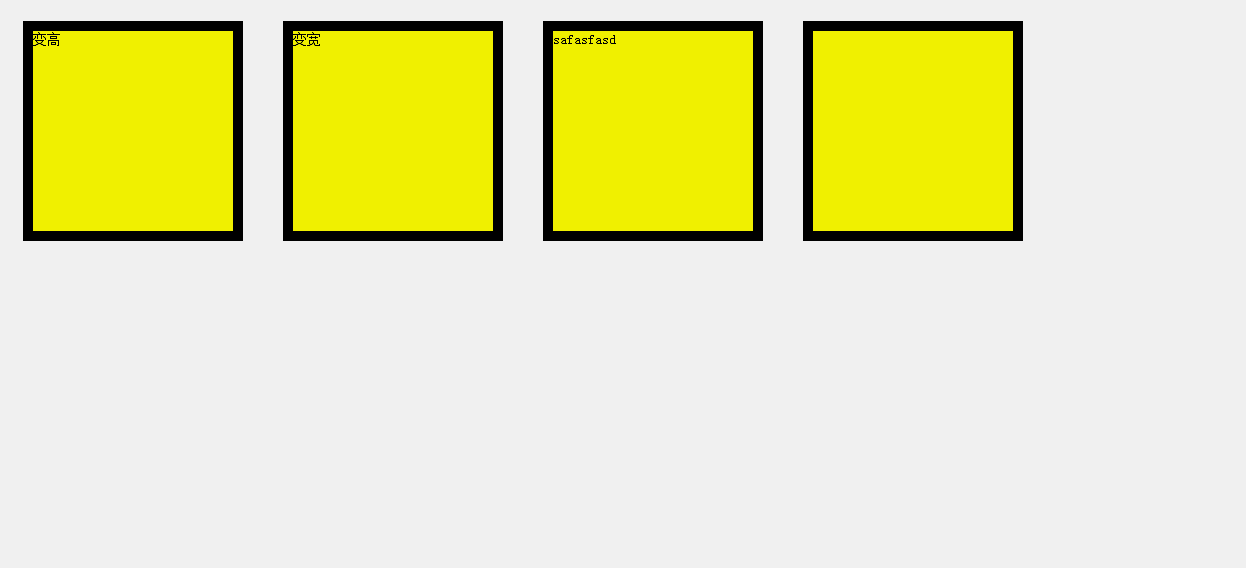
4.任意值运动
任意值运动的单位分为透明度和px。
px单位的任意值
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
div {width:200px; height:200px; margin:20px; float:left; background:yellow; border:10px solid black; font-size:14px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv1=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv1.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 400);};
oDiv1.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 200);};
var oDiv2=document.getElementById('div2');
oDiv2.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 400);};
oDiv2.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 200);};
var oDiv3=document.getElementById('div3');
oDiv3.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 50);};
oDiv3.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 14);};
var oDiv4=document.getElementById('div4');
oDiv4.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 100);};
oDiv4.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 10);};
};
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle){return obj.currentStyle[name];}
else{return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];}
}
function startMove(obj, attr, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
var speed=(iTarget-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">变高</div>
<div id="div2">变宽</div>
<div id="div3">safasfasd</div>
<div id="div4"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
div {width:200px; height:200px; margin:20px; float:left; background:yellow; border:10px solid black; font-size:14px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv1=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv1.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 400);};
oDiv1.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 200);};
var oDiv2=document.getElementById('div2');
oDiv2.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 400);};
oDiv2.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 200);};
var oDiv3=document.getElementById('div3');
oDiv3.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 50);};
oDiv3.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 14);};
var oDiv4=document.getElementById('div4');
oDiv4.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 100);};
oDiv4.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 10);};
};
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle){return obj.currentStyle[name];}
else{return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];}
}
function startMove(obj, attr, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
var speed=(iTarget-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">变高</div>
<div id="div2">变宽</div>
<div id="div3">safasfasd</div>
<div id="div4"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
透明度的任意值,需要做判断:
判断
var cur=0
if ( attr== 'opacity '){
cur=parseFloat ( getStyle ( obj, attr)) *100
}else{
}
设置样式判断
if ( attr== 'opacity '){
obj.style.fiIter = 'alpha ( opacity: '( cur+speed ) + ')'
obj.style.opacity= ( cur+speed ) /100
}else{
}
5.链式运动
多出来的一个参数,只有传进去的时候才调用
鼠标移入变宽,结束之后弹出abc
先横向展开.再以向展开
鼠标移出,先变回不透明,变矮,变窄
三.封装运动框架
基于以上的分析与总结,封装运动框架move.js如下:
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle)
{
return obj.currentStyle[name];
}
else
{
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];
}
}
function startMove(obj, json, fnEnd)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var bStop=true; //假设:所有值都已经到了
for(var attr in json)
{
var cur=0;
if(attr=='opacity')
{
cur=Math.round(parseFloat(getStyle(obj, attr))*100);
}
else
{
cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
}
var speed=(json[attr]-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur!=json[attr])
bStop=false;
if(attr=='opacity')
{
obj.style.filter='alpha(opacity:'+(cur+speed)+')';
obj.style.opacity=(cur+speed)/100;
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}
if(bStop)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
if(fnEnd)fnEnd();
}
}, 30);
}
move.js运动框架基本满足现在网页上所有动画的需求(不包括css3)。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。
 next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する(バックエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する(バックエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM私はあなたの日常的な技術ツールを使用して機能的なマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーション(EDTECHアプリ)を作成しましたが、あなたは同じことをすることができます。 まず、マルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションとは何ですか? マルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを使用すると、Singの複数の顧客にサービスを提供できます
 next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する方法(フロントエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
next.jsを使用してマルチテナントSaaSアプリケーションを構築する方法(フロントエンド統合)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMこの記事では、許可によって保護されたバックエンドとのフロントエンド統合を示し、next.jsを使用して機能的なedtech SaaSアプリケーションを構築します。 FrontEndはユーザーのアクセス許可を取得してUIの可視性を制御し、APIリクエストがロールベースに付着することを保証します
 JavaScript:Web言語の汎用性の調査Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript:Web言語の汎用性の調査Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScriptは、現代のWeb開発のコア言語であり、その多様性と柔軟性に広く使用されています。 1)フロントエンド開発:DOM操作と最新のフレームワーク(React、Vue.JS、Angularなど)を通じて、動的なWebページとシングルページアプリケーションを構築します。 2)サーバー側の開発:node.jsは、非ブロッキングI/Oモデルを使用して、高い並行性とリアルタイムアプリケーションを処理します。 3)モバイルおよびデスクトップアプリケーション開発:クロスプラットフォーム開発は、反応および電子を通じて実現され、開発効率を向上させます。
 JavaScriptの進化:現在の傾向と将来の見通しApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
JavaScriptの進化:現在の傾向と将来の見通しApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMJavaScriptの最新トレンドには、TypeScriptの台頭、最新のフレームワークとライブラリの人気、WebAssemblyの適用が含まれます。将来の見通しは、より強力なタイプシステム、サーバー側のJavaScriptの開発、人工知能と機械学習の拡大、およびIoTおよびEDGEコンピューティングの可能性をカバーしています。
 javascriptの分解:それが何をするのか、なぜそれが重要なのかApr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
javascriptの分解:それが何をするのか、なぜそれが重要なのかApr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptは現代のWeb開発の基礎であり、その主な機能には、イベント駆動型のプログラミング、動的コンテンツ生成、非同期プログラミングが含まれます。 1)イベント駆動型プログラミングにより、Webページはユーザー操作に応じて動的に変更できます。 2)動的コンテンツ生成により、条件に応じてページコンテンツを調整できます。 3)非同期プログラミングにより、ユーザーインターフェイスがブロックされないようにします。 JavaScriptは、Webインタラクション、シングルページアプリケーション、サーバー側の開発で広く使用されており、ユーザーエクスペリエンスとクロスプラットフォーム開発の柔軟性を大幅に改善しています。
 pythonまたはjavascriptの方がいいですか?Apr 06, 2025 am 12:14 AM
pythonまたはjavascriptの方がいいですか?Apr 06, 2025 am 12:14 AMPythonはデータサイエンスや機械学習により適していますが、JavaScriptはフロントエンドとフルスタックの開発により適しています。 1. Pythonは、簡潔な構文とリッチライブラリエコシステムで知られており、データ分析とWeb開発に適しています。 2。JavaScriptは、フロントエンド開発の中核です。 node.jsはサーバー側のプログラミングをサポートしており、フルスタック開発に適しています。
 JavaScriptをインストールするにはどうすればよいですか?Apr 05, 2025 am 12:16 AM
JavaScriptをインストールするにはどうすればよいですか?Apr 05, 2025 am 12:16 AMJavaScriptは、最新のブラウザにすでに組み込まれているため、インストールを必要としません。開始するには、テキストエディターとブラウザのみが必要です。 1)ブラウザ環境では、タグを介してHTMLファイルを埋め込んで実行します。 2)node.js環境では、node.jsをダウンロードしてインストールした後、コマンドラインを介してJavaScriptファイルを実行します。
 クォーツでタスクが開始される前に通知を送信する方法は?Apr 04, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
クォーツでタスクが開始される前に通知を送信する方法は?Apr 04, 2025 pm 09:24 PMQuartzタイマーを使用してタスクをスケジュールする場合、Quartzでタスク通知を事前に送信する方法、タスクの実行時間はCron式によって設定されます。今...


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
このプロジェクトは osdn.net/projects/mingw に移行中です。引き続きそこでフォローしていただけます。 MinGW: GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) のネイティブ Windows ポートであり、ネイティブ Windows アプリケーションを構築するための自由に配布可能なインポート ライブラリとヘッダー ファイルであり、C99 機能をサポートする MSVC ランタイムの拡張機能が含まれています。すべての MinGW ソフトウェアは 64 ビット Windows プラットフォームで実行できます。

PhpStorm Mac バージョン
最新(2018.2.1)のプロフェッショナル向けPHP統合開発ツール

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

SublimeText3 英語版
推奨: Win バージョン、コードプロンプトをサポート!

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境






