ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >Python チュートリアル >プログレスバーを表示するPythonメソッド
プログレスバーを表示するPythonメソッド
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBオリジナル
- 2016-06-16 08:42:001186ブラウズ
この記事の例では、Python でプログレス バーを表示する方法について説明します。これは、Python プログラミングにおいて非常に実践的なスキルです。皆さんの参考に共有してください。具体的な方法は以下の通りです。
まず第一に、プログレスバーと通常の印刷の違いは何でしょうか?
答えは、print は改行文字である n を出力するため、カーソルは次の行の先頭に移動し、stdout 経由で出力されたものは保持されます。以下の最新の出力結果が表示されることが保証されています。
それ以外の場合は、進行状況バーを適切な位置に出力して、それが進行状況バーであることを確認する必要があります。そうでない場合、なぜ新しい行の後にも進行状況バーと呼ばれるのですか?
最も簡単な方法は、出力が完了した後にカーソルを行の先頭に移動し、そこに長い進行状況バーを出力し続けることです。新しい長い進行状況バーが古い進行状況バーを上書きし、アニメーション効果を形成します。
エスケープ文字、つまり r を考えることができます。
エスケープ文字 r は行を改行せずにカーソルを行の先頭に移動でき、エスケープ文字 n はカーソルを行の先頭に移動して行を改行できます。
Python では、stdout (標準出力) を出力するには、sys.stdout.write
を使用できます。
例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
#Author: ihipop@gmail.com
##2010-10-27 22:07
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
j = '#'
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1,61):
j += '#'
sys.stdout.write(str(int((i/60)*100))+'% ||'+j+'->'+"\r")
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(0.5)
print
2 番目のアイデアは、エスケープ文字 b を使用することです
エスケープ文字 b はバックスペース キーです。これは、出力カーソルがグリッドの 1 つ後ろに移動し、+= が不要になることを意味します。例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
#Author: ihipop@gmail.com
#2010-10-27 22:07
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1,61):
sys.stdout.write('#'+'->'+"\b\b")
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(0.5)
print
カーソルは 2 スペース前に移動し、# を書き込み、その後戻って再び書き込み、成長の目的を達成します
しかし、こんなにたくさん書くのはナンセンスのように思えます。「車輪の再発明はやめてください」という言葉がよく聞こえます。実際、Python にはこれを実装するのに役立つライブラリがたくさんあります。これらの細かい点に注意を払うことなく、ロジック開発に完全に集中できます。
以下は「progressbar」クラス (http://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/) です。実際には、このクラス ライブラリは単なるファイルです。ファイルと同じディレクトリに直接インポートすることもできます以下に示すように:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
#Author: ihipop@gmail.com
#2010-10-27 22:53
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
from __future__ import division
import sys,time
from progressbar import *
total = 1000
#基本用法
progress = ProgressBar()
for i in progress(range(total)):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar = ProgressBar().start()
for i in range(1,1000):
pbar.update(int((i/(total-1))*100))
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.finish()
#高级用法
widgets = ['Progress: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(marker=RotatingMarker('>-=')),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10*i+1)
time.sleep(0.0001)
pbar.finish()
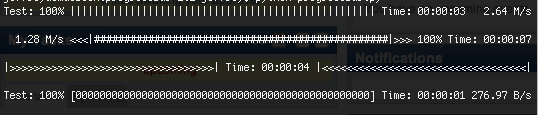
公式の例: http://code.google.com/p/python-progressbar/source/browse/progressbar/examples.py
#coding:utf-8
import sys
import time
from progressbar import AnimatedMarker, Bar, BouncingBar, Counter, ETA, \
FileTransferSpeed, FormatLabel, Percentage, \
ProgressBar, ReverseBar, RotatingMarker, \
SimpleProgress, Timer
examples = []
def example(fn):
try: name = 'Example %d' % int(fn.__name__[7:])
except: name = fn.__name__
def wrapped():
try:
sys.stdout.write('Running: %s\n' % name)
fn()
sys.stdout.write('\n')
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.stdout.write('\nSkipping example.\n\n')
examples.append(wrapped)
return wrapped
@example
def example0():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=[Percentage(), Bar()], maxval=300).start()
for i in range(300):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.update(i+1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example1():
widgets = ['Test: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(marker=RotatingMarker()),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10*i+1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example2():
class CrazyFileTransferSpeed(FileTransferSpeed):
"""It's bigger between 45 and 80 percent."""
def update(self, pbar):
if 45 < pbar.percentage() < 80:
return 'Bigger Now ' + FileTransferSpeed.update(self,pbar)
else:
return FileTransferSpeed.update(self,pbar)
widgets = [CrazyFileTransferSpeed(),' <<<', Bar(), '>>> ',
Percentage(),' ', ETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000)
# maybe do something
pbar.start()
for i in range(2000000):
# do something
pbar.update(5*i+1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example3():
widgets = [Bar('>'), ' ', ETA(), ' ', ReverseBar('<')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=10000000).start()
for i in range(1000000):
# do something
pbar.update(10*i+1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example4():
widgets = ['Test: ', Percentage(), ' ',
Bar(marker='0',left='[',right=']'),
' ', ETA(), ' ', FileTransferSpeed()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=500)
pbar.start()
for i in range(100,500+1,50):
time.sleep(0.2)
pbar.update(i)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example5():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=[SimpleProgress()], maxval=17).start()
for i in range(17):
time.sleep(0.2)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example6():
pbar = ProgressBar().start()
for i in range(100):
time.sleep(0.01)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example7():
pbar = ProgressBar() # Progressbar can guess maxval automatically.
for i in pbar(range(80)):
time.sleep(0.01)
@example
def example8():
pbar = ProgressBar(maxval=80) # Progressbar can't guess maxval.
for i in pbar((i for i in range(80))):
time.sleep(0.01)
@example
def example9():
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=['Working: ', AnimatedMarker()])
for i in pbar((i for i in range(50))):
time.sleep(.08)
@example
def example10():
widgets = ['Processed: ', Counter(), ' lines (', Timer(), ')']
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(150))):
time.sleep(0.1)
@example
def example11():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Processed: %(value)d lines (in: %(elapsed)s)')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(150))):
time.sleep(0.1)
@example
def example12():
widgets = ['Balloon: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='.oO@* ')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
@example
def example13():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Arrows: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='←↖↑↗→↘↓↙')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError: sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example14():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Arrows: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='◢◣◤◥')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError: sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example15():
# You may need python 3.x to see this correctly
try:
widgets = ['Wheels: ', AnimatedMarker(markers='◐◓◑◒')]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(24))):
time.sleep(0.3)
except UnicodeError: sys.stdout.write('Unicode error: skipping example')
@example
def example16():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Bouncer: value %(value)d - '), BouncingBar()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(180))):
time.sleep(0.05)
@example
def example17():
widgets = [FormatLabel('Animated Bouncer: value %(value)d - '),
BouncingBar(marker=RotatingMarker())]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets)
for i in pbar((i for i in range(180))):
time.sleep(0.05)
@example
def example18():
widgets = [Percentage(),
' ', Bar(),
' ', ETA(),
' ', AdaptiveETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=500)
pbar.start()
for i in range(500):
time.sleep(0.01 + (i < 100) * 0.01 + (i > 400) * 0.9)
pbar.update(i + 1)
pbar.finish()
@example
def example19():
pbar = ProgressBar()
for i in pbar([]):
pass
pbar.finish()
try:
for example in examples:
example()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.stdout('\nQuitting examples.\n')
Progress Bar 使用例子
別のクラスを送信します:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
#Using GPL v2
#Author: ihipop@gmail.com
#2010-10-30 13:59
"""
Usage:
Just A Template
"""
class progressbarClass:
def __init__(self, finalcount, progresschar=None):
import sys
self.finalcount=finalcount
self.blockcount=0
#
# See if caller passed me a character to use on the
# progress bar (like "*"). If not use the block
# character that makes it look like a real progress
# bar.
#
if not progresschar: self.block=chr(178)
else: self.block=progresschar
#
# Get pointer to sys.stdout so I can use the write/flush
# methods to display the progress bar.
#
self.f=sys.stdout
#
# If the final count is zero, don't start the progress gauge
#
if not self.finalcount : return
self.f.write('\n------------------- % Progress -------------------\n')
return
def progress(self, count):
#
# Make sure I don't try to go off the end (e.g. >100%)
#
count=min(count, self.finalcount)
#
# If finalcount is zero, I'm done
#
if self.finalcount:
percentcomplete=int(round(100*count/self.finalcount))
if percentcomplete < 1: percentcomplete=1
else:
percentcomplete=100
#print "percentcomplete=",percentcomplete
blockcount=int(percentcomplete/2)
#print "blockcount=",blockcount
if blockcount > self.blockcount:
for i in range(self.blockcount,blockcount):
self.f.write(self.block)
self.f.flush()
if percentcomplete == 100: self.f.write("\n")
self.blockcount=blockcount
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
from time import sleep
pb=progressbarClass(8,"*")
count=0
while count<9:
count+=1
pb.progress(count)
sleep(0.2)
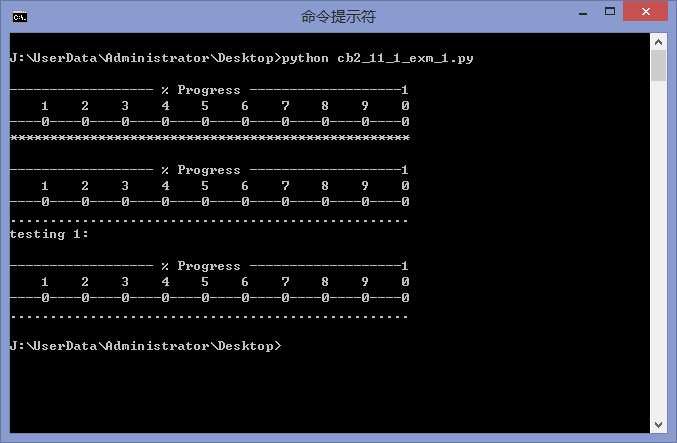
さらに、Python クックブックのセクション 11.1 にも優れたプログレス バー クラスが提供されています。コードは次のとおりです。
import sys
class progressbar(object):
def __init__(self, finalcount, block_char='.'):
self.finalcount = finalcount
self.blockcount = 0
self.block = block_char
self.f = sys.stdout
if not self.finalcount: return
self.f.write('\n------------------ % Progress -------------------1\n')
self.f.write(' 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0\n')
self.f.write('----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0----0\n')
def progress(self, count):
count = min(count, self.finalcount)
if self.finalcount:
percentcomplete = int(round(100.0*count/self.finalcount))
if percentcomplete < 1: percentcomplete = 1
else:
percentcomplete=100
blockcount = int(percentcomplete//2)
if blockcount <= self.blockcount:
return
for i in range(self.blockcount, blockcount):
self.f.write(self.block)
self.f.flush()
self.blockcount = blockcount
if percentcomplete == 100:
self.f.write("\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
from time import sleep
pb = progressbar(8, "*")
for count in range(1, 9):
pb.progress(count)
sleep(0.2)
pb = progressbar(100)
pb.progress(20)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(47)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(90)
sleep(0.3)
pb.progress(100)
print "testing 1:"
pb = progressbar(1)
pb.progress(1)
実行結果は以下のとおりです: