グラフの最小スパニング ツリーは、合計の重みが最小のスパニング ツリーです。
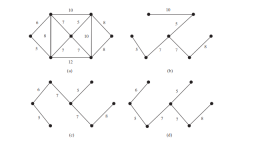
グラフには多数のスパニング ツリーが含まれる場合があります。エッジに重みが付けられているとします。最小スパニング ツリーには最小の合計重みがあります。たとえば、以下の図 b、c、d のツリーは、図 a のグラフのスパニング ツリーです。図 c と図 d のツリーは最小全域ツリーです。
最小スパニングツリーを見つける問題には、多くの用途があります。多くの都市に支店を持つ会社を考えてみましょう。会社はすべての支店を接続するために電話回線をリースしたいと考えています。電話会社は、異なる都市のペアを接続するために異なる金額を請求します。すべてのブランチを接続するにはさまざまな方法があります。最も安価な方法は、合計レートが最小のスパニング ツリーを見つけることです。
最小スパニング ツリー アルゴリズム
最小スパニングツリーはどのように見つけますか?これを行うためのよく知られたアルゴリズムがいくつかあります。このセクションではPrim のアルゴリズムを紹介します。 Prim のアルゴリズムは、任意の頂点を含むスパニング ツリー T から始まります。このアルゴリズムは、ツリー内の既存の頂点に最低コストエッジを持つ頂点を繰り返し追加することによってツリーを拡張します。 Prim のアルゴリズムは貪欲なアルゴリズムであり、以下のコードで説明されています。
Input: A connected undirected weighted G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: MST (a minimum spanning tree)
1 MST minimumSpanningTree() {
2 Let T be a set for the vertices in the spanning tree;
3 Initially, add the starting vertex to T;
4
5 while (size of T
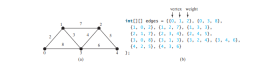
<p>アルゴリズムは、開始頂点を <strong>T</strong> に追加することから始まります。次に、<strong>V – T</strong> から <strong>T</strong> に頂点 (<strong>v</strong> とします) を継続的に追加します。 <strong>v</strong> は、エッジの重みが最小である <strong>T</strong> の頂点に隣接する頂点です。たとえば、以下の図に示すように、<strong>T</strong> と <strong>V – T</strong> には頂点を接続する 5 つのエッジがあり、(<strong>u</strong>, <strong>v</strong>) ) は最も重みが小さいものです。</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172557408574612.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Minimum Spanning Trees"></p>
<p>下の図のグラフを考えてみましょう。アルゴリズムは、次の順序で頂点を <strong>T</strong> に追加します:</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172557408660759.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Minimum Spanning Trees"></p>
<ol>
<li>頂点 <strong>0</strong> を <strong>T</strong> に追加します。</li>
<li>頂点 <strong>5</strong> を <strong>T</strong> に追加します。これは、<strong>Edge(5, 0, 5)</strong> が T<strong>、図aに示すとおり。 </strong>0<strong> から </strong>5<strong> までの矢印線は、</strong>0<strong> が </strong>5<strong> の親であることを示します。</strong>
</li>頂点 <li>1<strong> を </strong>T<strong> に追加します。これは、</strong>Edge(1, 0, 6)<strong> が T</strong>、図 b.<strong> に示すように
</strong>頂点 </li>6<li> を <strong>T</strong> に追加します。これは、<strong>Edge(6, 1, 7)</strong> が T<strong>、図 c に示すように</strong>
<strong>頂点 </strong>2</li> を <li>T<strong> に追加します。これは、</strong>Edge(2, 6, 5)<strong> が T</strong>、図 d に示すように<strong>
</strong>頂点 <strong>4</strong> を </li>T<li> に追加します。これは、<strong>Edge(4, 6, 7)</strong> が T<strong> (図 e に示すように)</strong>
<strong>Edge(3, 2, 8)</strong> の重みが 3 を </li>T<li> に追加します。 >T<strong>、図 f に示すように。</strong>
<strong>
</strong>最小スパニングツリーは一意ではありません。たとえば、次の図の (c) と (d) は両方とも、図 a のグラフの最小全域ツリーです。ただし、重みが異なる場合、グラフには固有の最小スパニング ツリーが含まれます。<strong>
</strong><strong></strong>
</li>グラフは接続されており、方向性がないと仮定します。グラフが接続または方向付けされていない場合、アルゴリズムは機能しません。アルゴリズムを変更して、任意の無向グラフのスパニング フォレストを見つけることができます。スパン フォレストは、各接続コンポーネントがツリーであるグラフです。</ol>
<h2>
Refining Prim’s MST Algorithm
</h2>
<p>To make it easy to identify the next vertex to add into the tree, we use <strong>cost[v]</strong> to store the cost of adding a vertex <strong>v</strong> to the spanning tree <strong>T</strong>. Initially <strong>cost[s]</strong> is <strong>0</strong> for a starting vertex and assign infinity to <strong>cost[v]</strong> for all other vertices. The algorithm repeatedly finds a vertex <strong>u</strong> in <strong>V – T</strong> with the smallest <strong>cost[u]</strong> and moves <strong>u</strong> to <strong>T</strong>. The refined version of the alogrithm is given in code below.<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">Input: A connected undirected weighted G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: a minimum spanning tree with the starting vertex s as the root
1 MST getMinimumSpanngingTree(s) {
2 Let T be a set that contains the vertices in the spanning tree;
3 Initially T is empty;
4 Set cost[s] = 0; and cost[v] = infinity for all other vertices in V;
5
6 while (size of T w(u, v)) { // Adjust cost[v]
11 cost[v] = w(u, v); parent[v] = u;
12 }
13 }
14 }
Implementation of the MST Algorithm
The getMinimumSpanningTree(int v) method is defined in the WeightedGraph class. It returns an instance of the MST class, as shown in Figure below.

The MST class is defined as an inner class in the WeightedGraph class, which extends the Tree class, as shown in Figure below.

The Tree class was shown in Figure below. The MST class was implemented in lines 141–153 in WeightedGraph.java.

The refined version of the Prim’s algoruthm greatly simplifies the implementation. The getMinimumSpanningTree method was implemented using the refined version of the Prim’s algorithm in lines 99–138 in Listing 29.2. The getMinimumSpanningTree(int startingVertex) method sets cost[startingVertex] to 0 (line 105) and cost[v] to infinity for all other vertices (lines 102–104). The parent of startingVertex is set to -1 (line 108). T is a list that stores the vertices added into the spanning tree (line 111). We use a list for T rather than a set in order to record the order of the vertices added to T.
Initially, T is empty. To expand T, the method performs the following operations:
- Find the vertex u with the smallest cost[u] (lines 118–123 and add it into T (line 125).
- After adding u in T, update cost[v] and parent[v] for each v adjacent to u in V-T if cost[v] > w(u, v) (lines 129–134).
After a new vertex is added to T, totalWeight is updated (line 126). Once all vertices are added to T, an instance of MST is created (line 137). Note that the method will not work if the graph is not connected. However, you can modify it to obtain a partial MST.
The MST class extends the Tree class (line 141). To create an instance of MST, pass root, parent, T, and totalWeight (lines 144-145). The data fields root, parent, and searchOrder are defined in the Tree class, which is an inner class defined in AbstractGraph.
Note that testing whether a vertex i is in T by invoking T.contains(i) takes O(n) time, since T is a list. Therefore, the overall time complexity for this implemention is O(n3).
The code below gives a test program that displays minimum spanning trees for the graph in Figure below and the graph in Figure below a, respectively.
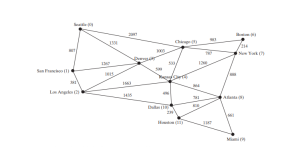
package demo;
public class TestMinimumSpanningTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097},
{1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267},
{2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435},
{3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003},
{4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496},
{5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787},
{6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214},
{7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888},
{8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810},
{9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187},
{10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239},
{11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239}
};
WeightedGraph<string> graph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
WeightedGraph<string>.MST tree1 = graph1.getMinimumSpanningTree();
System.out.println("Total weight is " + tree1.getTotalWeight());
tree1.printTree();
edges = new int[][]{
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<integer> graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5);
WeightedGraph<integer>.MST tree2 = graph2.getMinimumSpanningTree(1);
System.out.println("\nTotal weight is " + tree2.getTotalWeight());
tree2.printTree();
}
}
</integer></integer></string></string>
Total weight is 6513.0
Root is: Seattle
Edges: (Seattle, San Francisco) (San Francisco, Los Angeles)
(Los Angeles, Denver) (Denver, Kansas City) (Kansas City, Chicago)
(New York, Boston) (Chicago, New York) (Dallas, Atlanta)
(Atlanta, Miami) (Kansas City, Dallas) (Dallas, Houston)
Total weight is 14.0
Root is: 1
Edges: (1, 0) (3, 2) (1, 3) (2, 4)
程序为上图第 27 行创建一个加权图。然后调用 getMinimumSpanningTree()(第 28 行)返回一个 MST,它表示图形。在 MST 对象上调用 printTree()(第 30 行)会显示树中的边缘。请注意,MST 是 Tree 的子类。 printTree() 方法定义在 Tree 类中。
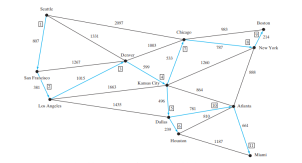
最小生成树的图示如下图所示。顶点按以下顺序添加到树中:西雅图、旧金山、洛杉矶、丹佛、堪萨斯城、达拉斯、休斯顿、芝加哥、纽约、波士顿、亚特兰大和迈阿密。
以上が最小スパニングツリーの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
 Javaプラットフォームは独立していますか?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Javaプラットフォームは独立していますか?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMJavaは、Java Virtual Machines(JVMS)とBytecodeに依存している「Write and Averywherewherewherewherewherewherewhere」の哲学のために、プラットフォームに依存しません。 1)Javaコードは、JVMによって解釈されるか、地元でその場でコンパイルされたBytecodeにコンパイルされます。 2)ライブラリの依存関係、パフォーマンスの違い、環境構成に注意してください。 3)標準ライブラリを使用して、クロスプラットフォームのテストとバージョン管理がプラットフォームの独立性を確保するためのベストプラクティスです。
 Javaのプラットフォームの独立性についての真実:それは本当に簡単ですか?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Javaのプラットフォームの独立性についての真実:それは本当に簡単ですか?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AMjava'splatformindepenceisnotsimple; itinvolvescomplexities.1)jvmcompatibilitymustbeensuredacrosplatforms.2)nativeLibrariesandsystemCallSneedCarefulHandling.3)依存症の依存症の依存症と依存症の依存症と依存関係の増加 - プラットフォームのパフォーマンス
 Javaプラットフォームの独立性:Webアプリケーションの利点May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Javaプラットフォームの独立性:Webアプリケーションの利点May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AMjava'splatformentedentencebenefitswebapplicationsbyAllowingCodeTorunOnySystemwithajvm、simpledifyifieddeploymentandscaling.itenables:1)easydeploymentddifferentservers、2)Seamlessscalingacroscloudplatforms、および3)deminvermentementmentmentmentmentementtodeploymentpoce
 JVM説明:Java Virtual Machineの包括的なガイドMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JVM説明:Java Virtual Machineの包括的なガイドMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMjvmistheruntimeenvironment forexecutingjavabytecode、Curivalforjavaの「writeonce、runanywhere」capability.itmanagesmemory、executessuressecurity、makingestessentionentionalforjavadevadedertionserstunterstanderforeffication devitivationdevation
 Javaの主な機能:なぜそれがトッププログラミング言語のままであるかMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Javaの主な機能:なぜそれがトッププログラミング言語のままであるかMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMJavareMainsAtopChoiceFordevelopersDuetoitsPlatformEndepentence、Object-OrientedDesign、stryngting、automaticmemorymanagement、およびcomprehensivestandardlibrary.thesefeaturesmavaversatilatileandpowerful、sustableforawiderangeofplications、daspitesomech
 Java Platform Independence:開発者にとってはどういう意味ですか?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java Platform Independence:開発者にとってはどういう意味ですか?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AMjava'splatformentencemeansdeveloperscancancodecodeonceanddevicewithoutrocompilling.cancodecodecodecodecodecodecodecodecodecodecodecode compilling
 最初の使用のためにJVMをセットアップする方法は?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AM
最初の使用のためにJVMをセットアップする方法は?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AMJVMをセットアップするには、次の手順に従う必要があります。1)JDKをダウンロードしてインストールする、2)環境変数を設定する、3)インストールの確認、4)IDEを設定する、5)ランナープログラムをテストします。 JVMのセットアップは、単に機能するだけでなく、メモリの割り当て、ガベージコレクション、パフォーマンスチューニング、エラー処理の最適化を行い、最適な動作を確保することも含まれます。
 製品のJavaプラットフォームの独立性を確認するにはどうすればよいですか?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
製品のJavaプラットフォームの独立性を確認するにはどうすればよいですか?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AMtoensurejavaplatformindopendence、soflowthesesteps:1)compileandrunyourapplicationOnMultiplePlatformsusingDifferentosAndjvversions.2)utilizeci/cdpipelines


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

AtomエディタMac版ダウンロード
最も人気のあるオープンソースエディター

SublimeText3 英語版
推奨: Win バージョン、コードプロンプトをサポート!

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Eclipse を SAP NetWeaver アプリケーション サーバーと統合します。

PhpStorm Mac バージョン
最新(2018.2.1)のプロフェッショナル向けPHP統合開発ツール

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
このプロジェクトは osdn.net/projects/mingw に移行中です。引き続きそこでフォローしていただけます。 MinGW: GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) のネイティブ Windows ポートであり、ネイティブ Windows アプリケーションを構築するための自由に配布可能なインポート ライブラリとヘッダー ファイルであり、C99 機能をサポートする MSVC ランタイムの拡張機能が含まれています。すべての MinGW ソフトウェアは 64 ビット Windows プラットフォームで実行できます。






