ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >C#.Net チュートリアル >C# で続行する
C# で続行する
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBオリジナル
- 2024-09-03 15:09:44870ブラウズ
Continue は、C# プログラミング言語の条件ループ ブロック内で使用できる多くの条件ステートメントの 1 つであり、反復条件が実行された後、次の処理に進むためにループの実行を継続する句として機能します。条件ループ内の次の反復の実行。通常、for-while ループ、do-while ループ、for-each ループなどの反復条件付きループと一緒に使用されます。
C# で Continue ステートメントはどのように機能しますか?
下の図では、ループが開始され、 continue ステートメントがある場合、現在の反復を停止し、ループの先頭に戻って制御を次の反復に渡します。
フローチャート
以下は、Continue ステートメントの実装方法を示すフロー図です。

以下は、for、while、do-while、foreach、内部ループなどのループ本体でどのように動作するかを示す例です。
例 #1
a. 以下の例では、for ループが使用されています。変数の値が 5 に等しい場合、Continue ステートメントは現在の反復をスキップし、次の反復にジャンプして値を表示します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System. Linq;
using System. Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for(int x=1; x<=6; x++ ) // loop runs six times
{
if (x == 5) // value is equal to 5
continue; // skips the iteration
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
出力:

b. 以下の例では、変数の値が 6 未満の場合、反復をスキップし、値が 6 以上である次の反復にジャンプして値を表示します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for(int x=1; x<=10; x++ ) // loop runs ten times
{
if (x < 6) // values less than six
continue; // skips the iteration
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
出力:

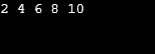
c. 以下の例では、ループが 10 回実行され、変数 x が奇数の場合は必ず反復をスキップし、制御を次の反復に渡し、変数 x が偶数の場合はその値を出力します。これは、 continue ステートメントを使用して偶数系列を出力する方法です。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int x = 2; x <= 10; x++) // loop runs ten times
{
if (x % 2 == 1) // logic to print even number
{
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.Write("{0} ", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
出力:
例 #2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 0; // initializing variable
while(x < 7) // loop runs seven times
x++; // incrementing the value of x
if(x==5) // value is equal to 5
continue; // skips the iteration
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
上記の例ではwhileループを使用しています。変数 x が初期化されます。 x の値が 5 に等しい場合、Continue ステートメントを使用して反復をスキップし、他の値を表示します。
出力:

例 #3
a. 以下の例では、do whileループ文が使用されています。変数 x が初期化され、x の値が 4 に等しい場合、Continue ステートメントは反復を停止し、次の実行に制御を渡し、値を表示します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 1; // initializing variable
do
{
Console.WriteLine("value is :{0}", x);
x++; // incrementing the value of x
if (x == 4)
continue; // skips the iteration
} while(x < 6) ;
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
出力:

b. 以下の例ではwhileループを使用しています。変数 x が初期化されます。 x の値が 8 に等しい場合、Continue ステートメントを使用して反復をスキップし、他の値を表示します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 8; // initializing variable
do
{
if (x == 13)
{
x = x + 1;
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.WriteLine("a: {0}", x);
x++; // incrementing the value of x
}
while (x < 15);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
出力:

例 #4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int x = 1; x <= 4; x++) // loops run four times
{
for (int y = 1; y <= 4; y++)
{
if (x == 3 && y == 3)
{
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.WriteLine(x + " " + y);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}
上記の例では、変数 x と y の値に基づいて反復をスキップするために、内部ループ内で continue ステートメントが使用されています。
出力:

例 #5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ContinueExample
{
class Demo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[]arr = { 2, 4, 25, 34, 28, 57}; // initializing array
foreach (int a in arr) // iteration
{
if (a == 25) //Array element value equal to 25
{
continue; // skips the iteration
}
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
上記の例では、反復に foreach が使用されています。 6 つの要素で構成される要素の配列が初期化されます。変数が 25 に等しい場合、Continue ステートメントは反復をスキップし、制御を次の反復に渡して値を表示します。
出力:

結論
これは、for、foreach、while、do-while などのさまざまなループ本体で continue ステートメントを使用し、条件に基づいて反復をスキップする方法です。ほとんどの場合、 continue ステートメントは for および foreach ループ本体とともに使用されます。
以上がC# で続行するの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

