ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Javaのキュー
Javaのキュー
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBオリジナル
- 2024-08-30 16:03:401143ブラウズ
キューのデータ構造は先入れ先出し (FIFO) 原理を使用します。これは、処理対象のオブジェクトを到着順に保持するために使用されます。これは、行列に並ぶ人々の列と非常によく似ています。 Java は Collection インターフェースの形式でデータ構造を大規模にサポートしているため、キューは Collection インターフェースで使用できるインターフェースです。これは Collection インターフェイスを拡張します。これは Java.util パッケージで使用でき、コレクション インターフェイスで使用できるすべての操作と、いくつかの追加の抽出、挿入、および検査操作をサポートします。
無料ソフトウェア開発コースを始めましょう
Web 開発、プログラミング言語、ソフトウェア テスト、その他
構文:
Interface Queue<E>
キューはクラスではなくインターフェースであるため、直接インスタンス化することはできません。この宣言は、キューがコレクションと同様に値をジェネリックとして受け入れ、任意のオブジェクトをキューに渡すことができることを示しています。 Java には Queue インターフェイスの実装が複数あり、Queue の使用中に使用できます。それは LinkedList と PriorityQueue です。
キューは次のように宣言できます:
Queue< Object > q = new LinkedList<>();
Queue< Object > q = new PriorityQueue<>();
Java ではキューはどのように機能しますか?
- 前に述べたように、キュー インターフェイスはコレクション インターフェイスを拡張します。したがって、そこで利用可能なすべての基本的な操作メソッドをサポートします。
- LinkedList や PriorityQueue などの実装は、Queue インターフェースで宣言されたキュー固有のメソッドを実装します。
- LinkedList は、LinkedList の標準として、つまり挿入順に要素を保持します。 PriorityQueue は、挿入された要素の自然な順序を維持します。
- これら 2 つの実装はスレッドセーフではないことに注意してください。このため、Java はスレッドセーフである PriorityBlockingQueue という別の実装を提供します。
Java のキュー メンバーの種類
- キューはインターフェイスであるため、抽象メソッドのみが含まれ、データ メンバーは含まれません。
- キューは、子クラスに実装された操作を定義する方法のみを提供します。
Java のキュー関数
- キューは FIFO 構造をサポートしているため、一方の端から要素を挿入し、もう一方の (フロント) 端から要素を削除できます。
- これらは、キューによってサポートされる 2 つの基本的な操作です。
- キューで使用できるすべてのメソッドは 2 つのカテゴリに分類できます。最初のタイプのメソッドは、要素が見つからないなど、操作が失敗した場合に例外をスローします。2 番目のタイプのメソッドでは、操作が失敗した場合、例外の代わりに null や false などの特定の値が返されます。 .
- キューの先頭という概念は、常にキューの最初の要素を表します。削除時には、この head 要素が最初に削除されます。
キューで使用可能なすべてのメソッドを以下に示します:
| Returns special value | Throws exception | |
| Insert | offer(e) | add(e) |
| Remove | poll() | remove() |
| Examine | peek() | element() |
So as explained, two types of methods throw an exception and return a special value. There are three types of operation in this kind of operation: insertion, the second is removal, and the third is retrieval or examination. In the case of the remove operation, an object will be removed from the queue. Still, in the case of examination, the object will be returned without actually removing from the queue.
Examples of Queue in Java
Given below are the different examples of Queue in Java:
Example #1 – Add operation with LinkedList implementation
Code:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
}
}
Output:

Note here that the order of insertion is the same with output from left to write.
Example #2 – Let’s remove the added elements one by one
Code:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(q.remove() + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(q);
}
}
Output:
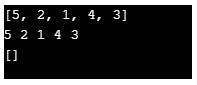
Here, we have used the function isEmpty() to check when the queue becomes empty after removing elements. The removal order is the same as per the insertion. After removing all the elements, we printed the queue and obtained an empty bracket at the end.
Example #3 – Insertion and Removal Operation on PriorityQueue
Code:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(q.remove() + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(q);
}
}
Output:

Here, we have used PriorityQueue, which will hold and return the elements depending upon the elements’ natural ordering or upon the comparator, if any passed. Note the insertion order and removal orders are not the same. The removal is based totally on the value of elements.
Example #4 – Examine operation on LinkedList
Code:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
System.out.println( q.peek() );
System.out.println(q);
}
}
Output:

Note here that we have used the peek() function, which will return the head of the queue without actually removing it. We printed the queue after performing the peek operation, and you can observe that the head element, which is 5, remains unchanged in the queue.
Example #5 – Examine operation on PriorityQueue
Code:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueOperations {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<Integer> ();
q.add(5);
q.add(2);
q.add(1);
q.add(4);
q.add(3);
System.out.println(q);
System.out.println( q.peek() );
System.out.println(q);
}
}
Output:

This is similar to the previous example’s LinkedList operation, but note the head element is 1 because it’s a PriorityQueue.
Conclusion
Java utilizes the Queue interface as a means to maintain elements in insertion order. It supports operations like insertion, retrieval, and removal. There are alternative methods available for all the methods. We have seen examples of the most commonly used methods in queue operation.
以上がJavaのキューの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

