ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >Java の数学関数
Java の数学関数
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBオリジナル
- 2024-08-30 15:33:091172ブラウズ
Java は最も便利なプログラミング言語の 1 つです。アーキテクチャの構築、科学の計算の解決、地図の構築など、さまざまなアプリケーションがあります。これらのタスクを簡単にするために、Java では、2 乗、指数関数などのいくつかの演算を実行する java.lang.Math クラスまたは Java の Math Functions が提供されています。 、天井、対数、立方体、絶対値、三角法、平方根、床など
広告 このカテゴリーの人気コース JAVA マスタリー - スペシャライゼーション | 78 コース シリーズ | 15 回の模擬テスト無料ソフトウェア開発コースを始めましょう
Web 開発、プログラミング言語、ソフトウェア テスト、その他
このクラスでは、数学の授業の基礎となる 2 つの分野を提供します。彼らは、
- 自然対数の底である「e」(718281828459045)
- 円周率と直径の比率である「pi」(141592653589793)
Java のさまざまな数学関数
Java は多数の Math メソッドを提供します。以下に示すように分類できます:
- 基本的な計算方法
- 三角関数の計算方法
- 対数演算方法
- 双曲線数学法
- 角度計算メソッド
それでは、詳しく見ていきましょう。
1.基本的な計算方法
よりよく理解するために、以下に示すように、上記のメソッドを Java プログラムに実装できます。
| メソッド | 戻り値 | 引数 |
例 |
|
腹筋() |
引数の絶対値。つまり、正の値 | long、int、float、double |
int n1 = Math.abs (80) //n1=80 int n2 =Math.abs (-60) //n2=60 |
|
sqrt() |
引数の平方根 | ダブル |
double n= Math.sqrt (36.0) // n=6.0 |
|
cbrt() |
引数の立方根 | ダブル |
double n= Math.cbrt (8.0) // n=2.0 |
|
max() |
引数に渡される 2 つの値の最大値 | long、int、float、double |
int n=Math.max(15,80) //n=80 |
|
分() |
引数に渡される 2 つの値の最小値 | long、int、float、double |
int n=Math.min(15,80) //n=15 |
|
ceil() |
浮動小数点値を整数値に丸めます | ダブル | double n=Math.ceil(6.34) //n=7.0 |
| フロア() | 浮動小数点値を整数値に切り捨てます | ダブル |
double n=Math.floor(6.34) //n=6.0 |
|
round() |
float または double 値を整数値に切り上げまたは切り捨てます | double、float | double n = Math.round(22.445);//n=22.0 double n2 = Math.round(22.545); //n=23.0 |
|
パウ() |
最初のパラメータを 2 番目のパラメータに引き上げた値 |
ダブル |
double n= Math.pow(2.0, 3.0) //n=8.0 |
|
ランダム() |
0 から 1 までの乱数 | ダブル | double n= Math.random() //n= 0.2594036953954201 |
|
シグナム() |
渡されたパラメータの符号。
正の場合は 1 が表示されます。 負の場合は -1 が表示されます。 0の場合は0が表示されます |
double、float |
double n = 数学。 signum (22.4);//n=1.0 double n2 = 数学。符号 (-22.5);//n=-1.0 |
|
addExact() |
パラメータの合計。取得した結果がlongまたはint値をオーバーフローした場合、例外がスローされます。 | int、long |
int n= Math.addExact(35, 21)//n=56 |
|
incrementExact() |
パラメータは 1 ずつ増加します。取得された結果が int 値をオーバーフローした場合、例外がスローされます。 | int、long |
int n=数学。 incrementExact(36) //n=37 |
|
subtractExact() |
パラメータの違い。取得した結果が int 値をオーバーフローした場合、例外がスローされます。 | int、long |
int n= Math.subtractExact(36, 11) //n=25 |
|
multiplyExact() |
パラメータの合計。取得した結果がlongまたはint値をオーバーフローした場合、例外がスローされます。 | int、long |
int n= Math.multiplyExact(5, 5) //n=25 |
|
decrementExact() |
パラメータは 1 ずつ減分されます。取得された結果が int または long 値をオーバーフローした場合、例外がスローされます。 | int、long |
int n=数学。 decrementExact (36) //n=35 |
|
negateExact() |
パラメータの否定。取得された結果が int または long 値をオーバーフローした場合、例外がスローされます。 | int、long |
int n=数学。 negateExact(36) //n=-36 |
|
copySign() |
最初のパラメータの絶対値と 2 番目のパラメータで指定された符号 | double、float |
double d= Math.copySign(29.3,-17.0) //n=-29.3 |
|
floorDiv() |
最初のパラメータを 2 番目のパラメータで除算し、フロア演算を実行します。 | 長整数、整数 |
int n= Math.floorDiv(25, 3) //n=8 |
|
ハイポット() |
パラメータの二乗和を求めて平方根演算を行います。中間のオーバーフローまたはアンダーフローがあってはなりません。 | ダブル |
double n=Math.hypot(4,3) //n=5.0 |
|
getExponent() |
不偏指数。この指数は double または float で表されます | int |
double n=Math.getExponent(50.45) //n=5 |
コード:
//Java program to implement basic math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = Math.abs(80);
System.out.println("absolute value of 80 is: "+n1);
int n2 = Math.abs(-60);
System.out.println("absolute value of -60 is: "+n2);
double n3 = Math.sqrt(36.0);
System.out.println("Square root of 36.0 is: "+n3);
double n4 = Math.cbrt(8.0);
System.out.println("cube root 0f 8.0 is: "+n4);
int n5= Math.max(15,80);
System.out.println("max value is: "+n5);
int n6 =Math.min(15,80);
System.out.println("min value is: "+n6);
double n7 = Math.ceil(6.34);
System.out.println("ceil value of 6.34 is "+n7);
double n8 = Math.floor(6.34);
System.out.println("floor value of 6.34 is: "+n8);
double n9 = Math.round(22.445);
System.out.println("round value of 22.445 is: "+n9);
double n10 = Math.round(22.545);
System.out.println("round value of 22.545 is: "+n10);
double n11= Math.pow(2.0, 3.0);
System.out.println("power value is: "+n11);
double n12= Math.random();
System.out.println("random value is: "+n12);
double n13 = Math. signum (22.4);
System.out.println("signum value of 22.4 is: "+n13);
double n14 = Math. signum (-22.5);
System.out.println("signum value of 22.5 is: "+n14);
int n15= Math.addExact(35, 21);
System.out.println("added value is: "+n15);
int n16=Math. incrementExact(36);
System.out.println("increment of 36 is: "+n16);
int n17 = Math.subtractExact(36, 11);
System.out.println("difference is: "+n17);
int n18 = Math.multiplyExact(5, 5);
System.out.println("product is: "+n18);
int n19 =Math. decrementExact (36);
System.out.println("decrement of 36 is: "+n19);
int n20 =Math. negateExact(36);
System.out.println("negation value of 36 is: "+n20);
}
}
出力:

2.三角関数の計算方法
以下は、表に記載されている三角関数関数を実装する Java プログラムです。
|
Method |
Return value | Arguments | Example |
|
sin() |
Sine value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.sine (value) //output is 0.8660254037844386 |
|
cos() |
Cosine value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.cos (value) //output is 0.5000000000000001 |
|
tan() |
tangent value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.tan(value) //output is 1.7320508075688767 |
|
asin() |
Arc Sine value of the parameter. Or Inverse sine value of the parameter | double |
Math.asin(1.0) // 1.5707963267948966 |
|
acos() |
Arc cosine value of the parameter Or Inverse Cosine value of the parameter | double |
Math.acos(1.0) //0.0 |
|
atan() |
Arctangent value of the parameter Or Inverse tangent value of the parameter | double |
Math.atan(6.267) // 1.4125642791467878 |
sin()
double num1 = 60; //値をラジアンに変換
double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.sine (value) //出力は 0.8660254037844386
cos()
double num1 = 60; //値をラジアンに変換
double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.cos (value) //出力は 0.5000000000000001
tan()
double num1 = 60; //値をラジアンに変換
double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.tan(value) //出力は 1.7320508075688767
asin()
Math.asin(1.0) // 1.5707963267948966
acos()
Math.acos(1.0) //0.0
atan()
Math.atan(6.267) // 1.4125642791467878
Code:
//Java program to implement trigonometric math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double num1 = 60;
// Conversion of value to radians
double value = Math.toRadians(num1);
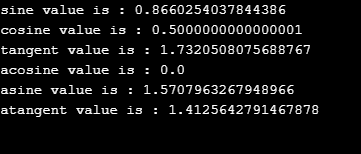
System.out.println("sine value is : "+Math.sin(value));
System.out.println("cosine value is : "+Math.cos(value));
System.out.println("tangent value is : "+Math.tan(value));
double num2 = 1.0;
System.out.println("acosine value is : "+Math.acos(num2));
System.out.println("asine value is : "+Math.asin(num2));
double num3 = 6.267;
System.out.println("atangent value is : "+Math.atan(num3)); <strong>Output:</strong>
3. Logarithmic Math Methods
Following is the sample program that implements Logarithmic math methods:
|
Method |
Return Value | Arguments |
Example |
|
expm1() |
Calculate E’s power and minus 1 from it. E is Euler’s number. So here, it is ex-1. | double |
double n = Math.expm1(2.0) // n = 6.38905609893065 |
|
exp() |
E’s power to the given parameter. That is, ex | double |
double n=Math.exp(2.0) //n = 7.38905609893065 |
|
log() |
Natural logarithm of parameter | double |
double n=Math.log(38.9) //n=3.6609942506244004 |
|
log10() |
Base 10 logarithm of parameter | double |
double n = Math.log10(38.9) //n= 1.5899496013257077 |
|
log1p() |
Natural logarithm of the sum of parameter and one. ln(x+1) | double |
double n = Math.log1p(26) //n= 3.295836866004329 |
Code:
//Java program to implement logarithmic math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.expm1(2.0);
double n2 = Math.exp(2.0);
double n3 = Math.log(38.9);
double n4 = Math.log10(38.9);
double n5 = Math.log1p(26);
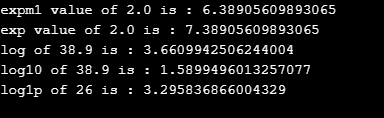
System.out.println("expm1 value of 2.0 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("exp value of 2.0 is : "+n2);
System.out.println("log of 38.9 is : "+n3);
System.out.println("log10 of 38.9 is : "+n4);
System.out.println("log1p of 26 is : "+n5);
}}
Output:
4. Hyperbolic Math Methods
Following is the Java program to implement hyperbolic math functions mentioned in the table:
|
Method |
Return value | Arguments |
Example |
|
sinh() |
Hyperbolic Sine value of the parameter. i.e (ex – e -x)/2 Here, E is the Euler’s number. | double |
double num1=Math.sinh (30) //output is 5.343237290762231E12 |
|
cosh() |
Hyperbolic Cosine value of the parameter. i.e. (ex + e -x)/2 Here, E is the Euler’s number. | double |
double num1 = Math.cosh (60.0) //output is 5.710036949078421E25 |
|
tanh() |
Hyperbolic tangent value of the parameter | double |
double num1= Math.tanh (60.0) //output is 1.0 |
Code:
//Java program to implement HYPERBOLIC math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.sinh (30);
double n2 = Math.cosh (60.0);
double n3 = Math.tanh (60.0);
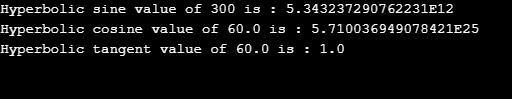
System.out.println("Hyperbolic sine value of 300 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic cosine value of 60.0 is : "+n2);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic tangent value of 60.0 is : "+n3);
}
}
Output:
5. Angular Math Methods
| Method | Return Value | Arguments | Example |
| toRadians() | Degree angle converts to radian angle | double |
double n = Math.toRadians(180.0) //n= 3.141592653589793 |
| toDegrees() | Radian angle converts to Degree angle | double |
double n = Math. toDegrees (Math.PI) //n=180.0 |
Now, let us see a sample program to demonstrate Angular Math methods.
Code:
//Java program to implement Angular math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.toRadians(180.0);
double n2 = Math. toDegrees (Math.PI);
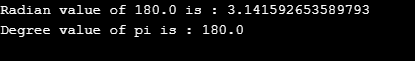
System.out.println("Radian value of 180.0 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("Degree value of pi is : "+n2);
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Java offers a wide variety of math functions to perform different tasks such as scientific calculations, architecture designing, structure designing, building maps, etc. This document discusses several basic, trigonometric, logarithmic and angular math functions in detail with sample programs and examples.
以上がJava の数学関数の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

