java - 如何准确的将科学计数法表示的Double类型转换为正常的字符串?
1.起因
最近在做Excel解析,要知道,在Excel中会将长数字自动转换为科学计数法表示,我的问题是如何原样
读取出来并用字符串表示,为了方便说明,我新建一个Workbook,在第一个Sheet的第一个Cell中填入:
123456729.326666,Excel中显示为:
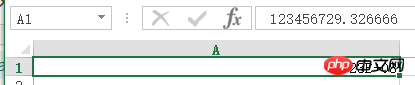
现在我需要利用POI将其读取出来,并原样打印:123456729.326666。2.我的代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
String filePath="C:/Users/yan/Desktop/testDouble.xlsx";
File file = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
file=new File(filePath);
is = new FileInputStream(file);
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(is);
XSSFCell cell1 = workbook.getSheetAt(0).getRow(0).getCell(0);
//获取double类型的值
Double d = cell1.getNumericCellValue();
System.err.println("科学计数法表示:\n\t"+d);//此时打印出来是科学计数法
/**
* 使用NumberFormat转换
*/
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
String s = nf.format(d);
System.err.println("经过NumberFormat格式化后:\n\t"+s);
/**
* 使用DecimalFormat转换字符串
*/
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat();
s=df.format(d);
System.err.println("经过DecimalFormat格式化后:\n\t"+s);
/**
* 直接使用BigDecimal表示
*/
BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal(d);
//转换为工程??我也不知道怎么称呼
s = bd.toEngineeringString();
System.err.println("toEngineeringString表示:\n\t" + s);
//使用网上普遍的解决办法toPlainString
s = bd.toPlainString();
System.err.println("toPlainString表示:\n\t" + s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}输出结果

疑问
可以看到,我并没有得到想要的结果(123456729.326666),使用*Format之后只保留3位小数,此处不设置#.####等格式是因为并不确定输入的小数可以达到多少位,继而使用了网上推荐的toPlainString方法得到的结果也并不精确,求各位大神指点。