Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Comment implémenter l'applet de la calculatrice dans l'interface graphique Java
Comment implémenter l'applet de la calculatrice dans l'interface graphique Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBavant
- 2023-05-17 12:55:061800parcourir
Rendu :
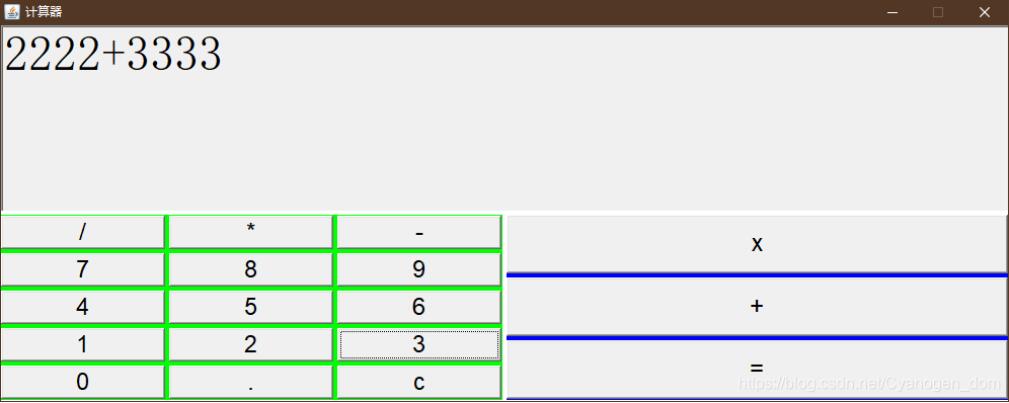
Code :
package gui;
/**
* 导入所需要的包
**/
import java.awt.*; // 这个是java的gui编程里面一个很重要的包
import java.awt.event.*; // 用来处理事件所需要
import java.util.Stack; // 栈 , 我用来处理运算的
public class Calculator extends Frame implements ActionListener{
/**
* 先声明一个公共类叫Calculator , 继承自Frame类 , 实现ActionListener接口功能
**/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // 这个是用来控制版本的序列化
int frame_width = 1000,frame_height = 400; //设置整个框架的长宽
Panel panel_textfield,panel_number,panel_op,panel_other; // 整个计算器布局我把它分成两个面板 , 一个是上面的输入框区 , 一个是下面的按钮区 , 然后按钮区又分成了左边和右边两个区 , 所以有三个panel
Button [] number_buttons; // 声明数字按钮(也就是上面说的左边区)
Button [] op_buttons; // 声明操作符按钮(也就是上面说的右边区)
TextField textfield; // 输入框
public Calculator() {
super("计算器"); // 完成实例域参数的初始化,调用构造器的语句只能作为另一个构造器(通常指的是子类构造器)的第一条语句出现
init(); // 自己写的初始化方法
setLayout(); // 设置布局管理方式
setBackground(); // 设置背景
setBounds(); // 设置位置
setFonts(); // 设置字体
addButtons(); // 添加按钮
textfield.setEditable(false); // 设置输入框为不可手动编辑 , 只能通过按钮输入 */
addWindowListener // 添加一个窗口监听器,便于按下关闭按钮时能关闭窗口 , 否则只能在ide里面停止调试来关闭程序
(
new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
}
);
setVisible(true); // 设置框架为可见,不然画了框你也看不见...一定要放在最后面,放在前面的话,
后面对窗体有改动得缩放拉伸一下窗体进行窗体重绘才能出现效果 , 我在这里卡了很久....
}
public void init() {
panel_textfield = new Panel(); // 实例化一个panel
panel_number = new Panel(); // 实例化一个panel
panel_op = new Panel(); // 实例化一个panel
panel_other = new Panel(); // 实例化一个panel
textfield = new TextField(frame_width);// 实例化一个文本输入框
setResizable(false); // 设置整个窗体为不可缩放拉伸
add(panel_textfield); // 往窗体中添加输入框面板
add(panel_other); // 往窗体中添加按钮面板
panel_textfield.add(textfield); // 在输入框面板中添加输入框
panel_other.add(panel_number); // 在下面面板中添加数字按钮面板
panel_other.add(panel_op); // 在下面面板中添加操作符按钮面板
}
public void setLayout() {
setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1,4,4)); // 设置窗体布局方式为网格布局,2*1的网格,网格之间间距为4个像素
panel_textfield.setLayout(null); // 输入框面板就一个组件,所以设置null
panel_other.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,2,4,4)); // 下面面板因为分成左边的数字区和右边的操作符区,所以设置1*2的网格布局方式,间距4个像素
panel_number.setLayout(new GridLayout(5,3,4,4)); // 数字区布局设置为5*3的网格布局
panel_op.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,1,4,4)); // 操作符区设置为3*1的网格布局方式
}
public void setBackground() { // 设置背景,没什么好说的....
panel_textfield.setBackground(Color.red);
panel_number.setBackground(Color.green);
panel_op.setBackground(Color.blue);
}
public void setBounds() { // 设置组件位置,没什么好说的....
setBounds(0, 0, frame_width, frame_height);
textfield.setBounds(0, 0, frame_width, frame_height / 2);
}
public void addButtons() {
String [] titles1 = {"/", "*", "-", // 数字区按钮的label值
"7", "8", "9",
"4", "5", "6",
"1", "2", "3",
"0", ".", "c"};
String [] titles2 = {"x", "+", "="}; // 操作符区按钮的label值
number_buttons = new Button[15]; // 申请15个按钮对象
op_buttons = new Button[3]; // 申请3个按钮对象
for(int i = 0; i < this.number_buttons.length; i++) {
number_buttons[i] = new Button(titles1[i]);
panel_number.add(number_buttons[i]); // 往数字区中添加按钮
number_buttons[i].addActionListener(this); // 按钮的事件监听器,处理方法为this,也就是下面重载的actionPerformed()方法,这个方法必须被重载
}
for(int i = 0; i < this.op_buttons.length; i++) {
op_buttons[i] = new Button(titles2[i]); // 往操作符区中添加按钮
panel_op.add(this.op_buttons[i]);
op_buttons[i].addActionListener(this); // 按钮的事件监听器,处理方法为this,也就是下面重载的actionPerformed()方法,这个方法必须被重载
}
}
@Override // 对ActionListener接口的此方法进行重载
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Button button = (Button) e.getSource(); // 获得按钮来源
/**
* 如果是数字键和操作符 , 则直接显示
**/
for(int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
if(button == number_buttons[i] || button == op_buttons[1]) {
textfield.setText(textfield.getText() + button.getLabel());
return;
}
}
/**
* 如果是c,则清空
**/
if(button == number_buttons[14]) {
textfield.setText("");
return;
}
/**
* 如果是回退按钮 , 则清除最近的一个字符
**/
if(button == op_buttons[0]) {
String s = textfield.getText();
if(s.length() > 0)
textfield.setText(s.substring(0, s.length() - 1));
return;
}
/**
* 如果是=,则计算结果
**/
if(button == op_buttons[2]) {
textfield.setText(getResult());
return;
}
}
public String getResult() {
/**
* 计算结果
**/
String s = textfield.getText(); // 先获得输入的字符串
String num = "";
Stack<Double> nums = new Stack<Double>();
Stack<String> ops = new Stack<String>();
/**
* 利用regex分离操作数和操作符,然后用栈进行结果的计算
**/
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
String temp = s.charAt(i) + "";
if(temp.matches("[0-9]") || temp.matches("[.]")) {
num += temp;
}
else if(temp.matches("[*+]") || temp.matches("[-]") | temp.matches("[/]")) {
if(!num.equals(""))
nums.push(Double.parseDouble(num));
if(ops.isEmpty() || cmpLevel(temp,ops.peek())) {
ops.push(temp);
}
else {
Double num1 = nums.pop();
Double num2 = nums.pop();
String op2 = ops.pop();
nums.push(compute(num2,num1,op2));
i--;
}
num = "";
}
}
while(!ops.isEmpty()) {
if(!num.equals("")) {
nums.push(compute(nums.pop(),Double.parseDouble(num),ops.pop()));
num = "";
}
else {
Double num1 = nums.pop();
Double num2 = nums.pop();
nums.push(compute(num2,num1,ops.pop()));
}
}
return nums.pop().toString();
}
/**
* 将两个操作数根据操作符进行运算 , 返回结果
** /
public Double compute(double num1,double num2,String op) {
if(op.equals("+")) {
return num1 + num2;
}
else if(op.equals("-")) {
return num1 - num2;
}
else if(op.equals("*")) {
return num1 * num2;
}
else
return num1 / num2;
}
/**
* 比较两个操作符的优先级
**/
public boolean cmpLevel(String s1,String s2) {
if(s1.equals("+") || s1.equals("-")) {
return false;
}
else {
if(s2.equals("+") || s2.equals("-"))
return true;
return false;
}
}
/**
* 设置每个组件的字体
**/
public void setFonts() {
panel_number.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",Font.PLAIN,24));
panel_op.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",Font.PLAIN,24));
panel_other.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",Font.PLAIN,24));
textfield.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",Font.PLAIN,48));
}
/**
* main方法
**/
public static void main(String [] args) {
new Calculator();
}
}Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Déclaration:
Cet article est reproduit dans:. en cas de violation, veuillez contacter admin@php.cn Supprimer
Article précédent:Comment Thread génère-t-il une interface en Java ?Article suivant:Comment Thread génère-t-il une interface en Java ?

