Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Comment SpringBoot intègre ShedLock pour implémenter des tâches planifiées distribuées
Comment SpringBoot intègre ShedLock pour implémenter des tâches planifiées distribuées
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBavant
- 2023-05-13 12:55:061289parcourir
1. Contexte
Lorsque le service de projet est déployé dans un cluster, le code aura des tâches planifiées pour tout le monde, mais il n'est pas approprié de laisser chaque nœud exécuter des tâches planifiées. ShedLock dans SpringBoot peut très bien résoudre ce problème. Ci-dessous, je présenterai en détail comment SpringBoot intègre ShedLock et comment ShedLock implémente le timing distribué.
2. Qu'est-ce que ShedLock
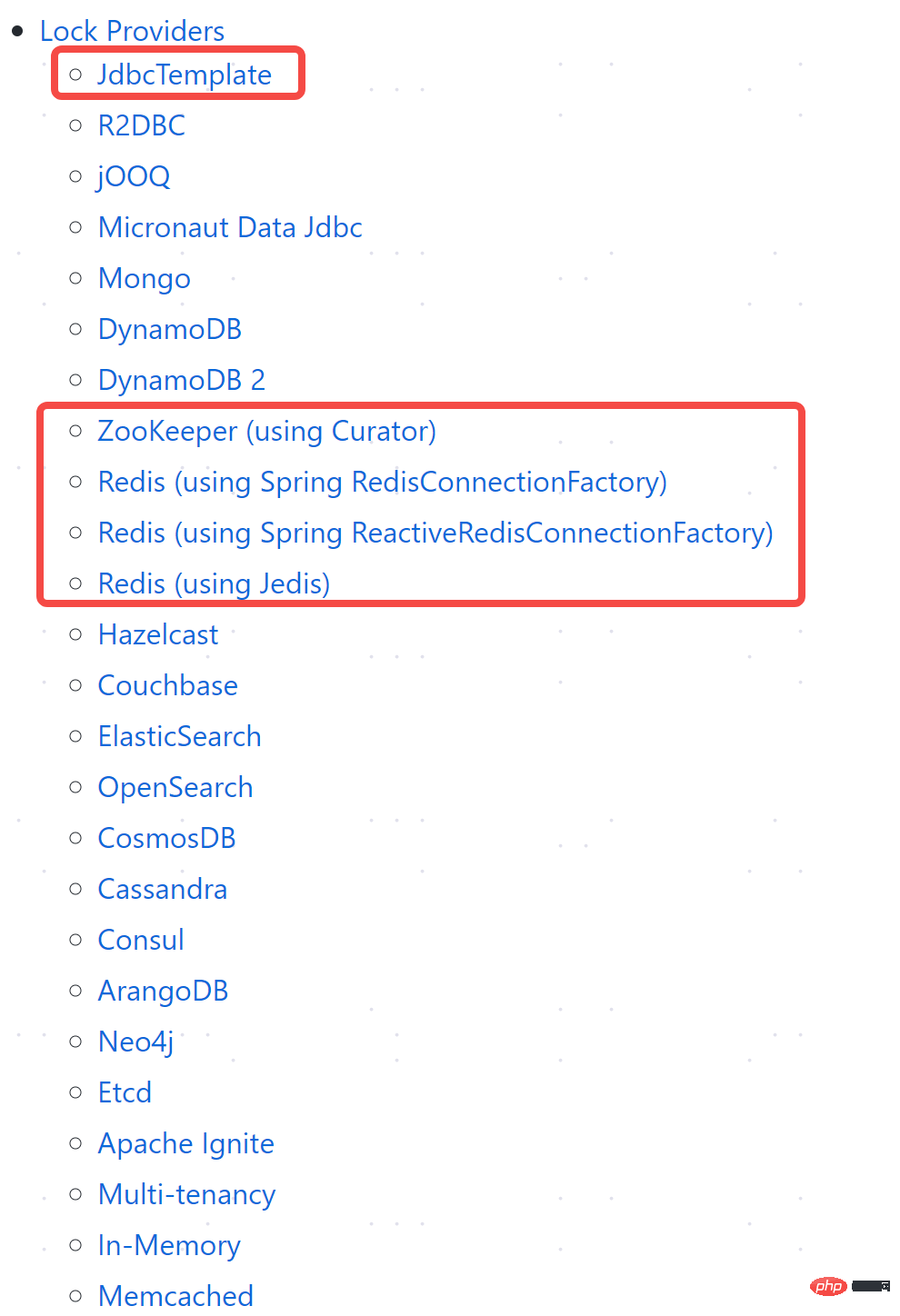
Voici le fournisseur de verrouillage ShedLock, qui implémente le verrouillage via le stockage externe. Comme le montre la figure ci-dessous, les bibliothèques intégrées au stockage externe sont toujours très riches :
3. . Implémentation
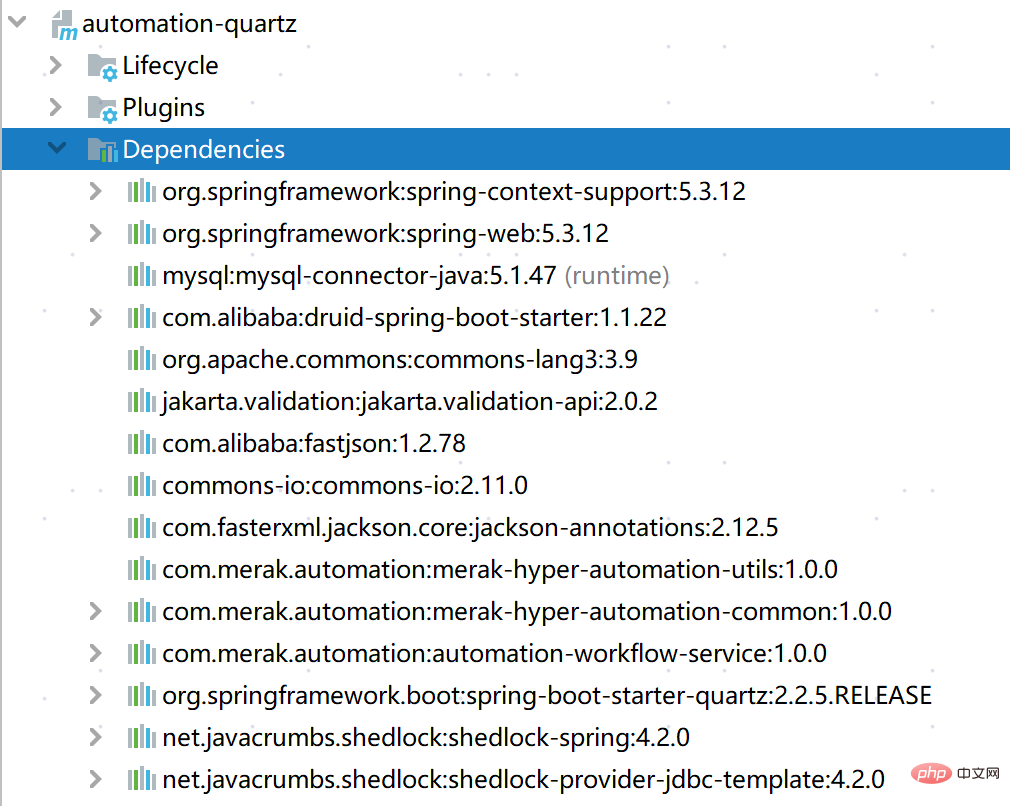
1.1 Présentation des packages de dépendances CShedlock Relying Pack :
<!-- web工程依赖包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.javacrumbs.shedlock</groupId>
<artifactId>shedlock-spring</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--每个外部存储实例所需依赖包不一样,这里是jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.javacrumbs.shedlock</groupId>
<artifactId>shedlock-provider-jdbc-template</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>E Arbre de paquets dépendants :
 1.2 Configurer les informations de connexion à la base de données
1.2 Configurer les informations de connexion à la base de données
PORT : 8105Spring :
1.3 Créer une table de données Mysql
DataSource :
URL : mysql : / /127.0.0.1:3306/testjdbc?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
nom d'utilisateur : root
mot de passe : 123456
nom de classe de pilote : com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type : com. mysql .cj.jdbc.MysqlDataSource
CREATE TABLE `shedlock` ( `name` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT 'name' , `lock_until` timestamp(3) NULL DEFAULT NULL , `locked_at` timestamp(3) NULL DEFAULT NULL , `locked_by` varchar(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC ;
1.4 Configurer LockProvider
ShedLockConfig.java :
import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.core.LockProvider;
import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.provider.jdbctemplate.JdbcTemplateLockProvider;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @description: Shedlock集成Jdbc配置类
*/
@Component
public class ShedLockConfig {
@Resource
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
private LockProvider lockProvider() {
return new JdbcTemplateLockProvider(dataSource);
}
}classe de démarrage principale Springboot MerakQuartzApplication :
import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.spring.annotation.EnableSchedulerLock;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName: MerakQuartzApplication
* @description: 工单任务调度
*/
// 开启定时器
@EnableScheduling
// 开启定时任务锁,指定一个默认的锁的时间30秒
@EnableSchedulerLock(defaultLockAtMostFor = "PT30S")
@EnableAsync
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.merak.hyper.automation.persist.**.mapper"})
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.merak.hyper.automation.**"}, exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class})
public class MerakQuartzApplication {
public static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MerakQuartzApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MerakQuartzApplication.class, args);
}
private int taskSchedulerCorePoolSize = 15;
private int awaitTerminationSeconds = 60;
private String threadNamePrefix = "taskExecutor-";
/**
* @description: 实例化ThreadPoolTaskScheduler对象,用于创建ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledFuture
*/
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler() {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
taskScheduler.setPoolSize(taskSchedulerCorePoolSize);
taskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix);
taskScheduler.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(false);
taskScheduler.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(awaitTerminationSeconds);
/**需要实例化线程*/
taskScheduler.initialize();
// isinitialized = true;
log.info("初始化ThreadPoolTaskScheduler ThreadNamePrefix=" + threadNamePrefix + ",PoolSize=" + taskSchedulerCorePoolSize
+ ",awaitTerminationSeconds=" + awaitTerminationSeconds);
return taskScheduler;
}
/**
* @description: 实例化ThreadPoolTaskExecutor对象,管理线程
*/
@Bean("asyncTaskExecutor")
public Executor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(5);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(50);
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(200);
taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("asyncTaskExecutor-");
taskExecutor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
taskExecutor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
//修改拒绝策略为使用当前线程执行
taskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//初始化线程池
taskExecutor.initialize();
return taskExecutor;
}
}1.5 Créer une tâche de synchronisation
Dig italEmpTask :
package com.merak.hyper.automation.quartz.task;
import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.spring.annotation.SchedulerLock;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName: BizOrderTask
* @description: 任务队列服务调度
*/
@Component
public class DigitalEmpTask {
public static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DigitalEmpTask.class);
@Scheduled(cron = "0/30 * * * * ?")
@SchedulerLock(name = "digitalEmpTaskScheduler", lockAtMostFor = "PT25S", lockAtLeastFor = "PT25S")
protected void digitalEmpTaskScheduler() {
log.info("云执行调度中心1:任务开始执行,时间:" + DateUtils.dateTimeNow(DateUtils.YYYY_MM_DD_HH_MM_SS));
try {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("云执行调度中心1调度失败,原因:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}Quatre, Analyse des résultats
1. Démarrez respectivement deux nœuds de service, la configuration est la suivante :
serveur :port : 12105Journal des opérations du nœud automation-quartz-one :servlet :
port : 12106
chemin de contexte : /automation-quartz-one
serveur :servlet :
2. Journal des opérations (extrait)
chemin de contexte : /automation-quartz-two
2023-02-22 12:01:00.143 [taskExecutor -1] INFO <46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
<46>
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

