Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Comment utiliser le conteneur Tomcat pour démarrer automatiquement au Springboot
Comment utiliser le conteneur Tomcat pour démarrer automatiquement au Springboot
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBavant
- 2023-05-12 10:25:141129parcourir
1. Spring importe les beans via des annotations d'environ quatre manières. Nous parlons principalement des deux méthodes d'implémentation suivantes :
1 En implémentant l'interface ImportSerlector pour implémenter le chargement de Bean :
public class TestServiceImpl {
public void testImpl() {
System.out.println("我是通过importSelector导入进来的service");
}
}
public class TestService implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.ycdhz.service.TestServiceImpl"};
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(value = {TestService.class})
public class TestConfig {
}
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private TestServiceImpl testServiceImpl;
@RequestMapping("testImpl")
public String testTuling() {
testServiceImpl.testImpl();
return "Ok";
}
}
2. pour implémenter le chargement du Bean :
public class TestService {
public TestService() {
System.out.println("我是通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar导入进来的组件");
}
}
public class TestImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//定义一个BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(TestService.class);
//把自定义的bean定义导入到容器中
registry.registerBeanDefinition("testService",beanDefinition);
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(TestImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)
public class TestConfig {
}
2. Springboot sera automatiquement assemblé pendant le processus de démarrage
Nous avons recherché la configuration appropriée de Tomcat à partir de spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.6.RELEASE.jar et avons constaté qu'il existe deux configurations automatiques. classes d'assemblage Contient trois personnalisateurs (principe de responsabilité unique orienté objet) et une classe d'usine.
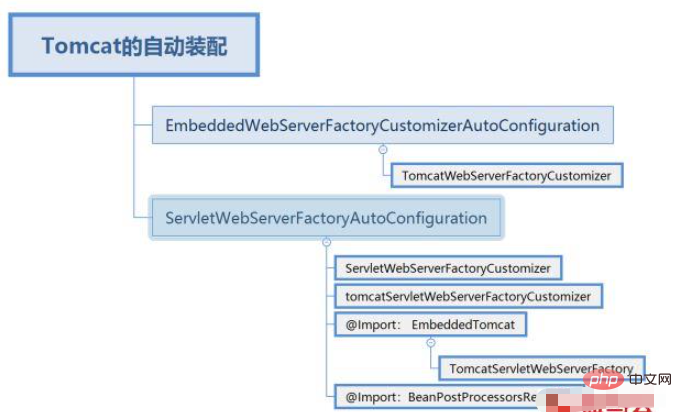
2.1, TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer : Personnalisez les fonctions spécifiques à Tomcat communes aux servlets et aux serveurs réactifs.
public class TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<configurabletomcatwebserverfactory>, Ordered {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory factory) {
ServerProperties properties = this.serverProperties;
ServerProperties.Tomcat tomcatProperties = properties.getTomcat();
PropertyMapper propertyMapper = PropertyMapper.get();
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getBasedir).whenNonNull()
.to(factory::setBaseDirectory);
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getBackgroundProcessorDelay).whenNonNull()
.as(Duration::getSeconds).as(Long::intValue)
.to(factory::setBackgroundProcessorDelay);
customizeRemoteIpValve(factory);
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMaxThreads).when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxThreads) -> customizeMaxThreads(factory,
tomcatProperties.getMaxThreads()));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMinSpareThreads).when(this::isPositive)
.to((minSpareThreads) -> customizeMinThreads(factory, minSpareThreads));
propertyMapper.from(() -> determineMaxHttpHeaderSize()).when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxHttpHeaderSize) -> customizeMaxHttpHeaderSize(factory,
maxHttpHeaderSize));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMaxHttpPostSize)
.when((maxHttpPostSize) -> maxHttpPostSize != 0)
.to((maxHttpPostSize) -> customizeMaxHttpPostSize(factory,
maxHttpPostSize));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getAccesslog)
.when(ServerProperties.Tomcat.Accesslog::isEnabled)
.to((enabled) -> customizeAccessLog(factory));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getUriEncoding).whenNonNull()
.to(factory::setUriEncoding);
propertyMapper.from(properties::getConnectionTimeout).whenNonNull()
.to((connectionTimeout) -> customizeConnectionTimeout(factory,
connectionTimeout));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMaxConnections).when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxConnections) -> customizeMaxConnections(factory, maxConnections));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getAcceptCount).when(this::isPositive)
.to((acceptCount) -> customizeAcceptCount(factory, acceptCount));
customizeStaticResources(factory);
customizeErrorReportValve(properties.getError(), factory);
}
}</configurabletomcatwebserverfactory>
2.2. ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer : WebServerFactoryCustomizer applique les propriétés ServerProperties au serveur Web Tomcat.
public class ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<configurableservletwebserverfactory>, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
PropertyMapper map = PropertyMapper.get().alwaysApplyingWhenNonNull();
map.from(this.serverProperties::getPort).to(factory::setPort);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getAddress).to(factory::setAddress);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getContextPath)
.to(factory::setContextPath);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getApplicationDisplayName)
.to(factory::setDisplayName);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getSession).to(factory::setSession);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getSsl).to(factory::setSsl);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getJsp).to(factory::setJsp);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getCompression).to(factory::setCompression);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getHttp2).to(factory::setHttp2);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getServerHeader).to(factory::setServerHeader);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getContextParameters)
.to(factory::setInitParameters);
}
}</configurableservletwebserverfactory>
2.3. ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer : WebServerFactoryCustomizer applique les propriétés ServerProperties au serveur Web Tomcat.
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer
implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<tomcatservletwebserverfactory>, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
@Override
public void customize(TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory) {
ServerProperties.Tomcat tomcatProperties = this.serverProperties.getTomcat();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(tomcatProperties.getAdditionalTldSkipPatterns())) {
factory.getTldSkipPatterns()
.addAll(tomcatProperties.getAdditionalTldSkipPatterns());
}
if (tomcatProperties.getRedirectContextRoot() != null) {
customizeRedirectContextRoot(factory,
tomcatProperties.getRedirectContextRoot());
}
if (tomcatProperties.getUseRelativeRedirects() != null) {
customizeUseRelativeRedirects(factory,
tomcatProperties.getUseRelativeRedirects());
}
}
}</tomcatservletwebserverfactory>
3. Avec TomcatServletWebServerFactory, cela équivaut à avoir l'entrée au chargement de Spring
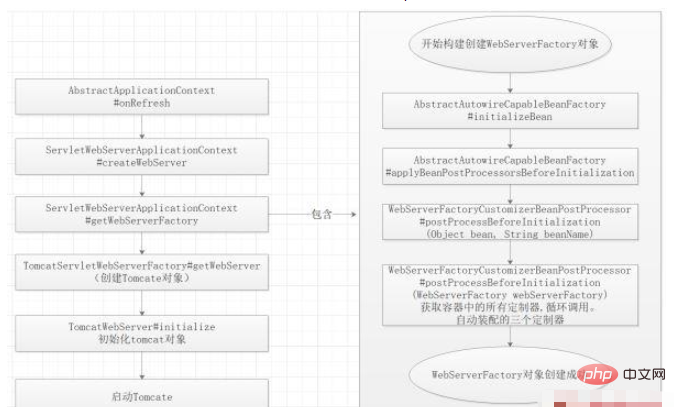
Utilisez AbstractApplicationContext#onReFresh() pour conduire Tomcat à démarrer dans le conteneur IOC, puis exécutez d'autres étapes du conteneur IOC.
Nous pouvons observer tout le cycle de vie du chargement de Tomcat à travers des points d'arrêt, ainsi que le processus de chargement des trois personnalisateurs.
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
//设置是否自动启动
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
//创建Tomcat引擎
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
//刷新上下文
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//准备启动
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
TomcatWebServer.logger
.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource())
&& Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(),
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
Remarques : Dans ce processus, nous devons comprendre le cycle de vie du Bean Tomcat. Les trois personnalisateurs sont tous chargés dans le processus BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar (post-processeur Bean)
Méthode de construction-->Bean post ; Définition du processeurAvant-->InitializingBean-->init-method-->Bean post-processorAfter
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//构造方法
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
......
return exposedObject;
}
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//Bean后置处理器Before
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//Bean后置处理器After
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}</object>Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Pourquoi ne puis-je pas charger des images dans mon fichier JAR exporté depuis Eclipse ?
- Comment effectuer efficacement des opérations d'intersection et d'union sur des ArrayLists Java ?
- Comment puis-je sérialiser et désérialiser des objets Java en tableaux d'octets ?
- Analyse approfondie des méthodes objet en Java : attendre et notifier
- Utilisation du super mot-clé en Java

