Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Analyse du code source Java FutureTask et détails d'utilisation
Analyse du code source Java FutureTask et détails d'utilisation
- PHPzavant
- 2023-04-23 23:37:051175parcourir
Comprenez ce qu'est FutureTask ?
FutureTask est un calcul asynchrone annulable.
FutureTask fournit l'implémentation de base de Future. Vous pouvez appeler des méthodes pour démarrer et annuler un calcul, demander si le calcul est terminé et obtenir les résultats du calcul. FutureTask提供了对Future的基本实现,可以调用方法去开始和取消一个计算,可以查询计算是否完成,并且获取计算结果。
FutureTask只能在计算完成后获取到计算结果,一旦计算完成,将不能重启或者取消,除非调用runAndReset方法。
FutureTask除了实现了Future接口以外,还实现了Runnable接口,因此FutureTask是可以交由线程池的Executor执行,也可以直接使用一个异步线程调用执行(futureTask.run())。
FutureTask 是如何实现的呢?
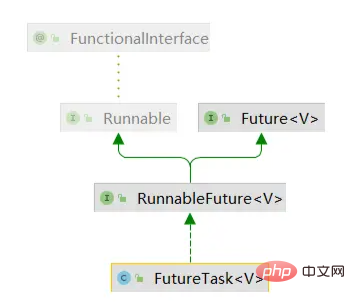
首先,我们看一下FutureTask类的继承结构,如下图,它实现的是RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture继承自Future和函数式接口Runnable,所以说FutureTask本质就是一个可运行的Future。
Future 接口约定了一些异步计算类必须要实现的功能,源码如下:
package java.util.concurrent;
public interface Future<V> {
/**
* 尝试取消任务的执行,并返回取消结果。
* 参数mayInterruptIfRunning:是否中断线程。
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
/**
* 判断任务是否被取消(正常结束之前被被取消返回true)
*/
boolean isCancelled();
/**
* 判断当前任务是否执行完毕,包括正常执行完毕、执行异常或者任务取消。
*/
boolean isDone();
/**
* 获取任务执行结果,任务结束之前会阻塞。
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* 在指定时间内尝试获取执行结果。若超时则抛出超时异常TimeoutException
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}Runnable 接口我们都很熟悉,他就是一个函数式接口,我们常用其创建一个线程。
package java.lang;
?
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
? ?
? ?public abstract void run();
}FutureTask就是一个将要被执行的任务,它包含了以上接口具体的实现,FutureTask内部定义了任务的状态state和一些状态的常量,它的内部核心是一个Callable callable,我们通过构造函数可以传入callable或者是runnable,最后都会内部转为callable,因为我们需要获取异步任务的执行结果,只有通过Callable创建的线程才会返回结果。
我们可以通过此时的状态判断Future中isCancelled(),isDone()的返回结果。
以下为FutureTask源码,内含核心源码分析注释
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
/**
* 任务的运行状态
*/
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0; // 新建
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; // 完成
private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 正常
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 异常
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 取消
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 中断中
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 中断的
private Callable<V> callable;
/**
* 返回结果
*/
private Object outcome;
private volatile Thread runner;
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
...
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW;
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW;
}
public boolean isCancelled() {
return state >= CANCELLED;
}
public boolean isDone() {
return state != NEW;
}
/*
* 取消任务实现
* 如果任务还没有启动就调用了cancel(true),任务将永远不会被执行。
* 如果任务已经启动,参数mayInterruptIfRunning将决定任务是否应该中断执行该任务的线程,以尝试中断该任务。
* 如果任务任务已经取消、已经完成或者其他原因不能取消,尝试将失败。
*/
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!(state == NEW &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,
mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally { // final state
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();
}
return true;
}
/*
* 等待获取结果
* 获取当前状态,判断是否执行完成。并且判断时间是否超时
* 如果任务没有执行完成,就阻塞等待完成,若超时抛出超时等待异常。
*/
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
/*
* 等待获取结果
* 获取当前状态,判断是否执行完成。
* 如果任务没有执行完成,就阻塞等待完成。
*/
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
/**
* 根据状态判断返回结果还是异常
*/
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
protected void done() { }
/**
* 设置结果借助CAS确认状态是否完成状态
*/
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/**
* 设置异常,当运行完成出现异常,设置异常状态
*/
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/*
* 执行callable获取结果,或者异常
* 判断状态是不是启动过的,如果是新建才可以执行run方法
*/
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
runner = null;
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
/**
* 重新执行
*/
protected boolean runAndReset() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return false;
boolean ran = false;
int s = state;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
c.call(); // don't set result
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
setException(ex);
}
}
} finally {
runner = null;
s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
return ran && s == NEW;
}
/*
* 处理可能取消的中断
*/
private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {
if (s == INTERRUPTING)
while (state == INTERRUPTING)
Thread.yield();
}
static final class WaitNode {
volatile Thread thread;
volatile WaitNode next;
WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); }
}
/**
* 移除并唤醒所有等待线程,执行done,置空callable
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
/**
* 等待完成
* 首先判断是否超时
* 处理中断的,然后处理异常状态的,处理完成的...
*/
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
/**
* 去除等待
*/
private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {
if (node != null) {
node.thread = null;
retry:
for (;;) { // restart on removeWaiter race
for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {
s = q.next;
if (q.thread != null)
pred = q;
else if (pred != null) {
pred.next = s;
if (pred.thread == null) // check for race
continue retry;
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q, s))
continue retry;
}
break;
}
}
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long runnerOffset;
private static final long waitersOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = FutureTask.class;
stateOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("state"));
runnerOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("runner"));
waitersOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("waiters"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}FutureTask 运行流程
一般来说,我们可以认为FutureTask具有以下三种状态:
未启动:新建的FutureTask,在run()没执行之前,FutureTask处于未启动状态。
private static final int NEW = 0; // 新建
已启动:FutureTask对象的run方法启动并执行的过程中,FutureTask处于已启动状态。
已完成:FutureTask正常执行结束,或者FutureTask
Une fois le calcul terminé, il ne peut pas être redémarré ou annulé à moins que la méthode runAndReset ne soit appelée.
En plus d'implémenter l'interface Future, FutureTask implémente également l'interface Runnable, donc FutureTask peut être exécuté par l'exécuteur du pool de threads, ou il peut être exécuté directement à l'aide d'un appel de thread asynchrone ( futureTask.run( )).
Tout d'abord, examinons la structure d'héritage de la classe FutureTask, comme indiqué ci-dessous. Elle implémente l'interface RunnableFuture et RunnableFuture. hérite de l'interface Future et Functional Runnable, donc FutureTask est essentiellement un Future exécutable.
 🎜🎜🎜Future interface convention Nous connaissons tous l'interface
🎜🎜🎜Future interface convention Nous connaissons tous l'interface Runnable . C'est une interface fonctionnelle, et nous l'utilisons souvent pour créer un thread. 🎜private static final int COMPLETING = 1; // 完成 private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 完成后正常设置结果 private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 完成后异常设置异常 private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 执行取消 private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 中断中 private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 中断的🎜FutureTask est une tâche à exécuter. Elle contient l'implémentation spécifique de l'interface ci-dessus. FutureTask définit en interne l'état de la tâche et certaines constantes d'état. Son noyau interne est un callable callable, que l'on peut passer par le constructeur. La saisie de callable ou runnable sera finalement convertie en callable en interne, car nous devons obtenir les résultats d'exécution des tâches asynchrones, et seuls les threads créés via Callable renverront les résultats. 🎜🎜Nous pouvons juger les résultats de retour de
isCancelled() et isDone() dans Future à travers l'état actuel. 🎜🎜🎜Ce qui suit est le code source de FutureTask, y compris les annotations d'analyse du code source principal🎜🎜FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return sum();
}
});
new Thread(task).stat();
Integer result = task.get();🎜Processus en cours d'exécution de FutureTask🎜🎜🎜De manière générale, nous pouvons considérer FutureTask comme ayant les trois états suivants : 🎜🎜🎜🎜Non démarré : 🎜 Nouvelle FutureTask, avant l'exécution de run(), FutureTask n'est pas démarrée. 🎜FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return sum();
}
});
Executors.newCachedThreadPool().submit(task);
Integer result = task.get();🎜🎜Started🎜 : Lorsque la méthode d'exécution de l'objet FutureTask est démarrée et exécutée, la FutureTask est dans l'état démarré. 🎜🎜🎜Completed : 🎜FutureTask se termine normalement, ou l'exécution de FutureTask est annulée (méthode Cancel de l'objet FutureTask), ou la méthode d'exécution de l'objet FutureTask lève une exception et se termine par un statut Complete. . 🎜rrreee🎜Utilisation de FutureTask🎜🎜🎜Utilisez-en un (créez directement un nouvel appel de thread) : 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜Utilisez-en deux (à utiliser en combinaison avec un pool de threads)🎜🎜rrreeeCe qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

