Maison >Périphériques technologiques >IA >Python Deep Learning 18-DeepDream d'apprentissage profond génératif
Python Deep Learning 18-DeepDream d'apprentissage profond génératif
- WBOYavant
- 2023-04-16 21:34:011711parcourir
Introduction à DeepDream
DeepDream est une technologie de modification d'image artistique, principalement basée sur le réseau neuronal convolutif formé CNN pour générer des images.
Lors de la génération d'images, le réseau neuronal est gelé, c'est-à-dire que les poids du réseau ne sont plus mis à jour, seules les images d'entrée doivent être mises à jour. Les réseaux convolutifs pré-entraînés couramment utilisés incluent Inception de Google, le réseau VGG et le réseau ResNet, etc.
Étapes de base de DeePDream :
- Obtenir l'image d'entrée
- Entrez l'image dans le réseau et obtenez la valeur de sortie du neurone que vous souhaitez visualiser
- Calculez le gradient de la valeur de sortie du neurone pour chaque pixel de l'image
- Utilisez la descente de gradient pour mettre à jour continuellement l'image
Répétez les étapes 2, 3 et 4 jusqu'à ce que les conditions définies soient remplies
Voici le processus général d'utilisation de Keras pour implémenter DeepDream :
Utilisation de Keras pour implémenter DeepDream
Obtenez la photo de test
Dans [1] :
# ---------------
from tensorflow import keras
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
base_image_path = keras.utils.get_file(
"coast.jpg",
origin="https://img-datasets.s3.amazonaws.com/coast.jpg")
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(keras.utils.load_img(base_image_path))
plt.show()

Ce ci-dessus est une photo du littoral fournie avec Keras. Voici les changements apportés à cette image.
Préparez le modèle pré-entraîné InceptionV3
Dans [2] :
# 使用Inception V3实现 from keras.applications import inception_v3 # 使用预训练的ImageNet权重来加载模型 model = inception_v3.InceptionV3(weights="imagenet", # 构建不包含全连接层的Inceptino include_top=False) Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/keras-applications/inception_v3/inception_v3_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5 87916544/87910968 [==============================] - 74s 1us/step 87924736/87910968 [==============================] - 74s 1us/step
Dans [3] :
model.summary()
Définir la configuration de DeepDream
Dans [4] :
# 层的名称 + 系数:该层对需要最大化的损失的贡献大小
layer_settings = {"mixed4":1.0,
"mixed5":1.5,
"mixed6":2.0,
"mixed7":2.5}
outputs_dict = dict(
[
(layer.name, layer.output) # 层的名字 + 该层的输出
for layer in [model.get_layer(name) for name in layer_settings.keys()]
]
)
outputs_dictOut[4] :
{'mixed4': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, None, None, 768) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'mixed4')>,
'mixed5': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, None, None, 768) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'mixed5')>,
'mixed6': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, None, None, 768) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'mixed6')>,
'mixed7': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, None, None, 768) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'mixed7')>} Dans [5]:
# 特征提取 feature_extractor = keras.Model(inputs=model.inputs, outputs=outputs_dict) feature_extractor
Out[5]:
<keras.engine.functional.Functional at 0x15b5ff0d0>
Perte de calcul
Dans [6]:
def compute_loss(image): features = feature_extractor(image)# 特征提取 loss = tf.zeros(shape=())# 损失初始化 for name in features.keys():# 遍历层 coeff = layer_settings[name] # 某个层的系数 activation = features[name]# 某个层的激活函数 #为了避免出现边界伪影,损失中仅包含非边界的像素 loss += coeff * tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(activation[:, 2:-2, 2:-2, :])) # 将该层的L2范数添加到loss中; return loss
Processus d'ascension de dégradé
Dans [7]:
import tensorflow as tf
@tf.function
def gradient_ascent_step(image, lr): # lr--->learning_rate学习率
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(image)
loss = compute_loss(image)# 调用计算损失方法
grads = tape.gradient(loss, image)# 梯度更新
grads = tf.math.l2_normalize(grads)
image += lr * grads
return loss, image
def gradient_ascent_loop(image, iterations, lr, max_loss=None):
for i in range(iterations):
loss, image = gradient_ascent_step(image, lr)
if max_loss is not None and loss > max_loss:
break
print(f"第{i}步的损失值是{loss:.2f}")
return imageGénération d'image
np. Utilisation de expand_dims (Ajout personnel)
In [8]:
import numpy as np array = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]] ) array
Out[8]:
array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
In [9]:
array.shape
Out[9]:
(2, 3)
In [10]:
array1 = np.expand_dims(array,axis=0) array1
Out[ 10] :
array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]])
Dans [11]:
array1.shape
Sortie[11]:
(1, 2, 3)
Dans [12]:
array2 = np.expand_dims(array,axis=1) array2
Out[12]:
array([[[1, 2, 3]], [[4, 5, 6]]])
Dans [13]:
array2.shape
Out[13] :
(2, 1, 3)
In [14]:
array3 = np.expand_dims(array,axis=-1) array3
Out[14]:
array([[[1], [2], [3]], [[4], [5], [6]]])
In [15]:
array3.shape
Out[15]:
(2, 3, 1)
fonction np.clip (ajout personnel)
np.clip( array, min(array), max(array), out=None):
In [16 ] :
array = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6]) np.clip(array, 2, 5)# 输出长度和原数组相同
Out[16]:
array([2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5])
In [17]:
array = np.arange(18).reshape((6,3)) array
Out[17]:
array([[ 0,1,2], [ 3,4,5], [ 6,7,8], [ 9, 10, 11], [12, 13, 14], [15, 16, 17]])
In [18]:
np.clip(array, 5, 15)
Out[18]:
array([[ 5,5,5], [ 5,5,5], [ 6,7,8], [ 9, 10, 11], [12, 13, 14], [15, 15, 15]])
Paramètres
In [19 ]:
step = 20.#梯度上升的步长 num_octave = 3# 运行梯度上升的尺度个数 octave_scale = 1.4# 两个尺度间的比例大小 iterations = 30# 在每个尺度上运行梯度上升的步数 max_loss = 15.# 损失值若大于15,则中断梯度上升过程
prétraitement de l'image
Dans [20]:
import numpy as np
def preprocess_image(image_path):# 预处理
img = keras.utils.load_img(image_path)# 导入图片
img = keras.utils.img_to_array(img)# 转成数组
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)# 增加数组维度;见上面解释(x,y) ---->(1,x,y)
img = keras.applications.inception_v3.preprocess_input(img)
return img
def deprocess_image(img):# 图片压缩处理
img = img.reshape((img.shape[1], img.shape[2], 3))
img /= 2.0
img += 0.5
img *= 255.
# np.clip:截断功能,保证数组中的取值在0-255之间
img = np.clip(img, 0, 255).astype("uint8")
return imgimage générée
Dans [21]:
# step = 20.#梯度上升的步长 # num_octave = 3# 运行梯度上升的尺度个数 # octave_scale = 1.4# 两个尺度间的比例大小 # iterations = 30# 在每个尺度上运行梯度上升的步数 # max_loss = 15.0# 损失值若大于15,则中断梯度上升过程 original_img = preprocess_image(base_image_path)# 预处理函数 original_shape = original_img.shape[1:3] print(original_img.shape)# 四维图像 print(original_shape)# 第2和3维度的值 (1, 900, 1200, 3) (900, 1200)
Dans [22]:
successive_shapes = [original_shape]
for i in range(1, num_octave):
shape = tuple([int(dim / (octave_scale ** i)) for dim in original_shape])
successive_shapes.append(shape)
successive_shapes = successive_shapes[::-1]# 翻转
shrunk_original_img = tf.image.resize(original_img, successive_shapes[0])
img = tf.identity(original_img)
for i, shape in enumerate(successive_shapes):
print(f"Processing octave {i} with shape {shape}")
# resize
img = tf.image.resize(img, shape)
img = gradient_ascent_loop(# 梯度上升函数调用
img,
iteratinotallow=iterations,
lr=step,
max_loss=max_loss
)
# resize
upscaled_shrunk_original_img = tf.image.resize(shrunk_original_img, shape)
same_size_original = tf.image.resize(original_img, shape)
lost_detail = same_size_original - upscaled_shrunk_original_img
img += lost_detail
shrunk_original_img = tf.image.resize(original_img, shape)
keras.utils.save_img("dream.png", deprocess_image(img.numpy()))Le résultat est :
Processing octave 0 with shape (459, 612) 第0步的损失值是0.80 第1步的损失值是1.07 第2步的损失值是1.44 第3步的损失值是1.82 ...... 第26步的损失值是11.44 第27步的损失值是11.72 第28步的损失值是12.03 第29步的损失值是12.49
En même temps , une nouvelle image est générée localement Photo, jetez un oeil à l'effet :
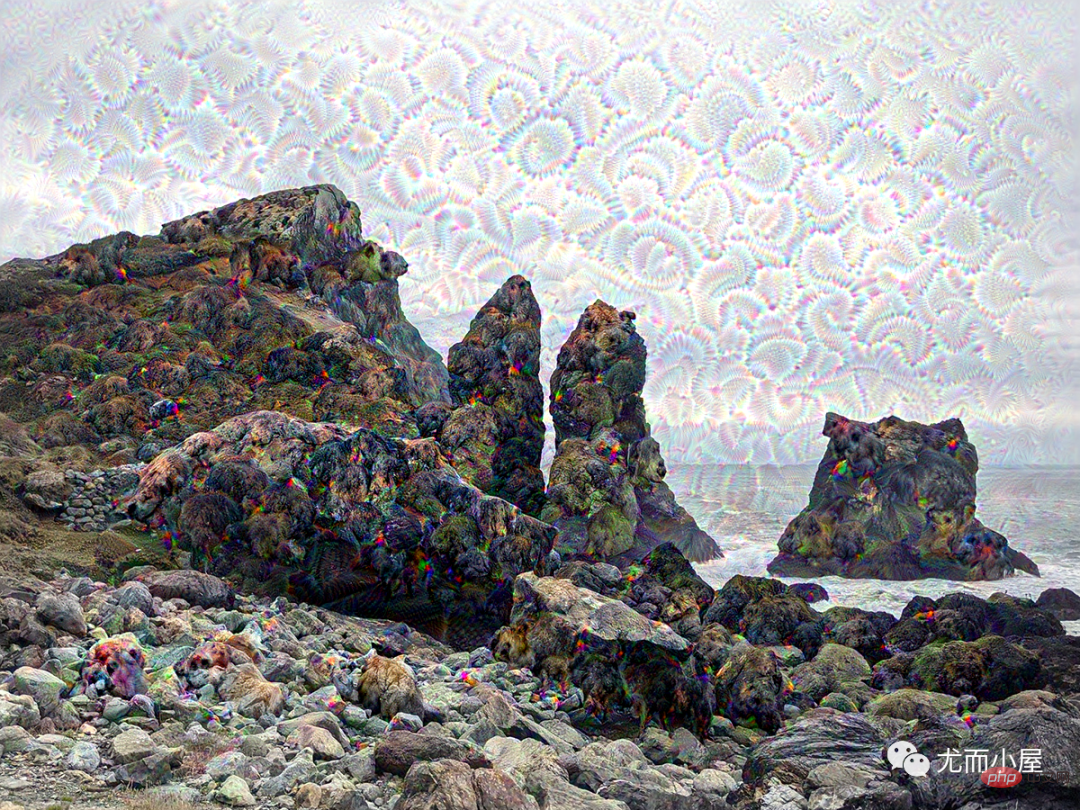

Regarde l'image originale : En comparaison, la nouvelle image fait un peu rêver !

Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Tendances technologiques à surveiller en 2023
- Comment l'intelligence artificielle apporte un nouveau travail quotidien aux équipes des centres de données
- L'intelligence artificielle ou l'automatisation peuvent-elles résoudre le problème de la faible efficacité énergétique des bâtiments ?
- Co-fondateur d'OpenAI interviewé par Huang Renxun : les capacités de raisonnement de GPT-4 n'ont pas encore atteint les attentes
- Bing de Microsoft surpasse Google en termes de trafic de recherche grâce à la technologie OpenAI

