Maison >base de données >Redis >Un article pour parler des opérations d'expiration et des stratégies d'expiration dans Redis
Un article pour parler des opérations d'expiration et des stratégies d'expiration dans Redis
- 青灯夜游avant
- 2022-02-09 10:12:372596parcourir
Cet article vous présentera les opérations d'expiration et les stratégies d'expiration dans Redis, présentera les quatre méthodes de définition du délai d'expiration dans Redis, les clés expirées en persistance, le processus d'exécution des clés expirées, etc. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile !

S'il n'y a pas de notion d'expiration dans Redis, cela signifie que toutes les clés que nous écrivons seront toujours enregistrées dans Redis tant qu'elles ne le sont pas activement supprimé Et Redis est une base de données basée sur la mémoire et l'espace mémoire est très limité. [Recommandations associées : Tutoriel vidéo Redis]Redis 中没有过期这个概念,这就意味着我们所有写入的键只要不主动删除就会一直保存在 Redis 中,而 Redis 又是一个基于内存的数据库,内存空间是非常有限的。【相关推荐:Redis视频教程】
过期操作
过期设置
Redis 中设置过期时间主要通过以下四种方式:
-
expire key seconds:设置key在 n 秒后过期。 -
pexpire key milliseconds:设置key在 n 毫秒后过期。 -
expireat key timestamp:设置key在某个时间戳(精确到秒)之后过期。 -
pexpireat key millisecondsTimestamp:设置key在某个时间戳(精确到毫秒)之后过期。
可用命令 ttl key (以秒为单位)或 pttl key (以毫秒为单位)来查看 key 还有多久过期。
Redis 可以使用 time 命令查询当前时间的时间戳(精确到秒)。
字符串中几个直接操作过期时间的方法,如下列表:
-
set key value ex seconds:设置键值对的同时指定过期时间(精确到秒)。 -
set key value px milliseconds:设置键值对的同时指定过期时间(精确到毫秒)。 -
setex key seconds valule:设置键值对的同时指定过期时间(精确到秒)。
移除过期时间
使用命令: persist key 可以移除键值的过期时间。-1 表示永不过期。
Java 实现过期操作
使用 Jedis 来实现对 Redis 的操作,代码:
public class TTLTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建 Redis 连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx", 6379);
// 设置 Redis 密码(如果没有密码,此行可省略)
jedis.auth("xxx");
// 存储键值对(默认情况下永不过期)
jedis.set("k", "v");
// 查询 TTL(过期时间)
Long ttl = jedis.ttl("k");
// 打印过期日志
// 过期时间:-1
System.out.println("过期时间:" + ttl);
// 设置 100s 后过期
jedis.expire("k", 100);
// 等待 1s 后执行
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 打印过期日志
// 执行 expire 后的 TTL=99
System.out.println("执行 expire 后的 TTL=" + jedis.ttl("k"));
}
}更多过期操作方法,如下列表:
-
pexpire(String key, long milliseconds):设置 n 毫秒后过期。 -
expireAt(String key, long unixTime):设置某个时间戳后过期(精确到秒)。 -
pexpireAt(String key, long millisecondsTimestamp):设置某个时间戳后过期(精确到毫秒)。 -
persist(String key):移除过期时间。
public class TTLTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建 Redis 连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx", 6379);
// 设置 Redis 密码(如果没有密码,此行可省略)
jedis.auth("xxx");
// 存储键值对(默认情况下永不过期)
jedis.set("k", "v");
// 查询 TTL(过期时间)
Long ttl = jedis.ttl("k");
// 打印过期日志
System.out.println("过期时间:" + ttl);
// 设置 100s 后过期
jedis.expire("k", 100);
// 等待 1s 后执行
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 打印过期日志
System.out.println("执行 expire 后的 TTL=" + jedis.ttl("k"));
// 设置 n 毫秒后过期
jedis.pexpire("k", 100000);
// 设置某个时间戳后过期(精确到秒)
jedis.expireAt("k", 1573468990);
// 设置某个时间戳后过期(精确到毫秒)
jedis.pexpireAt("k", 1573468990000L);
// 移除过期时间
jedis.persist("k");
}
}持久化中的过期键
RDB 中的过期键
RDB 文件分为两个阶段,RDB 文件生成阶段和加载阶段。
1. RDB 文件生成
RDB 加载分为以下两种情况:
- 如果
Redis是主服务器运行模式的话,在载入RDB文件时,程序会对文件中保存的键进行检查,过期键不会被载入到数据库中。所以过期键不会对载入RDB文件的主服务器造成影响; - 如果
Redis是从服务器运行模式的话,在载入RDB文件时,不论键是否过期都会被载入到数据库中。但由于主从服务器在进行数据同步时,从服务器的数据会被清空。所以一般来说,过期键对载入RDB文件的从服务器也不会造成影响。
RDB 文件加载的源码可以在 rdb.c 文件的 rdbLoad() 函数中找到,源码所示:
/* Check if the key already expired. This function is used when loading
* an RDB file from disk, either at startup, or when an RDB was
* received from the master. In the latter case, the master is
* responsible for key expiry. If we would expire keys here, the
* snapshot taken by the master may not be reflected on the slave.
*
* 如果服务器为主节点的话,
* 那么在键已经过期的时候,不再将它们关联到数据库中去
*/
if (server.masterhost == NULL && expiretime != -1 && expiretime < now) {
decrRefCount(key);
decrRefCount(val);
// 跳过
continue;
}AOF 中的过期键
1. AOF 文件写入
当 Redis 以 AOF 模式持久化时,如果数据库某个过期键还没被删除,那么 AOF 文件会保留此过期键,当此过期键被删除后,Redis 会向 AOF 文件追加一条 DEL 命令来显式地删除该键值。
2. AOF 重写
执行 AOF 重写时,会对 Redis 中的键值对进行检查已过期的键不会被保存到重写后的 AOF 文件中,因此不会对 AOF
Opération d'expiration
Paramètres d'expiration
Redis Il existe principalement quatre façons de définir le délai d'expiration : 🎜-
touche d'expiration secondes: définissez laclépour qu'elle expire après n secondes. -
pexpire key milliseconds: définit lakeypour qu'elle expire après n millisecondes. -
horodatage de la clé d'expiration: définissezclépour qu'elle expire après un certain horodatage (précis à la seconde près). -
pexpireat key millisecondsTimestamp: définit laclépour qu'elle expire après un certain horodatage (précis en millisecondes).
ttl key (en secondes) ou pttl key (en millisecondes) pour afficher la key Comment combien de temps faut-il pour que le code> expire. 🎜🎜<code>Redis Vous pouvez utiliser la commande time pour interroger l'horodatage de l'heure actuelle (précis à la seconde près). 🎜🎜Plusieurs méthodes pour gérer directement le délai d'expiration dans les chaînes, comme indiqué ci-dessous : 🎜-
définir la valeur clé en secondes: définir la paire clé-valeur et spécifier le délai d'expiration (précis à secondes) ). -
définir la valeur clé px millisecondes: définissez la paire clé-valeur et spécifiez le délai d'expiration (précis en millisecondes). -
Valeur des secondes clés setex: définissez la paire clé-valeur et spécifiez le délai d'expiration (précis à la seconde près).
persist key pour supprimer le délai d'expiration de la valeur de la clé. -1 signifie n'expire jamais. 🎜🎜🎜🎜Java implémente les opérations d'expiration🎜🎜🎜🎜Utilisez Jedis pour implémenter les opérations sur Redis, code : 🎜/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* 数据库键空间,存放着所有的键值对 */
dict *expires; /* 键的过期时间 */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;🎜🎜Plus de méthodes d'opération d'expiration🎜, comme indiqué ci-dessous : 🎜-
pexpire(String key, long milliseconds): défini pour expirer après n millisecondes. -
expireAt(String key, long unixTime): Expire après avoir défini un certain horodatage (précis à la seconde près). -
pexpireAt(String key, long millisecondsTimestamp): Expire après avoir défini un certain horodatage (précis en millisecondes). -
persist(String key): supprime le délai d'expiration.
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
// 判断键是否过期
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
/* 删除过期键 */
// 增加过期键个数
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
// 传播键过期的消息
propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",key,db->id);
// server.lazyfree_lazy_expire 为 1 表示异步删除(懒空间释放),反之同步删除
return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
// 判断键是否过期
int keyIsExpired(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */
/* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
if (server.loading) return 0;
mstime_t now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime();
return now > when;
}
// 获取键的过期时间
long long getExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
dictEntry *de;
/* No expire? return ASAP */
if (dictSize(db->expires) == 0 ||
(de = dictFind(db->expires,key->ptr)) == NULL) return -1;
/* The entry was found in the expire dict, this means it should also
* be present in the main dict (safety check). */
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr) != NULL);
return dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
}🎜🎜🎜Clés expirées en persistance🎜🎜🎜🎜Clés expirées dans RDB🎜
🎜RDB Le fichier est divisé en deux étapes, l'étape de génération du fichier <code>RDB et l'étape de chargement. 🎜🎜🎜1. La génération de fichiers RDB🎜🎜🎜Le chargement de RDB est divisé selon les deux situations suivantes : 🎜- Si
Redisest le 🎜serveur principal🎜 mode de fonctionnement Si tel est le cas, lors du chargement du fichierRDB, le programme vérifiera les clés enregistrées dans le fichier et les clés expirées ne seront pas chargées dans la base de données. Par conséquent, la clé expirée n'affectera pas le serveur principal qui charge le fichierRDB; - Si
Redisest le mode d'exécution du serveur 🎜slave🎜, lorsque chargement Lors du chargement d'un fichierRDB, la clé sera chargée dans la base de données, qu'elle ait expiré ou non. Mais🎜lorsque les serveurs maître et esclave synchronisent les données, les données du serveur esclave seront effacées🎜. Donc, d'une manière générale, les clés expirées n'affecteront pas les serveurs esclaves chargeant les fichiersRDB.
RDB se trouve dans la fonction rdbLoad() du rdb.c code>. Le code source affiché : 🎜<pre class="brush:js;toolbar:false;">void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* 上次定期删除遍历到的数据库ID */
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* 上一次执行快速定期删除的时间点 */
int j, iteration = 0;
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL; // 每次定期删除,遍历的数据库的数量
long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;
if (clientsArePaused()) return;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
if (!timelimit_exit) return;
// ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 是快速定期删除的执行时长
if (start < last_fast_cycle + ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION*2) return;
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
// 慢速定期删除的执行时长
timelimit = 1000000*ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION; /* 删除操作的执行时长 */
long total_sampled = 0;
long total_expired = 0;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
int expired;
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
current_db++;
do {
// .......
expired = 0;
ttl_sum = 0;
ttl_samples = 0;
// 每个数据库中检查的键的数量
if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP;
// 从数据库中随机选取 num 个键进行检查
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl;
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
ttl = dictGetSignedInteger
// 过期检查,并对过期键进行删除
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
total_sampled++;
}
total_expired += expired;
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);
}
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
elapsed = ustime()-start;
if (elapsed > timelimit) {
timelimit_exit = 1;
server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;
break;
}
}
/* 每次检查只删除 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4 个过期键 */
} while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4);
}
// .......
}</pre><h4 data-id="heading-6">🎜Clés expirées dans AOF🎜</h4>🎜🎜1 écriture du fichier AOF🎜🎜🎜Quand <code>Rediscode> se termine par AOF est persistant, si une clé expirée dans la base de données n'a pas été supprimée, alors le fichier AOF conservera la clé expirée une fois expirée. la clé est supprimée, Redis ajoutera une commande DEL au fichier AOF pour supprimer explicitement la valeur de la clé. 🎜🎜🎜2. Réécriture AOF🎜🎜🎜Lors de la réécriture de AOF, les paires clé-valeur dans les Redi seront vérifiées. Les clés expirées ne seront pas enregistrées dans le fichier. fichier AOF réécrit, il n'aura donc aucun impact sur la réécriture AOF. 🎜🎜🎜🎜Clé expirée de la bibliothèque maître-esclave🎜🎜🎜当 Redis 运行在主从模式下时,从库不会进行过期扫描,从库对过期的处理是被动的。也就是即使从库中的 key 过期了,如果有客户端访问从库时,依然可以得到 key 对应的值,像未过期的键值对一样返回。
从库的过期键处理依靠主服务器控制,主库在 key 到期时,会在 AOF 文件里增加一条 del 指令,同步到所有的从库,从库通过执行这条 del 指令来删除过期的 key。
过期策略
在
Redis中我们可以给一些元素设置过期时间,那当它过期之后Redis是如何处理这些过期键呢?
过期键执行流程
Redis 之所以能知道那些键值过期,是因为在 Redis 中维护了一个字典,存储了所有设置了过期时间的键值,我们称之为过期字典。
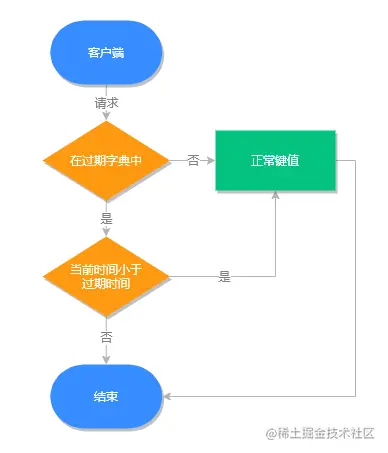
过期键源码分析
过期键存储在 redisDb 结构中,源代码在 src/server.h 文件中(基于 Redis 5):
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* 数据库键空间,存放着所有的键值对 */
dict *expires; /* 键的过期时间 */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;过期键数据结构如下图所示:
过期策略
Redis 会删除已过期的键值,以此来减少 Redis 的空间占用,但因为 Redis 本身是单线的,如果因为删除操作而影响主业务的执行就得不偿失了,为此 Redis 需要制定多个(过期)删除策略来保证正常执行的性能。
定时删除
在设置键值过期时间时,创建一个定时事件,当过期时间到达时,由事件处理器自动执行键的删除操作。
- 优点:保证内存可以被尽快地释放。
-
缺点:在
Redis高负载的情况下或有大量过期键需要同时处理时,会造成Redis服务器卡顿,影响主业务执行。
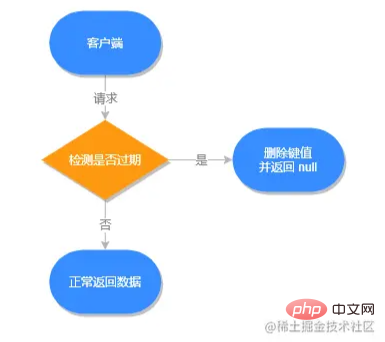
惰性删除
不主动删除过期键,每次从数据库获取键值时判断是否过期,如果过期则删除键值,并返回 null。
- 优点:因为每次访问时,才会判断过期键,所以此策略只会使用很少的系统资源。
- 缺点:系统占用空间删除不及时,导致空间利用率降低,造成了一定的空间浪费。
源码解析
惰性删除的源码位于 src/db.c 文件的 expireIfNeeded 方法中,源码如下:
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
// 判断键是否过期
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
/* 删除过期键 */
// 增加过期键个数
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
// 传播键过期的消息
propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",key,db->id);
// server.lazyfree_lazy_expire 为 1 表示异步删除(懒空间释放),反之同步删除
return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
// 判断键是否过期
int keyIsExpired(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */
/* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
if (server.loading) return 0;
mstime_t now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime();
return now > when;
}
// 获取键的过期时间
long long getExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
dictEntry *de;
/* No expire? return ASAP */
if (dictSize(db->expires) == 0 ||
(de = dictFind(db->expires,key->ptr)) == NULL) return -1;
/* The entry was found in the expire dict, this means it should also
* be present in the main dict (safety check). */
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr) != NULL);
return dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
}所有对数据库的读写命令在执行之前,都会调用 expireIfNeeded 方法判断键值是否过期,过期则会从数据库中删除,反之则不做任何处理。
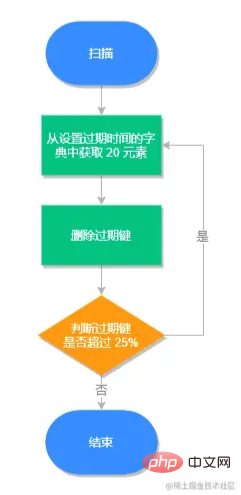
定期删除
每隔一段时间检查一次数据库,随机删除一些过期键。
Redis 默认每秒进行 10 次过期扫描,此配置可通过 Redis 的配置文件 redis.conf 进行配置,配置键为 hz 它的默认值是 hz 10。
注意:Redis 每次扫描并不是遍历过期字典中的所有键,而是采用随机抽取判断并删除过期键的形式执行的。
定期删除流程
从过期字典中随机取出 20 个键。
删除这 20 个键中过期的键。
如果过期
key的比例超过 25%,重复步骤 1。
同时为了保证过期扫描不会出现循环过度,导致线程卡死现象,算法还增加了扫描时间的上限,默认不会超过 25ms。
-
优点:通过限制删除操作的时长和频率,来减少删除操作对
Redis主业务的影响,同时也能删除一部分过期的数据减少了过期键对空间的无效占用。 - 缺点:内存清理方面没有定时删除效果好,同时没有惰性删除使用的系统资源少。
源码解析
定期删除的核心源码在 src/expire.c 文件下的 activeExpireCycle 方法中,源码如下:
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* 上次定期删除遍历到的数据库ID */
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* 上一次执行快速定期删除的时间点 */
int j, iteration = 0;
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL; // 每次定期删除,遍历的数据库的数量
long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;
if (clientsArePaused()) return;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
if (!timelimit_exit) return;
// ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 是快速定期删除的执行时长
if (start < last_fast_cycle + ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION*2) return;
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
// 慢速定期删除的执行时长
timelimit = 1000000*ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION; /* 删除操作的执行时长 */
long total_sampled = 0;
long total_expired = 0;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
int expired;
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
current_db++;
do {
// .......
expired = 0;
ttl_sum = 0;
ttl_samples = 0;
// 每个数据库中检查的键的数量
if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP;
// 从数据库中随机选取 num 个键进行检查
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl;
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
ttl = dictGetSignedInteger
// 过期检查,并对过期键进行删除
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
total_sampled++;
}
total_expired += expired;
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);
}
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
elapsed = ustime()-start;
if (elapsed > timelimit) {
timelimit_exit = 1;
server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;
break;
}
}
/* 每次检查只删除 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4 个过期键 */
} while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4);
}
// .......
}activeExpireCycle 方法在规定的时间,分多次遍历各个数据库,从过期字典中随机检查一部分过期键的过期时间,删除其中的过期键。
这个函数有两种执行模式,一个是快速模式一个是慢速模式,体现是代码中的 timelimit 变量,这个变量是用来约束此函数的运行时间的。快速模式下 timelimit 的值是固定的,等于预定义常量 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION,慢速模式下,这个变量的值是通过 1000000 * ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100 计算的。
Redis 使用的过期策略
Redis 使用的是惰性删除加定期删除的过期策略。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Une brève analyse du principe de la réplication maître-esclave du cluster dans Redis
- Une brève analyse du principe du mode sentinelle dans Redis
- Assurer la cohérence des doubles écritures entre MySQL et Redis
- Une brève analyse des modèles monothread et multithread dans Redis6
- Analyse du code source Redis et compréhension approfondie des fichiers Makefile
- Qu'est-ce qu'un verrou réentrant ? Explication détaillée de la façon dont Redis implémente les verrous de réentrance distribués


