Maison >base de données >tutoriel mysql >En savoir plus sur l'utilisation de group by dans MySql ? (Explication détaillée de l'utilisation)
En savoir plus sur l'utilisation de group by dans MySql ? (Explication détaillée de l'utilisation)
- 青灯夜游avant
- 2022-01-17 19:28:3424834parcourir
Comment utiliser group by dans MySql ? L'article suivant vous donnera une analyse approfondie de l'utilisation de group by. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile.

Dans le développement quotidien, nous utilisons souvent group by. Chers amis, savez-vous comment fonctionne le group by ? Quelle est la différence entre grouper par et avoir ? Quelle est l'idée d'optimisation de group by ? Quels sont les problèmes auxquels il faut prêter attention lors de l'utilisation de group by ? Dans cet article, nous apprendrons avec vous à surmonter le group by~group by。亲爱的小伙伴,你是否知道group by的工作原理呢?group by和having有什么区别呢?group by的优化思路是怎样的呢?使用group by有哪些需要注意的问题呢?本文将跟大家一起来学习,攻克group by~
- 使用group by的简单例子
- group by 工作原理
- group by + where 和 group by + having的区别
- group by 优化思路
- group by 使用注意点
- 一个生产慢SQL如何优化
【相关推荐:mysql视频教程】
1. 使用group by的简单例子
group by一般用于分组统计,它表达的逻辑就是根据一定的规则,进行分组。我们先从一个简单的例子,一起复习一下哈。
假设用一张员工表,表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `staff` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id', `id_card` varchar(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '身份证号码', `name` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `age` int(4) NOT NULL COMMENT '年龄', `city` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '城市', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=15 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工表';
表存量的数据如下:
我们现在有这么一个需求:统计每个城市的员工数量。对应的 SQL 语句就可以这么写:
select city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city;
执行结果如下:

这条SQL语句的逻辑很清楚啦,但是它的底层执行流程是怎样的呢?
2. group by 原理分析
2.1 explain 分析
我们先用explain查看一下执行计划
explain select city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city;

- Extra 这个字段的
Using temporary表示在执行分组的时候使用了临时表 - Extra 这个字段的
Using filesort表示使用了排序
group by 怎么就使用到临时表和排序了呢?我们来看下这个SQL的执行流程
2.2 group by 的简单执行流程
explain select city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city;
我们一起来看下这个SQL的执行流程哈
- 创建内存临时表,表里有两个字段
city和num; - 全表扫描
staff的记录,依次取出city = 'X'的记录。
- 判断临时表中是否有为 city='X'的行,没有就插入一个记录 (X,1);
- 如果临时表中有city='X'的行的行,就将x 这一行的num值加 1;
- 遍历完成后,再根据字段
city做排序,得到结果集返回给客户端。
这个流程的执行图如下:

临时表的排序是怎样的呢?
就是把需要排序的字段,放到sort buffer,排完就返回。在这里注意一点哈,排序分全字段排序和rowid排序
- 如果是
全字段排序,需要查询返回的字段,都放入sort buffer,根据排序字段排完,直接返回- 如果是
rowid排序,只是需要排序的字段放入sort buffer,然后多一次回表操作,再返回。- 怎么确定走的是全字段排序还是rowid 排序排序呢?由一个数据库参数控制的,
max_length_for_sort_data
- Un exemple simple d'utilisation du group by
- le principe de fonctionnement du group by
- group by +where et group La différence entre by + have
1. Utiliser le groupe Un exemple simple de by
🎜group by est généralement utilisé pour regrouper les statistiques. La logique qu'il exprime est de grouper selon certaines règles . Passons-le en revue avec un exemple simple. 🎜🎜Supposons qu'une table d'employés soit utilisée. La structure de la table est la suivante : 🎜select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age> 30 group by city; //加索引 alter table staff add index idx_age (age);🎜Les données d'inventaire de la table sont les suivantes : 🎜🎜
 🎜🎜Nous avons désormais un tel besoin : Compter le nombre d'employés dans chaque ville. L'instruction SQL correspondante peut s'écrire ainsi : 🎜
🎜🎜Nous avons désormais un tel besoin : Compter le nombre d'employés dans chaque ville. L'instruction SQL correspondante peut s'écrire ainsi : 🎜explain select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age> 30 group by city;🎜Le résultat de l'exécution est le suivant : 🎜🎜
 🎜🎜La logique de cette instruction SQL est très claire, mais quel est son processus d'exécution sous-jacent ? 🎜
🎜🎜La logique de cette instruction SQL est très claire, mais quel est son processus d'exécution sous-jacent ? 🎜2. Analyse de groupe par principe
2.1 Expliquer l'analyse
🎜 Utilisons d'abordexplain pour vérifier le plan d'exécution🎜select city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city having num >= 3;🎜
 🎜
🎜- Extra
Utilisation temporairede ce champ indique qu'une table temporaire est utilisée lors de l'exécution grouping 🎜 - Extra Le
Using filesortde ce champ indique l'utilisation du tri🎜🎜🎜group byComment utiliser letable temporaire et triée? Jetons un coup d'œil au processus d'exécution de ce SQL🎜2.2 Processus d'exécution simple du groupe par
select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age> 19 group by city having num >= 3;
🎜Jetons un coup d'œil au processus d'exécution de ce processus d'exécution SQL🎜- Créer une table de mémoire temporaire avec deux champs
cityetnum🎜 - Analyse complète de la table
; des enregistrements du personnel, retirez tour à tour les enregistrements de city = 'X'. 🎜
- Déterminez s'il y a une ligne avec city='X' dans la table temporaire. Sinon, insérez un enregistrement (X,1) ; >Si temporaire S'il y a une ligne avec city='X' dans le tableau, ajoutez 1 à la valeur numérique de la ligne x 🎜🎜
- Une fois le parcours terminé, alors selon ; au champ
ville code>Faites <strong>trier</strong> et obtenez le jeu de résultats et renvoyez-le au client. 🎜
 🎜🎜Qu'est-ce que le tri des tables temporaires ? 🎜
🎜🎜Qu'est-ce que le tri des tables temporaires ? 🎜🎜Placez simplement les champs qui doivent être triés dans le tampon de tri et revenez après le tri. Une chose à noter ici est que le tri est divisé en tri par champ complet et tri par ligne🎜
- S'il s'agit d'un
tri par champ complet, vous devez interroger. Les champs renvoyés sont placés dans untampon de tri, triés selon le champ de tri et renvoyés directement 🎜 - S'il s'agit d'un
tri Rowid, c'est juste nécessaire. Les champs triés sont placés dans untampon de tri, puis une autre opération de retour à la table est effectuée, puis renvoyée. 🎜 - Comment déterminer s'il faut utiliser le tri par champ complet ou le tri par rangée ? Contrôlé par un paramètre de base de données,
max_length_for_sort_data🎜🎜🎜🎜Les amis qui souhaitent en savoir plus sur le tri peuvent lire cet article. 🎜3. where 和 having的区别
- group by + where 的执行流程
- group by + having 的执行流程
- 同时有where、group by 、having的执行顺序
3.1 group by + where 的执行流程
有些小伙伴觉得上一小节的SQL太简单啦,如果加了where条件之后,并且where条件列加了索引呢,执行流程是怎样?
好的,我们给它加个条件,并且加个
idx_age的索引,如下:select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age> 30 group by city; //加索引 alter table staff add index idx_age (age);
再来expain分析一下:
explain select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age> 30 group by city;

从explain 执行计划结果,可以发现查询条件命中了
idx_age的索引,并且使用了临时表和排序Using index condition:表示索引下推优化,根据索引尽可能的过滤数据,然后再返回给服务器层根据where其他条件进行过滤。这里单个索引为什么会出现索引下推呢?explain出现并不代表一定是使用了索引下推,只是代表可以使用,但是不一定用了。大家如果有想法或者有疑问,可以加我微信讨论哈。
执行流程如下:
1、创建内存临时表,表里有两个字段
city和num;2、扫描索引树
idx_age,找到大于年龄大于30的主键ID3、通过主键ID,回表找到city = 'X'
- 判断临时表中是否有为 city='X'的行,没有就插入一个记录 (X,1);
- 如果临时表中有city='X'的行的行,就将x 这一行的num值加 1;
4、继续重复2,3步骤,找到所有满足条件的数据,
5、最后根据字段
city做排序,得到结果集返回给客户端。3.2 group by + having 的执行
如果你要查询每个城市的员工数量,获取到员工数量不低于3的城市,having可以很好解决你的问题,SQL酱紫写:
select city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city having num >= 3;
查询结果如下:

having称为分组过滤条件,它对返回的结果集操作。3.3 同时有where、group by 、having的执行顺序
如果一个SQL同时含有
where、group by、having子句,执行顺序是怎样的呢。比如这个SQL:
select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age> 19 group by city having num >= 3;
执行
where子句查找符合年龄大于19的员工数据group by子句对员工数据,根据城市分组。对
group by子句形成的城市组,运行聚集函数计算每一组的员工数量值;最后用
having子句选出员工数量大于等于3的城市组。
3.4 where + having 区别总结
-
having子句用于分组后筛选,where子句用于行条件筛选 -
having一般都是配合group by和聚合函数一起出现如(count(),sum(),avg(),max(),min()) -
where条件子句中不能使用聚集函数,而having子句就可以。 -
having只能用在group by之后,where执行在group by之前
4. 使用 group by 注意的问题
使用group by 主要有这几点需要注意:
-
group by一定要配合聚合函数一起使用嘛? -
group by的字段一定要出现在select中嘛 -
group by导致的慢SQL问题
4.1 group by一定要配合聚合函数使用嘛?
group by 就是分组统计的意思,一般情况都是配合聚合函数
如(count(),sum(),avg(),max(),min())一起使用。- count() 数量
- sum() 总和
- avg() 平均
- max() 最大值
- min() 最小值
如果没有配合聚合函数使用可以吗?
我用的是Mysql 5.7 ,是可以的。不会报错,并且返回的是,分组的第一行数据。
比如这个SQL:
select city,id_card,age from staff group by city;
查询结果是

大家对比看下,返回的就是每个分组的第一条数据

当然,平时大家使用的时候,group by还是配合聚合函数使用的,除非一些特殊场景,比如你想去重,当然去重用
distinct也是可以的。4.2 group by 后面跟的字段一定要出现在select中嘛。
不一定,比如以下SQL:
select max(age) from staff group by city;
执行结果如下:

分组字段
city不在select 后面,并不会报错。当然,这个可能跟不同的数据库,不同的版本有关吧。大家使用的时候,可以先验证一下就好。有一句话叫做,纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。4.3
<span style="font-size: 16px;">group by</span>导致的慢SQL问题到了最重要的一个注意问题啦,
group by使用不当,很容易就会产生慢SQL 问题。因为它既用到临时表,又默认用到排序。有时候还可能用到磁盘临时表。- 如果执行过程中,会发现内存临时表大小到达了上限(控制这个上限的参数就是
tmp_table_size),会把内存临时表转成磁盘临时表。 - 如果数据量很大,很可能这个查询需要的磁盘临时表,就会占用大量的磁盘空间。
这些都是导致慢SQL的x因素,我们一起来探讨优化方案哈。
5. group by的一些优化方案
从哪些方向去优化呢?
- 方向1: 既然它默认会排序,我们不给它排是不是就行啦。
- 方向2:既然临时表是影响group by性能的X因素,我们是不是可以不用临时表?
我们一起来想下,执行
group by语句为什么需要临时表呢?group by的语义逻辑,就是统计不同的值出现的个数。如果这个这些值一开始就是有序的,我们是不是直接往下扫描统计就好了,就不用临时表来记录并统计结果啦?- group by 后面的字段加索引
- order by null 不用排序
- 尽量只使用内存临时表
- 使用SQL_BIG_RESULT
5.1 group by 后面的字段加索引
如何保证
group by后面的字段数值一开始就是有序的呢?当然就是加索引啦。我们回到一下这个SQL
select city ,count(*) as num from staff where age= 19 group by city;
它的执行计划

如果我们给它加个联合索引
idx_age_city(age,city)alter table staff add index idx_age_city(age,city);
再去看执行计划,发现既不用排序,也不需要临时表啦。

加合适的索引是优化
group by最简单有效的优化方式。5.2 order by null 不用排序
并不是所有场景都适合加索引的,如果碰上不适合创建索引的场景,我们如何优化呢?
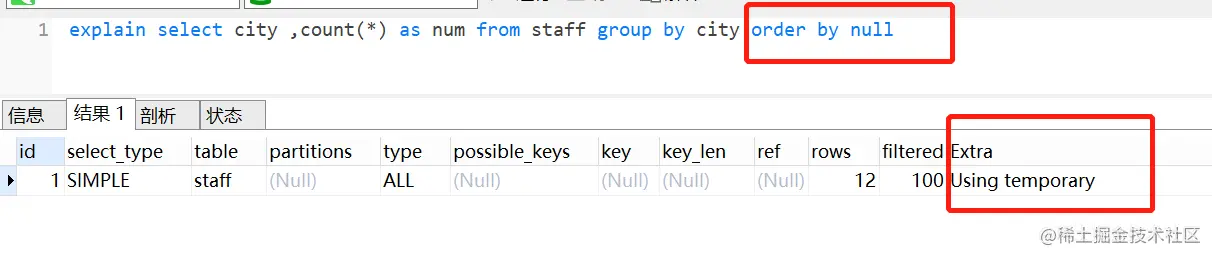
如果你的需求并不需要对结果集进行排序,可以使用
order by null。select city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city order by null
执行计划如下,已经没有
filesort啦
5.3 尽量只使用内存临时表
如果
group by需要统计的数据不多,我们可以尽量只使用内存临时表;因为如果group by 的过程因为数据放不下,导致用到磁盘临时表的话,是比较耗时的。因此可以适当调大tmp_table_size参数,来避免用到磁盘临时表。5.4 使用SQL_BIG_RESULT优化
如果数据量实在太大怎么办呢?总不能无限调大
tmp_table_size吧?但也不能眼睁睁看着数据先放到内存临时表,随着数据插入发现到达上限,再转成磁盘临时表吧?这样就有点不智能啦。因此,如果预估数据量比较大,我们使用
SQL_BIG_RESULT这个提示直接用磁盘临时表。MySQl优化器发现,磁盘临时表是B+树存储,存储效率不如数组来得高。因此会直接用数组来存示例SQl如下:
select SQL_BIG_RESULT city ,count(*) as num from staff group by city;
执行计划的
Extra字段可以看到,执行没有再使用临时表,而是只有排序执行流程如下:
初始化 sort_buffer,放入city字段;
扫描表staff,依次取出city的值,存入 sort_buffer 中;
扫描完成后,对 sort_buffer的city字段做排序
排序完成后,就得到了一个有序数组。
根据有序数组,统计每个值出现的次数。
6. 一个生产慢SQL如何优化
最近遇到个生产慢SQL,跟group by相关的,给大家看下怎么优化哈。
表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `staff` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id', `id_card` varchar(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '身份证号码', `name` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `status` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Y-已激活 I-初始化 D-已删除 R-审核中', `age` int(4) NOT NULL COMMENT '年龄', `city` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '城市', `enterprise_no` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '企业号', `legal_cert_no` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '法人号码', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=15 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工表';
查询的SQL是这样的:
select * from t1 where status = #{status} group by #{legal_cert_no}我们先不去探讨这个SQL的=是否合理。如果就是这么个SQL,你会怎么优化呢?有想法的小伙伴可以留言讨论哈,也可以加我微信加群探讨。如果你觉得文章那里写得不对,也可以提出来哈,一起进步,加油呀
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
- Une fois le parcours terminé, alors selon ; au champ
- Créer une table de mémoire temporaire avec deux champs
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Solution au mot de passe oublié MySQL : connectez-vous sans mot de passe et réinitialisez le mot de passe root
- Expliquez comment MySQL supprime les données en double
- Apprenez étape par étape à jouer avec MySQL binlog
- Comprenez-vous les variables, le contrôle de flux et les curseurs dans MySQL ?
- Parlons des comptes et des autorisations dans MySQL
- Exemple de partage de problèmes causés par l'horodatage MySQL 8.0


)