Maison >base de données >tutoriel mysql >Que faire si Mac MySQL est tronqué ?
Que faire si Mac MySQL est tronqué ?
- 藏色散人original
- 2021-12-21 15:10:531578parcourir
Solution au code tronqué Mac MySQL : 1. Recherchez et ouvrez le fichier my.cnf ; 2. Ajoutez le code comme "character-set-server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8...".

L'environnement d'exploitation de cet article : système macOS10.15, Mysql version 5.7.26, ordinateur macbook pro 2020.
Que faire si mac mysql est tronqué ?
Comment résoudre le problème des caractères tronqués dans MySQL sous mac
Cet article parle du traitement sous mac En fait, la méthode de traitement est la même. La version MySQL de mon ordinateur est 5.7.26-log
De nombreux messages sur Internet disent d'aller dans le répertoire /usr/local/mysql/support-files et de copier my-default.cnf dans /etc/my.cnf et puis modifiez-le de la même manière que Linux. Voici l'explication : La version Mac de MySQL est en Après 5.7.18, my-default.cnf a été annulé, donc ni my-default.cnf ni my.cnf n'ont pu être trouvés. my-default.cnf est un fichier qui n'existait que dans la version précédente.
Si malheureusement votre version de MySQL est postérieure à 5.7.18, créez-en simplement une nouvelle
cd /etc sudo vim my.cnf
Copiez le code suivant sur my.cnf
# Example MySQL config file for medium systems. # # This is for a system with little memory (32M - 64M) where MySQL plays # an important part, or systems up to 128M where MySQL is used together with # other programs (such as a web server) # # MySQL programs look for option files in a set of # locations which depend on the deployment platform. # You can copy this option file to one of those # locations. For information about these locations, see: # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/option-files.html # # In this file, you can use all long options that a program supports. # If you want to know which options a program supports, run the program # with the "--help" option. # The following options will be passed to all MySQL clients [client] default-character-set=utf8 #password = your_password port = 3306 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock # Here follows entries for some specific programs # The MySQL server [mysqld] character-set-server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8 port = 3306 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock skip-external-locking key_buffer_size = 16M max_allowed_packet = 1M table_open_cache = 64 sort_buffer_size = 512K net_buffer_length = 8K read_buffer_size = 256K read_rnd_buffer_size = 512K myisam_sort_buffer_size = 8M character-set-server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8' # Don't listen on a TCP/IP port at all. This can be a security enhancement, # if all processes that need to connect to mysqld run on the same host. # All interaction with mysqld must be made via Unix sockets or named pipes. # Note that using this option without enabling named pipes on Windows # (via the "enable-named-pipe" option) will render mysqld useless! # #skip-networking # Replication Master Server (default) # binary logging is required for replication log-bin=mysql-bin # binary logging format - mixed recommended binlog_format=mixed # required unique id between 1 and 2^32 - 1 # defaults to 1 if master-host is not set # but will not function as a master if omitted server-id = 1 # Replication Slave (comment out master section to use this) # # To configure this host as a replication slave, you can choose between # two methods : # # 1) Use the CHANGE MASTER TO command (fully described in our manual) - # the syntax is: # # CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST=<host>, MASTER_PORT=<port>, # MASTER_USER=<user>, MASTER_PASSWORD=<password> ; # # where you replace <host>, <user>, <password> by quoted strings and # <port> by the master's port number (3306 by default). # # Example: # # CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='125.564.12.1', MASTER_PORT=3306, # MASTER_USER='joe', MASTER_PASSWORD='secret'; # # OR # # 2) Set the variables below. However, in case you choose this method, then # start replication for the first time (even unsuccessfully, for example # if you mistyped the password in master-password and the slave fails to # connect), the slave will create a master.info file, and any later # change in this file to the variables' values below will be ignored and # overridden by the content of the master.info file, unless you shutdown # the slave server, delete master.info and restart the slaver server. # For that reason, you may want to leave the lines below untouched # (commented) and instead use CHANGE MASTER TO (see above) # # required unique id between 2 and 2^32 - 1 # (and different from the master) # defaults to 2 if master-host is set # but will not function as a slave if omitted #server-id = 2 # # The replication master for this slave - required #master-host = <hostname> # # The username the slave will use for authentication when connecting # to the master - required #master-user = <username> # # The password the slave will authenticate with when connecting to # the master - required #master-password = <password> # # The port the master is listening on. # optional - defaults to 3306 #master-port = <port> # # binary logging - not required for slaves, but recommended #log-bin=mysql-bin # Uncomment the following if you are using InnoDB tables #innodb_data_home_dir = /usr/local/mysql/data #innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:10M:autoextend #innodb_log_group_home_dir = /usr/local/mysql/data # You can set .._buffer_pool_size up to 50 - 80 % # of RAM but beware of setting memory usage too high #innodb_buffer_pool_size = 16M #innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 2M # Set .._log_file_size to 25 % of buffer pool size #innodb_log_file_size = 5M #innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M #innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 1 #innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 50 [mysqldump] quick max_allowed_packet = 16M [mysql] no-auto-rehash # Remove the next comment character if you are not familiar with SQL #safe-updates default-character-set=utf8 [myisamchk] key_buffer_size = 20M sort_buffer_size = 20M read_buffer = 2M write_buffer = 2M [mysqlhotcopy] interactive-timeout
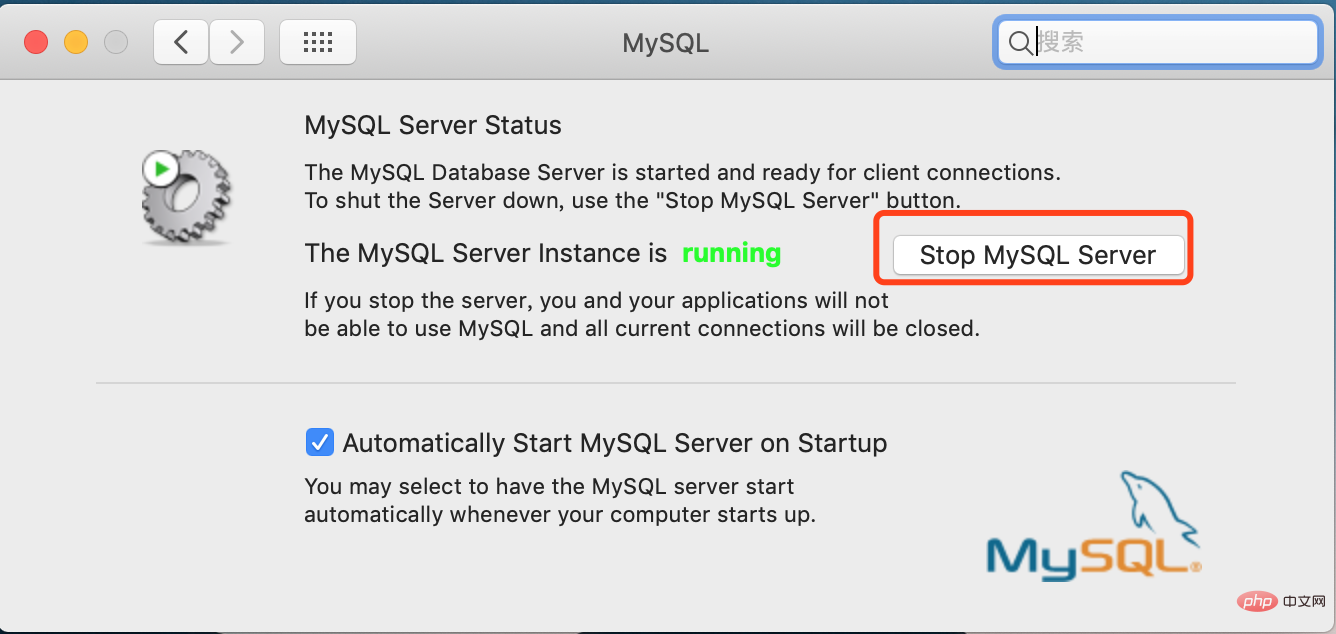
La dernière étape consiste à redémarrer le service MySQL
Apprentissage recommandé : "tutoriel vidéo mysql"
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

