Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Un aperçu des exceptions en Java
Un aperçu des exceptions en Java
- 王林avant
- 2019-11-29 15:18:432679parcourir

1. Qu'est-ce qu'une exception
Une exception est un phénomène anormal qui se produit lors de l'exécution du programme.
try : Enveloppez le code là où des exceptions peuvent se produire. Lorsqu'une exception se produit, lancez l'exception
catch : Capturez l'exception et gérez-la
: sera exécuté indépendamment du fait qu'une exception se produise ou non. finally
: déclenche manuellement une exception throw
: définit des exceptions pour toute méthode appelée throws
2. Raisons de l'anomalie
Erreur de saisie utilisateur Erreur de codeFacteurs environnementaux ;Le mécanisme d'exception assure la robustesse du programme !
3. Classification des exceptions
Exception de référence nulleNullPointerException
Exception d'indice hors limitesIndexOutOfBoundException
4. Obtenir des informations sur l'exception
Lorsqu'une exception se produit dans le programme, le programme sera exécuté directement du bloc d'instruction try au catch et ne continuera pas à exécuter ici.public class text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main开始执行");
text3 a=new text3();
a.text();
System.out.println("main执行结束");
}
public void text() {
int a;
try {
a=2/0;
System.out.println(a);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("程序发生了异常");
}
}
}Le programme ne sera pas interrompu une fois l'exception interceptéepublic class text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main开始执行");
text3 a=new text3();
a.text();
System.out.println("main执行结束");
}
public void text() {
int a;
//try {
a=2/0;
System.out.println(a);
//}catch(ArithmeticException e){
//System.out.println("程序发生了异常");
//}
}
}Résultat de la console : 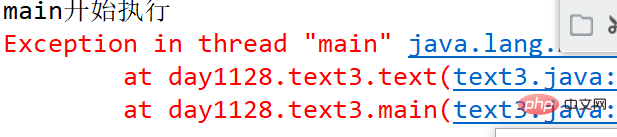
5. Lancer des exceptions manuellement
throw exception; Le paramètre exception représente l'objet d'exception à lever, qui est une sous-classe de la classe jetable et ne peut en être qu'un. .public void text1() throws ArithmeticException{
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Text t=new Text();
try {
t.text();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public void text() throws Exception {
//手动抛出异常
throw new Exception("这是手动抛出来的");
}
}
6. Utilisation imbriquée de try catch finalement
public class Textthrow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a=Math.random();
try {
if(a>0.5) {
System.out.println(a+"程序不报错");
}
else {
throw new Exception();
}
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("这是外层捕获的对象"+e);
try {
a=1/0;
}catch(ArithmeticException e1) {
System.out.println("这是内层捕获的对象"+e1);
}finally {
System.out.println("这是内层的finally块");
}
}finally {
System.out.println("这是外层的finally块 ");
}
}
}
7. Chaîne d'exception
définition : deux ou plusieurs différents les exceptions apparaissent dans le même programme et un lancement imbriqué se produit, ce que l'on appelle une chaîne d'exceptions.public class ExceptionChainText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator c=new Calculator();
try {
c.chufa(1, 0);
}catch(NumberCalculateExcetption e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("错误原因"+e);
}
}
}
class Calculator{
public int chufa(int i,int j) throws NumberCalculateExcetption {
if(j==0) {
NumberCalculateExcetption e = new
NumberCalculateExcetption ("计算错误");
NegativeNumberException e1= new
NegativeNumberException("除数不能为0");
e.initCause(e1);//由e1引起的异常
throw e;
}
return 0;
}
}
class NegativeNumberException extends Exception{
public NegativeNumberException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
class NumberCalculateExcetption extends Exception{
public NumberCalculateExcetption(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
} Articles et tutoriels connexes recommandés : Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

