Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Quelles sont les méthodes de tri séquentiel ?
Quelles sont les méthodes de tri séquentiel ?
- angryTomoriginal
- 2019-07-23 14:54:1912673parcourir

Tutoriel recommandé : tutoriel Java
En Informatique et Mathématiques, un algorithme de Tri (Anglais : Sorting algorithm) est un algorithme qui peut organiser une série de données selon une méthode de tri spécifique. Cet article résumera plusieurs algorithmes de tri couramment utilisés, notamment le tri à bulles, le tri par sélection, le tri par insertion, le tri rapide et le tri par fusion.
1. Tri des bulles
Diagramme schématique
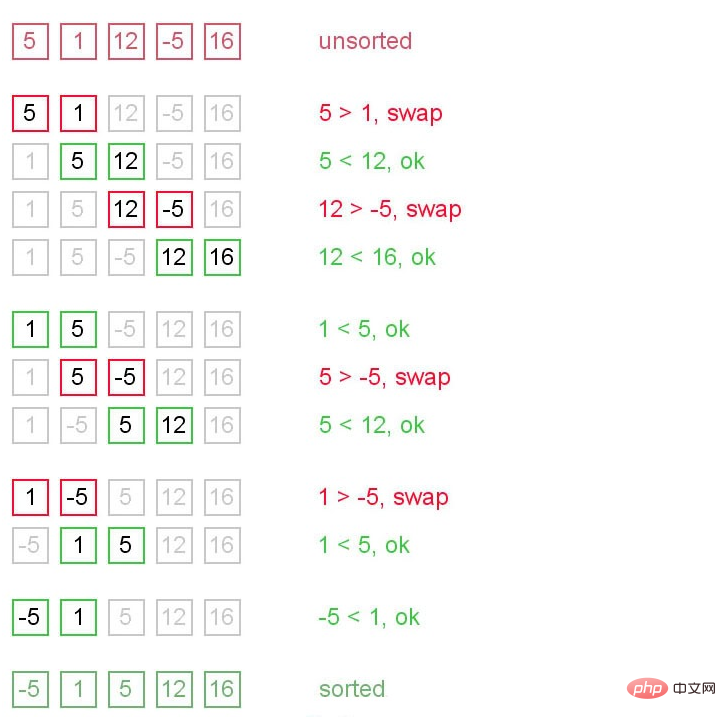
Comprendre : En parcourant de manière itérative la liste à trier, en comparant chaque paire d'éléments adjacents et en les échangeant s'ils sont dans le mauvais ordre.
Code :
public class BubbleSort {
// logic to sort the elements
public static void bubble_srt(int array[]) { int n = array.length; int k; for (int m = n; m >= 0; m--) { for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
k = i + 1; if (array[i] > array[k]) {
swapNumbers(i, k, array);
}
}
printNumbers(array);
}
}
private static void swapNumbers(int i, int j, int[] array) {
int temp;
temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp;
}
private static void printNumbers(int[] input) {
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
System.out.print(input[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] input = { 4, 2, 9, 6, 23, 12, 34, 0, 1 };
bubble_srt(input);
}
}2. Tri de sélection
Principe Figure
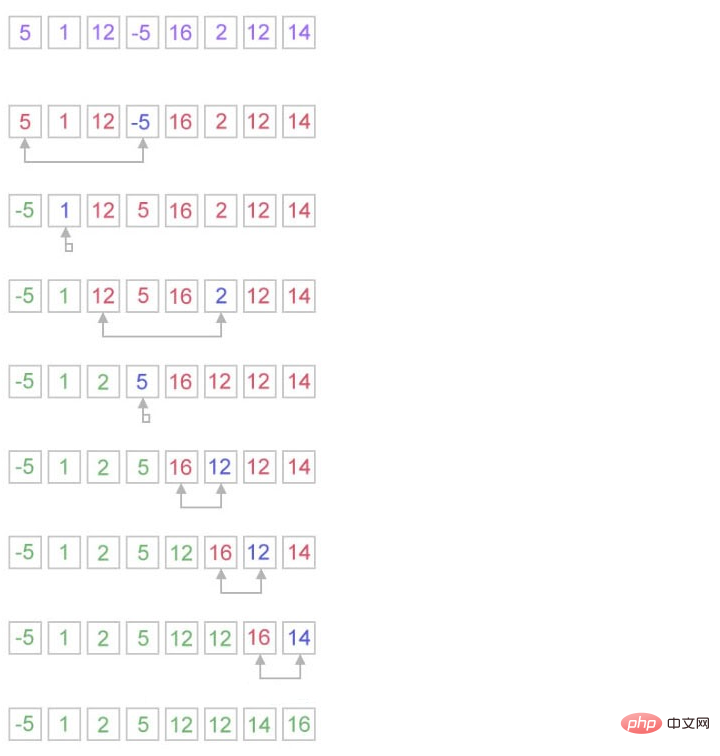
Compréhension : La boucle interne trouve la prochaine valeur minimale (ou maximale) et la boucle externe met la valeur dans c'est un emplacement approprié.
Code :
public class SelectionSort {
public static int[] doSelectionSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++)
{ int index = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) if (arr[j] < arr[index])
index = j;
int smallerNumber = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[i];
arr[i] = smallerNumber;
} return arr;
}
public static void main(String a[]){
int[] arr1 = {10,34,2,56,7,67,88,42}; int[] arr2 = doSelectionSort(arr1); for(int i:arr2){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}3. Tri par insertion
Principe Figure
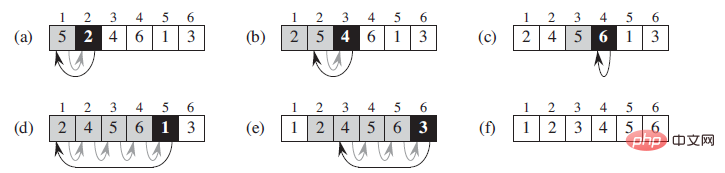
Compréhension : Chaque étape insère un enregistrement à trier dans la séquence ordonnée précédemment triée jusqu'à ce que tous les éléments soient insérés.
Code :
public class InsertionSort {
public static void main(String a[]){ int[] arr1 = {10,34,2,56,7,67,88,42}; int[] arr2 = doInsertionSort(arr1); for(int i:arr2){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
public static int[] doInsertionSort(int[] input){
int temp; for (int i = 1; i < input.length; i++) { for(int j = i ; j > 0 ; j--){ if(input[j] < input[j-1]){
temp = input[j]; input[j] = input[j-1]; input[j-1] = temp;
}
}
} return input;
}
}4. Tri rapide
Diagramme schématique
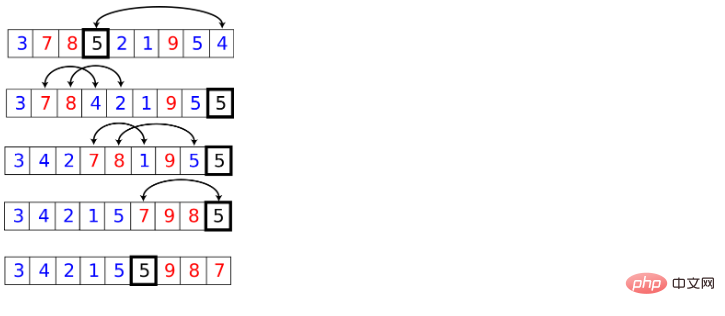
Compréhension : Décomposer le problème d'origine en plusieurs sous-problèmes de plus petite taille mais de structure similaire au problème d'origine, et résoudre ceux-ci résoudre les sous-problèmes de manière récursive, puis combiner les solutions de ces sous-problèmes en une solution au problème d'origine.
Code :
public class QuickSort {
private int array[]; private int length;
public void sort(int[] inputArr) {
if (inputArr == null || inputArr.length == 0) { return;
} this.array = inputArr;
length = inputArr.length;
quickSort(0, length - 1);
}
private void quickSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex) {
int i = lowerIndex; int j = higherIndex; // calculate pivot number, I am taking pivot as middle index number
int pivot = array[lowerIndex+(higherIndex-lowerIndex)/2]; // Divide into two arrays
while (i <= j) { /**
* In each iteration, we will identify a number from left side which
* is greater then the pivot value, and also we will identify a number
* from right side which is less then the pivot value. Once the search
* is done, then we exchange both numbers.
*/
while (array[i] < pivot) {
i++;
} while (array[j] > pivot) {
j--;
} if (i <= j) {
exchangeNumbers(i, j); //move index to next position on both sides
i++;
j--;
}
} // call quickSort() method recursively
if (lowerIndex < j)
quickSort(lowerIndex, j); if (i < higherIndex)
quickSort(i, higherIndex);
}
private void exchangeNumbers(int i, int j) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String a[]){
MyQuickSort sorter = new MyQuickSort(); int[] input = {24,2,45,20,56,75,2,56,99,53,12};
sorter.sort(input); for(int i:input){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}5. Tri par fusion
Principe Figure
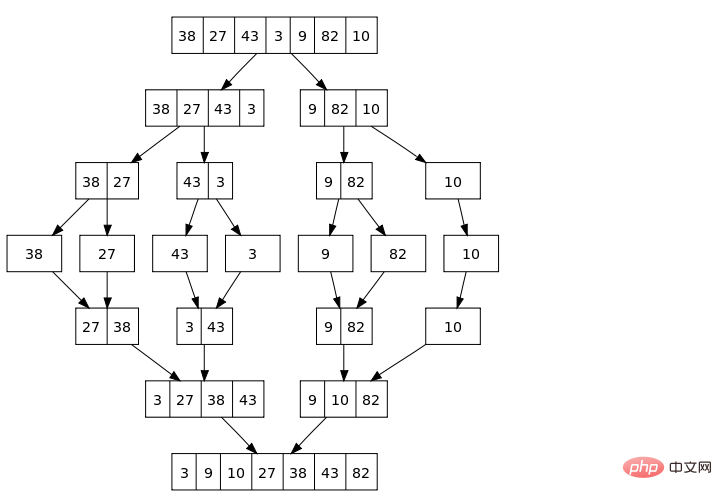
Compréhension : Diviser la séquence à trier en plusieurs sous-séquences de longueur 1, puis diviser ces séquences en deux, fusionnez deux ; obtenez plusieurs séquences ordonnées de longueur 2, puis fusionnez ces séquences deux par deux ; obtenez plusieurs séquences ordonnées de longueur 4, puis fusionnez-les deux par deux jusqu'à ce qu'elles soient directement fusionnées en une seule séquence ;
Code :
public class MergeSort {
private int[] array; private int[] tempMergArr; private int length;
public static void main(String a[]){
int[] inputArr = {45,23,11,89,77,98,4,28,65,43};
MyMergeSort mms = new MyMergeSort();
mms.sort(inputArr); for(int i:inputArr){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
public void sort(int inputArr[]) { this.array = inputArr; this.length = inputArr.length; this.tempMergArr = new int[length];
doMergeSort(0, length - 1);
}
private void doMergeSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex) {
if (lowerIndex < higherIndex) { int middle = lowerIndex + (higherIndex - lowerIndex) / 2; // Below step sorts the left side of the array
doMergeSort(lowerIndex, middle); // Below step sorts the right side of the array
doMergeSort(middle + 1, higherIndex); // Now merge both sides
mergeParts(lowerIndex, middle, higherIndex);
}
}
private void mergeParts(int lowerIndex, int middle, int higherIndex) {
for (int i = lowerIndex; i <= higherIndex; i++) {
tempMergArr[i] = array[i];
} int i = lowerIndex; int j = middle + 1; int k = lowerIndex; while (i <= middle && j <= higherIndex) { if (tempMergArr[i] <= tempMergArr[j]) { array[k] = tempMergArr[i];
i++;
} else { array[k] = tempMergArr[j];
j++;
}
k++;
} while (i <= middle) { array[k] = tempMergArr[i];
k++;
i++;
}
}
}Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

