Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Pratique Java : une implémentation simple d'un tableau dynamique
Pratique Java : une implémentation simple d'un tableau dynamique
- php是最好的语言original
- 2018-08-09 14:07:022014parcourir
Une implémentation simple d'un tableau dynamique
Sur la base de l'implémentation du tableau, l'ajout de 10 W de capacité et la suppression de toute la capacité prennent en moyenne 0,4 seconde. Cette efficacité est considérable. codez ensemble
package com.array;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
*
* @author XiaoTian
* @date 2018-08-08
*/
//基于动态数组的实现 E 是泛型
//借用了一下 Java中的ArrayList的代码
//研究源码也是一种乐趣
//还能让我们技术有所提高
public class ArrayList<E> implements java.io.Serializable{
/**
* 初始容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 用于空实例的共享空数组实例。
*/
transient Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 数组缓冲区,其中存储ArrayList的元素。
* ArrayList的容量是这个数组缓冲区的长度。
*/
transient Object[] elementData;
/**
* 用于默认大小的空实例的共享空数组实例。
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 大小
*/
private int size;
/**
* 默认为空
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 自定义空间大小
* @param initialCapacity
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* 添加一个元素 元素位置是最后
* @param e
*/
public void add(E e) {
ExtendElement(size + 1);
this.elementData[size++] = e;
}
/**
* 在头部添加元素
* @param e
*/
public void addHead(E e) {
this.elementData[0] = e;
}
/**
* 扩展元素
*/
private void ExtendElement(int size) {
//容量
if(this.elementData.length == 0) {
elementData = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}else if(this.elementData.length < size) {
EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = elementData;
//获取当前容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//扩展容量 i + i >> 1 就是 i的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
elementData = new Object[newCapacity];
//1.源数组 2.源数组要复制的起始位置 3.目的数组 4.目的数组放置的起始位置 5.复制的长度
/**
* 调用 System的静态方法 arraycopy() 进行数组拷贝
* 标识为native意味JDK的本地库
* 如果频繁扩容会降低ArrayList的使用性能
* 赋值过程
*/
System.arraycopy(EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,0,elementData,0,size-1);
}
}
/**
* 删除一个元素
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//index + 1 是当前 index 下一个 之 赋给 index 就全部替换了
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // 清楚地让GC完成它的工作
//判断容量是否是当前的1/4 是就 缩容 不要浪费不必要的内存空间
ShrinkageCapacity();
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 删除最后一个
* @return
*/
public E removeLast() {
return remove(this.size - 1);
}
/**
* 判断是否大于size
* @param index
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//输出 Index 和 Size
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* 获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* 查询当前元素的值
* @param index
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
//获取索引位置的元素
return (E) elementData[index];
}
/**
* 缩容
* @param args
*/
public void ShrinkageCapacity() {
if(size == elementData.length / 4 && elementData.length / 2 != 0) {
EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = elementData;
//缩二分之一
int oldCapacity = elementData.length / 2;
elementData = new Object[oldCapacity];
System.arraycopy(EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,0,elementData,0,size-1);
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
long then = System.currentTimeMillis();
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
arrayList.add(random.nextInt());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 99999; i++) {
arrayList.remove(0);
}
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Elapsed time:" + (now - then)+" 毫秒");
}
} 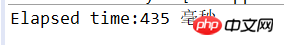
C'est le moment d'exécuter le code ci-dessus. La machine de chacun est différente, et l'effet d'exécution est également différent pour référence seulement
<.>Recommandations associées :Un exemple simple de journal d'implémentation de classe proxy dynamique en Java
java Une implémentation simple de chargement dynamique de classes à l'aide du mécanisme de réflexion Java
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Verrouillage de classe Java, verrouillage d'objet, test de conflit de verrouillage privé
- Java réalise un exemple simple de connexion à la fonction de base de données Oracle/mysql
- Exercice pratique Java appelant un exemple de publication d'interface http
- Le mot-clé synchronisé en Java est utilisé pour réaliser la synchronisation des threads
- Stratégies et techniques d'optimisation de la recherche dans les bases de données Java, analyse et partage pratiques d'applications

