Maison >interface Web >js tutoriel >jQuery 1.9.1 série d'analyse du code source (quinze) animation traitement_jquery
jQuery 1.9.1 série d'analyse du code source (quinze) animation traitement_jquery
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBoriginal
- 2016-05-16 15:27:581281parcourir
Vous devez d'abord avoir des connaissances de base sur la file d'attente. Voir chapitre précédent.
Tutoriel associé : Résumé du traitement de l'animation sous jQuery : http://www.jb51.net/article/42000.htm
Série d'analyses de code source jQuery 1.9.1 (15) Traitement de l'animation et facilitation du noyau d'animation Tween : http://www.jb51.net/article/75821.htm
a. Explication détaillée du processus d'exécution de la fonction jQuery.fn.animate d'entrée d'animation
-------------------------------------------------------------- --- ------------------------------------
Appelez d'abord jQuery.speed en fonction des paramètres pour obtenir les paramètres liés à l'animation, obtenez un objet similaire à celui-ci et générez la fonction d'exécution d'animation doAnimation
;
optall = {
complete: fnction(){...},//动画执行完成的回调
duration: 400,//动画执行时长
easing: "swing",//动画效果
queue: "fx",//动画队列
old: false/fnction(){...},
}
var empty = jQuery.isEmptyObject( prop ),
optall = jQuery.speed( speed, easing, callback ),
doAnimation = function() {
//在特征的副本上操作,保证每个特征效果不会被丢失
var anim = Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall );
doAnimation.finish = function() {
anim.stop( true );
};
//空动画或完成需要立马解决
if ( empty || jQuery._data( this, "finish" ) ) {
anim.stop( true );
}
};
doAnimation.finish = doAnimation;
Si aucune animation n'est en cours d'exécution, l'animation sera exécutée immédiatement, sinon l'animation sera poussée dans la file d'attente d'animation en attente d'exécution
//没有动画在执行则马上执行动画,否则将动画压入动画队列等待执行 return empty || optall.queue === false ? this.each( doAnimation ) : this.queue( optall.queue, doAnimation );
On peut voir que l'endroit où l'animation est réellement exécutée est la fonction Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall )
b. Explication détaillée de la fonction interne de jQuery Animation
-------------------------------------------------------------- --- ------------------------------------
Animation (elem, propriétés, options). Les propriétés sont des fonctionnalités CSS à animer, les options sont des options liées à l'animation {complète : fonction () {…}, durée : 400, assouplissement : non défini, ancien : faux, file d'attente : "effet"}.
Tout d'abord, initialisez un objet de retard, qui est utilisé pour traiter la file d'attente d'animation.
deferred = jQuery.Deferred().always( function() {
// don't match elem in the :animated selector
delete tick.elem;
}),
Ensuite, générez une fonction tick qui sera exécutée à chaque instant (l'intervalle d'événement entre deux points temporels adjacents est de 13 millisecondes par défaut. Cette fonction tick sera enregistrée dans jQuery.timers, puis tous les). time Il sera retiré et exécuté lorsque jQuery.fx.tick sera exécuté.
tick = function() {
if ( stopped ) {
return false;
}
var currentTime = fxNow || createFxNow(),
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime ),
// archaic crash bug won't allow us to use 1 - ( 0.5 || 0 ) (#12497)
temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,
percent = 1 - temp,
index = 0,
length = animation.tweens.length;
//执行动画效果
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
animation.tweens[ index ].run( percent );
}
//生成进度报告
deferred.notifyWith( elem, [ animation, percent, remaining ]);
if ( percent < 1 && length ) {
return remaining;
} else {
//动画执行完毕,执行所有延时队列中的函数(包括清除动画相关的数据)
deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation ] );
return false;
}
}
Nous voyons la gestion par jQuery de la progression de l'animation :
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime )temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,percent = 1 - temp,
Pourcentage de progression = 1 - pourcentage de temps restant.
Habituellement, nous le traitons comme ceci : supposons que l'animation est exécutée une fois toutes les 13 millisecondes, que l'exécution en cours est la nième et que la durée totale de l'animation est T. Alors
Pourcentage de progression = (n*13)/T
En fait, le temps n*13 obtenu par cet algorithme est inexact, car le CPU ne se contente pas d'exécuter votre programme, et la tranche de temps qui vous est allouée est souvent supérieure à n*13. De plus, il s’agit d’une valeur très imprécise, ce qui rend l’animation rapide, lente et incohérente. La méthode jQuery garantit l'exactitude du résultat de l'exécution de l'animation au point d'événement actuel. Après tout, l'événement est le dernier résultat de calcul.
Troisièmement, générez l'animation de l'objet composée de toutes les fonctionnalités utilisées pour l'animation (la structure de cet objet est celle indiquée dans le code source). Ce qui est enregistré dans animation.props sont les fonctionnalités transmises par l'utilisateur. (la cible finale de l'animation).
animation = deferred.promise({
elem: elem,
props: jQuery.extend( {}, properties ),
opts: jQuery.extend( true, { specialEasing: {} }, options ),
originalProperties: properties,
originalOptions: options,
startTime: fxNow || createFxNow(),
duration: options.duration,
tweens: [],
createTween: function( prop, end ) {
var tween = jQuery.Tween( elem, animation.opts, prop, end,
animation.opts.specialEasing[ prop ] || animation.opts.easing );
animation.tweens.push( tween );
return tween;
},
stop: function( gotoEnd ) {
var index = 0,
// if we are going to the end, we want to run all the tweens
// otherwise we skip this part
length = gotoEnd ? animation.tweens.length : 0;
if ( stopped ) {
return this;
}
stopped = true;
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
animation.tweens[ index ].run( 1 );
}
// resolve when we played the last frame
// otherwise, reject
if ( gotoEnd ) {
deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] );
} else {
deferred.rejectWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] );
}
return this;
}
})
Quatrièmement, appelez propFilter pour corriger le nom de la fonctionnalité CSS afin qu'elle puisse être reconnue par le navigateur. Il convient de noter que borderWidth/padding/margin ne fait pas référence à une fonctionnalité CSS, mais à quatre (haut, bas). , gauche et droite)
//经过propFilter,animation.opts.specialEasing添加了相应的特征 propFilter( props, animation.opts.specialEasing );
Donnez un exemple des résultats de la correction propFilter.
Exemple 1, le résultat modifié de la fonctionnalité CSS {hauteur : 200} est :
props = { height: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = {height: undefined}
Exemple 2 : Le résultat de la correction de la fonctionnalité CSS {margin:200} est :
props = { marginBottom: 200,marginLeft: 200,marginRight: 200,marginTop: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = { marginBottom: undefined,marginLeft: undefined,marginRight: undefined,marginTop: undefined }
Cinquièmement, appelez defaultPrefilter pour le traitement d'adaptation : par exemple, l'animation hauteur/largeur nécessite que l'affichage et le débordement soient des valeurs spécifiques pour avoir un effet, par exemple, l'animation afficher/masquer nécessite beaucoup de CSS ; valeurs des fonctionnalités Animation et appelez createTweens dans la fonction pour générer une animation d'accélération.
// animationPrefilters[0] = defaultPrefilter
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
result = animationPrefilters[ index ].call( animation, elem, props, animation.opts );
if ( result ) {
return result;
}
}
La fonction de valeur de animationPrefilters[index] est defaultPrefilter. Il existe plusieurs aspects importants du traitement de la fonction defaultPrefilter
.
DefaultPrefilter Key Point 1 : Les animations liées à la hauteur/largeur dans les éléments en ligne doivent définir la valeur de la fonctionnalité d'affichage sur inline-block
// height/width overflow pass
if ( elem.nodeType === 1 && ( "height" in props || "width" in props ) ) {
//确保没有什么偷偷出来
//记录3个overflow相关特征,因为IE不能改变overflow特征值,
//当overflowX和overflowY设置了相同的值
opts.overflow = [ style.overflow, style.overflowX, style.overflowY ];
// 内联元素中height/width相关动画需要设置display特征值为inline-block
if ( jQuery.css( elem, "display" ) === "inline" &&
jQuery.css( elem, "float" ) === "none" ) {
// 内联元素接受inline-block;
// 块级元素必须内嵌在布局上
if ( !jQuery.support.inlineBlockNeedsLayout || css_defaultDisplay( elem.nodeName ) === "inline" ) {
style.display = "inline-block";
} else {
style.zoom = 1;
}
}
}
Point clé 2 de defaultPrefilter : pour le débordement d'animation hauteur/largeur, définissez-le sur "caché" et restaurez-le une fois l'animation terminée. Cela contribue à améliorer la vitesse de rendu.
//对于height/width动画overflow都要设置为"hidden",动画完成后恢复
if ( opts.overflow ) {
style.overflow = "hidden";
//收缩包装块
if ( !jQuery.support.shrinkWrapBlocks ) {
anim.always(function() {
style.overflow = opts.overflow[ 0 ];
style.overflowX = opts.overflow[ 1 ];
style.overflowY = opts.overflow[ 2 ];
});
}
}
DefaultPrefilter focus 3 : Traitement spécial de l'animation afficher/masquer : l'animation afficher/masquer appelle genFx pour obtenir la forme
props = {
height: "hide"
marginBottom: "hide"
marginLeft: "hide"
marginRight: "hide"
marginTop: "hide"
opacity: "hide"
paddingBottom: "hide"
paddingLeft: "hide"
paddingRight: "hide"
paddingTop: "hide"
width: "hide"
}
Poussez les fonctionnalités qui doivent être animées dans la liste des poignées, supprimez les fonctionnalités correspondantes, puis générez l'animation d'assouplissement correspondante.
for ( index in props ) {
value = props[ index ];
//rfxtypes = /^(?:toggle|show|hide)$/。可以看到最终只有和show/hide的动画才会被饶茹handled中
if ( rfxtypes.exec( value ) ) {
delete props[ index ];
toggle = toggle || value === "toggle";
//如果当前节点的状态和指定的状态相同则不需要处理直接进行下一个状态判断
if ( value === ( hidden ? "hide" : "show" ) ) {
continue;
}
handled.push( index );
}
}
//有需要执行的动画处理则进入分支,里面会对各个特征动画生成缓动动画
length = handled.length;
if ( length ) {
dataShow = jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow" ) || jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow", {} );
if ( "hidden" in dataShow ) {
hidden = dataShow.hidden;
}
// toggle需要保存状态 - enables .stop().toggle() to "reverse"
if ( toggle ) {
dataShow.hidden = !hidden;
}
if ( hidden ) {
jQuery( elem ).show();
} else {
anim.done(function() {
jQuery( elem ).hide();
});
}
anim.done(function() {
var prop;
jQuery._removeData( elem, "fxshow" );
for ( prop in orig ) {
jQuery.style( elem, prop, orig[ prop ] );
}
});
for ( index = 0 ; index < length ; index++ ) {
prop = handled[ index ];
//生成缓动动画
tween = anim.createTween( prop, hidden ? dataShow[ prop ] : 0 );
orig[ prop ] = dataShow[ prop ] || jQuery.style( elem, prop );
if ( !( prop in dataShow ) ) {
dataShow[ prop ] = tween.start;
if ( hidden ) {
tween.end = tween.start;
tween.start = prop === "width" || prop === "height" ? 1 : 0;
}
}
}
}
Sixièmement, générer une animation d'assouplissement, afficher/masquer a été traité dans la fonction defaultPrefilter (code source ci-dessus).
createTweens( animation, props );
我们来看一看createTweens中具体做了什么,先看一下createTweens之前的animation对象

然后看一下经过createTweens之后的animation对象的tweens数组变成了
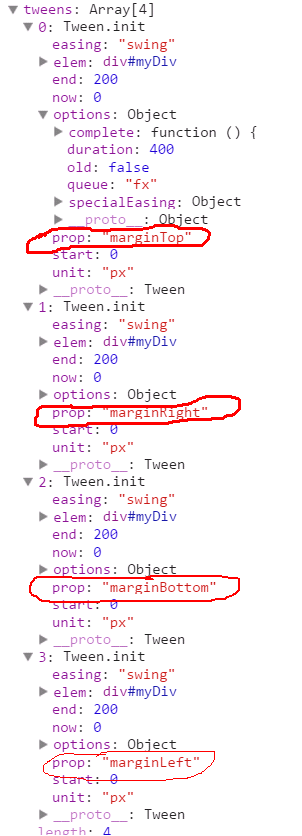
将margin分解成了四个属性(marginTop/Right/Bottom/Left)并且每个属性都有自己的动画特征。
第七,启动动画计时,定时执行tick
//启动动画计时
jQuery.fx.timer(
jQuery.extend( tick, {
elem: elem,
anim: animation,
queue: animation.opts.queue
})
);
最后,将传入的动画结束回调加入延时队列
//从options中获取回调函数添加到延时队列中 return animation.progress( animation.opts.progress ) .done( animation.opts.done, animation.opts.complete ) .fail( animation.opts.fail ) .always( animation.opts.always );
Animation函数流程到此为止
拓展:
前面提到的genFx函数是专门用在toggle、hide、show时获取相关的需要动画的特征的
最终生成的attrs = {
height: "show",
marginTop: "show",
marginRight: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有
marginBottom: "show",
marginLeft: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有
opacity: "show",
width: "show"
}
function genFx( type, includeWidth ) {
var which,
attrs = { height: type },
i = 0;
//如果包括宽度,步长值为1来完成所有cssExpand值,
//如果不包括宽度,步长值是2跳过左/右值
//cssExpand = [ "Top", "Right", "Bottom", "Left" ]
includeWidth = includeWidth? 1 : 0;
for( ; i < 4 ; i += 2 - includeWidth ) {
which = cssExpand[ i ];
attrs[ "margin" + which ] = attrs[ "padding" + which ] = type;
}
if ( includeWidth ) {
attrs.opacity = attrs.width = type;
}
return attrs;
}
Animation函数比较复杂,童鞋们可以随便使用例子去跟踪代码。这个是理解jQuery源码的一种比较好的方式。推荐两个例子:
第一个,有hide/show的例子:$("#id").hide(1000);
第二个,其他例子:$("#id").animate({"marginLeft":500},1000);
jQuery 1.9.1源码分析系列(十五)之动画处理 的全部内容就给大家介绍到这里,有问题随时给我留言,谢谢。!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Une analyse approfondie du composant de groupe de liste Bootstrap
- Explication détaillée du currying de la fonction JavaScript
- Exemple complet de génération de mot de passe JS et de détection de force (avec téléchargement du code source de démonstration)
- Angularjs intègre l'interface utilisateur WeChat (weui)
- Comment basculer rapidement entre le chinois traditionnel et le chinois simplifié avec JavaScript et l'astuce permettant aux sites Web de prendre en charge le basculement entre les compétences en chinois simplifié et traditionnel_javascript

