Maison >développement back-end >Tutoriel Python >Introduction à la méthode de fusion du contenu d'un fichier texte dans l'opération de fichier Python
Introduction à la méthode de fusion du contenu d'un fichier texte dans l'opération de fichier Python
- 巴扎黑original
- 2017-09-20 09:55:552076parcourir
众所周知Python文件处理操作方便快捷,下面这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于Python文件操作之合并文本文件内容的相关资料,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,需要的朋友可以参考借鉴,下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧。
前言
相信大家初入某个项目,一般都要看代码。有时候,想把代码文件打印下来看,不过一般代码文件数量都在两位数或更多,逐一打开、打印,确实太耗费精力了,此外,也会出现某个代码文件打印到纸上只占了一两行的情况,很浪费纸。如果可以合并到一个文本文件里面上面这些问题就解决。
目前一个用的比较多的功能:将多个小文件的内容合并在一个统一的文件中,对原始文件重命名标记其已被处理过。
之前使用其他脚本写的,尝试用python写了一下,顺便熟悉一下python的文件处理命令。
原始文件
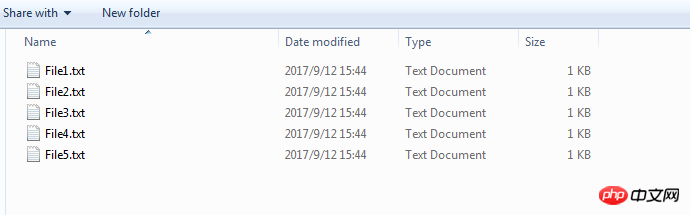
经过处理之后
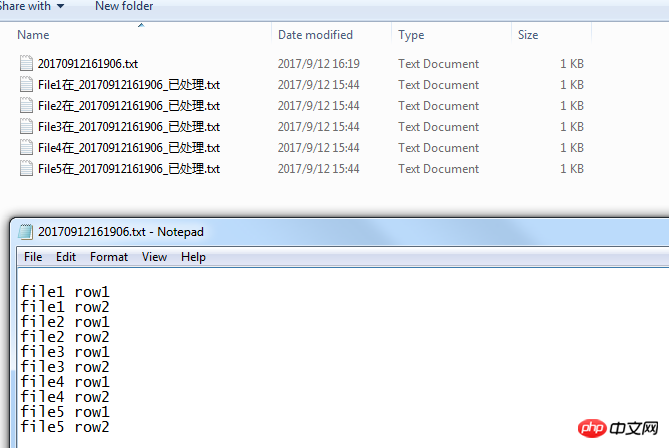
最后还有一个蛋疼的因为缩进产生的第一个回车符
其中包含了文件的创建和移除,文件内容的读写,文件的重命名的语法命令等等
示例代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import time
import datetime
def merge_file(file_path,file_name):
#file_path must exits
if(os.path.exists(file_path) is False):
print('file_path is not exists')
return
if(os.path.exists(os.path.join(file_path, file_name))):
os.remove(os.path.join(file_path, file_name))
#'%Y_%m_%d%H%M%S',创建一个以日期命名的文本文件
targetfilename = str(time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S'))+'.txt'
fobj = open(os.path.join(file_path, targetfilename), 'w')
fobj.close()
# a 是以追加的方式打开文件写入
with open(os.path.join(file_path, targetfilename), 'a', encoding='GBK') as f_wirte:
files = os.listdir(file_path)
for file in files:
print(os.path.join(file_path, file))
with open(file_path+'\\'+file, 'r', encoding='GBK') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
if(line.strip().__len__()) > 0:# 排除空行
f_wirte.write(line)
f_wirte.write('\n')# 每读完一个文件之后,加一个回车,否则第一个文件的最后一行跟第二个文件的第一行没有回车
# 文件合并之后,重命名原始的文件,
# os.path.splitext(file)[0] 提取文件名,不包括后缀名
# os.path.splitext(file)[1] 提取文件后缀名
if (file != targetfilename):
os.rename(os.path.join(file_path, file),os.path.join(file_path, os.path.splitext(file)[0] + '在_' +str(time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')) +'_已处理' + '.txt'))
merge_file('D:\TestPythonMergeFile','auoto_create_a_category_file')Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Déclaration:
Le contenu de cet article est volontairement contribué par les internautes et les droits d'auteur appartiennent à l'auteur original. Ce site n'assume aucune responsabilité légale correspondante. Si vous trouvez un contenu suspecté de plagiat ou de contrefaçon, veuillez contacter admin@php.cn

