Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Explication détaillée d'exemples d'ActionMapping dans Struts1
Explication détaillée d'exemples d'ActionMapping dans Struts1
- 黄舟original
- 2017-09-05 10:55:262170parcourir
Cet article présente principalement le tutoriel ActionMapping du Struts1. L'éditeur pense qu'il est plutôt bon, je vais le partager avec vous maintenant et le donner comme référence. Suivons l'éditeur et jetons un coup d'œil
Tout d'abord, le point d'arrêt est hors de la méthode processpath
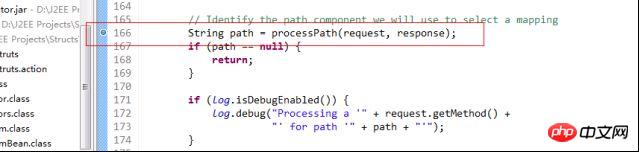
package com.cjq.servlet;
import java.util.Map;
public class ActionMapping {
private String path;
private Object type;
private Map forwardMap;
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public Object getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Object type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Map getForwardMap() {
return forwardMap;
}
public void setForwardMap(Map forwardMap) {
this.forwardMap = forwardMap;
}
} Et l'Actionconfig dans Struts (car ActionMapping hérite de cette ActionConfig, donc we (C'est plus simple de regarder ActionConfig) Le code est le suivant : 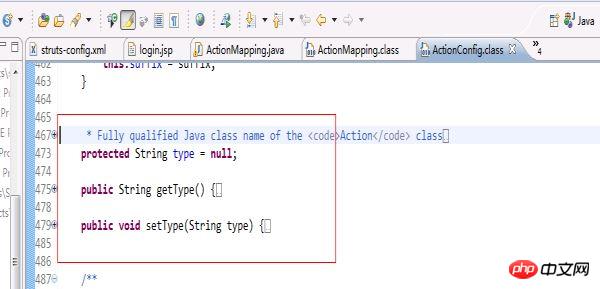
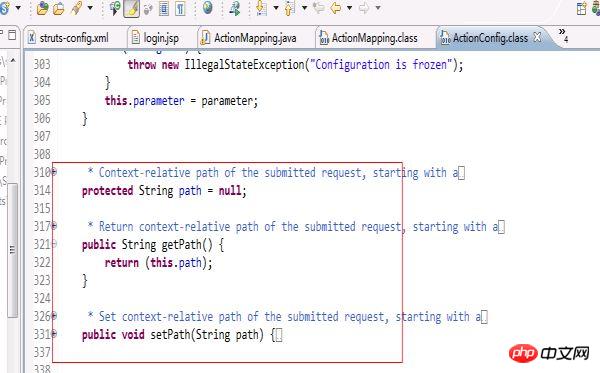


/**
* <p>Select the mapping used to process theselection path for this request
* If no mapping can be identified, createan error response and return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param path The portion of the requestURI for selecting a mapping
*
* @exception IOException if an input/outputerror occurs
*/
protectedActionMapping processMapping(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
String path)
throws IOException {
// Is there a mapping for this path?
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping)
moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
// If a mapping is found, put it in the request and return it
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
// Locate the mapping for unknown paths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfig.findActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configs.length; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;
}Nous transmettons d'abord ce que nous avons intercepté dans le Étape précédente Chemin, recherchez ActionConfig via la méthode findAction de moduleConfig et renvoyez ActionMapping. Le code spécifique est : ActionMapping mapping =(ActionMapping) moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);S'il est trouvé, alors l'ActionMapping est stocké dans le contexte de la requête. Code :
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}Si le mappage n'est pas trouvé via le chemin, parcourez l'Actionconfig pour trouver le mappage du chemin inconnu, et s'il est trouvé, stockez dans la requête. Si s'il n'est pas trouvé, un message d'erreur sera renvoyé. Le code spécifique est le suivant : // Locate the mapping for unknownpaths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfigfindActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configslength; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null; Jetons un coup d'œil à. processActionForm, une méthode dans ActionServlet. Lorsque nous interceptons une chaîne, après avoir obtenu l'ActionMapping basé sur la chaîne (ceci est introduit dans les deux premiers articles), nous utiliserons ActionMapping pour créer l'ActionForm et placerons l'ActionForm dans la requête ou séance pour la gestion. /**
* <p>Retrieve and return the <code>ActionForm</code> associatedwith
* this mapping, creating and retaining oneif necessary. If there is no
* <code>ActionForm</code> associated with this mapping,return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param mapping The mapping we are using
*/
protectedActionForm processActionForm(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
ActionMapping mapping) {
// Create (if necessary) a form bean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtilscreateActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}
// Store the new instance in the appropriate scope
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Storing ActionForm bean instance in scope '" +
mapping.getScope() + "' under attribute key '" +
mapping.getAttribute() + "'");
}
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())) {
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =requestgetSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}
return (instance);
}Le processus général de cette méthode est : Selon Le nom dans ActionMapping recherche ActionForm. Si ActionForm est configuré, il est recherché dans la demande ou la session. Si un ActionForm a été créé dans la demande ou la session, il sera renvoyé. S'il n'existe pas, il sera créé par réflexion selon le chemin d'achèvement de l'ActionForm, puis l'ActionForm créé sera placé dans la demande ou la session, puis l'ActionForm sera renvoyé. // Create (if necessary) a formbean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtils.createActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}Générer la chaîne ActionForm dans ActionMapping en appelant l'objet méthode RequestUtils.createActionForm et revint. Entrez ce code : publicstaticActionForm createActionForm(
HttpServletRequest request,
ActionMapping mapping,
ModuleConfig moduleConfig,
ActionServlet servlet) {
// Is there a form bean associated with this mapping?
String attribute = mappinggetAttribute();
if (attribute == null) {
return (null);
}
// Look up the form bean configuration information to use
String name = mapping.getName();
FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfigfindFormBeanConfig(name);
if (config == null) {
log.warn("No FormBeanConfig found under '"+ name + "'");
return (null);
}
ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mappinggetScope());
// Can we recycle the existing form bean instance (if there is one)?
try {
if (instance != null && canReuseActionForm(instance,config)) {
return (instance);
}
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error(servlet.getInternal().getMessage("formBean",config.getType()), e);
return (null);
}
return createActionForm(config,servlet);
}La méthode définit d'abord le nom de la variable et obtient la valeur du mappage, String name = mapping.getName(); est la chaîne LoginForm dans notre exemple. Ensuite, la chaîne LoginForm correspondante est générée dans l'objet correspondant en appelant FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfig.findFormBeanConfig(name);. <form-beans>
<form-bean name="loginForm" type=".struts.LoginActionForm"/>
</form-beans>这个标签在服务器一启动的时候就会利用digester读取这里的配置信息,并且放在FormBeanConfig类中,这样我们可以通过上面那一句话就可以把LoginForm字符串生成相应的对象。
之后调用了ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mapping.getScope());这个方法,这个方法主要是查找scope属性中有没有存在ActionForm。具体实现:
if ("request".equals(scope)){
instance = (ActionForm)request.getAttribute(attribute);
} else {
session = request.getSession();
instance = (ActionForm)session.getAttribute(attribute);
}这里判断scope属性值是否为request,如果是则从request中读出ActionForm,如果不是则从session中读出。程序如果是第一次执行,那么ActionForm会是为空的。因为这里的ActionForm为空,所以就进入了if判断语句中,最后通过调用return createActionForm(config, servlet);创建ActionForm并且返回。
之后processActionForm就会把返回来的ActionForm放入request或者session中。具体实现就是:
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())){
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}到此为止,ActionForm就创建完成,当ActionForm创建完成之后,就要用其他的方法来往ActionForm中赋值了
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

