Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Implémentation Java de l'analyse de la méthode de liaison secondaire de la collection Map
Implémentation Java de l'analyse de la méthode de liaison secondaire de la collection Map
- 巴扎黑original
- 2017-07-20 13:23:431477parcourir
La collection de cartes peut enregistrer des relations de cartographie clé-valeur, ce qui est très approprié pour la structure de données requise par cet exemple. Toutes les informations de province peuvent être enregistrées en tant que clés de la collection de cartes, et chaque clé peut enregistrer les informations de ville correspondantes. Cet exemple utilise Map La collection implémente les boîtes de sélection en cascade de province et de ville. Lorsque les informations sur la province sont sélectionnées, le contenu correspondant à la boîte de sélection déroulante de la ville sera modifié.
Analyse d'idées :
1. Créez une collection cartographique nationale (province, commune, région autonome), c'est-à-dire un objet LinkedHashMap, et utilisez la méthode put() de l'interface Map pour ajoutez les provinces et les villes spécifiées à la relation de mappage, où la valeur est un tableau unidimensionnel de type String.
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CityMap {
/**
* 全国(省,直辖市,自治区)映射集合
*/
public static Map<String,String[]> model=new LinkedHashMap<String, String[]>();
static{
model.put("北京", new String[]{"北京"});
model.put("上海", new String[]{"上海"});
model.put("天津", new String[]{"天津"});
model.put("重庆", new String[]{"重庆"});
model.put("黑龙江", new String[]{"哈尔滨","齐齐哈尔","牡丹江","大庆","伊春","双鸭山","鹤岗","鸡西","佳木斯","七台河","黑河","绥化","大兴安岭"});
model.put("吉林", new String[]{"长春","延边","吉林","白山","白城","四平","松原","辽源","大安","通化"});
model.put("辽宁", new String[]{"沈阳","大连","葫芦岛","旅顺","本溪","抚顺","铁岭","辽阳","营口","阜新","朝阳","锦州","丹东","鞍山"});
model.put("内蒙古", new String[]{"呼和浩特","呼伦贝尔","锡林浩特","包头","赤峰","海拉尔","乌海","鄂尔多斯","通辽"});
model.put("河北", new String[]{"石家庄","唐山","张家口","廊坊","邢台","邯郸","沧州","衡水","承德","保定","秦皇岛"});
model.put("河南", new String[]{"郑州","开封","洛阳","平顶山","焦作","鹤壁","新乡","安阳","濮阳","许昌","漯河","三门峡","南阳","商丘","信阳","周口","驻马店"});
model.put("山东", new String[]{"济南","青岛","淄博","威海","曲阜","临沂","烟台","枣庄","聊城","济宁","菏泽","泰安","日照","东营","德州","滨州","莱芜","潍坊"});
model.put("山西", new String[]{"太原","阳泉","晋城","晋中","临汾","运城","长治","朔州","忻州","大同","吕梁"});
model.put("江苏", new String[]{"南京","苏州","昆山","南通","太仓","吴县","徐州","宜兴","镇江","淮安","常熟","盐城","泰州","无锡","连云港","扬州","常州","宿迁"});
model.put("安徽", new String[]{"合肥","巢湖","蚌埠","安庆","六安","滁州","马鞍山","阜阳","宣城","铜陵","淮北","芜湖","毫州","宿州","淮南","池州"});
model.put("陕西", new String[]{"西安","韩城","安康","汉中","宝鸡","咸阳","榆林","渭南","商洛","铜川","延安"});
model.put("宁夏", new String[]{"银川","固原","中卫","石嘴山","吴忠"});
model.put("甘肃", new String[]{"兰州","白银","庆阳","酒泉","天水","武威","张掖","甘南","临夏","平凉","定西","金昌"});
model.put("青海", new String[]{"西宁","海北","海西","黄南","果洛","玉树","海东","海南"});
model.put("湖北", new String[]{"武汉","宜昌","黄冈","恩施","荆州","神农架","十堰","咸宁","襄樊","孝感","随州","黄石","荆门","鄂州"});
model.put("湖南", new String[]{"长沙","邵阳","常德","郴州","吉首","株洲","娄底","湘潭","益阳","永州","岳阳","衡阳","怀化","韶山","张家界"});
model.put("浙江", new String[]{"杭州","湖州","金华","宁波","丽水","绍兴","雁荡山","衢州","嘉兴","台州","舟山","温州"});
model.put("江西", new String[]{"南昌","萍乡","九江","上饶","抚州","吉安","鹰潭","宜春","新余","景德镇","赣州"});
model.put("福建", new String[]{"福州","厦门","龙岩","南平","宁德","莆田","泉州","三明","漳州"});
model.put("贵州", new String[]{"贵阳","安顺","赤水","遵义","铜仁","六盘水","毕节","凯里","都匀"});
model.put("四川", new String[]{"成都","泸州","内江","凉山","阿坝","巴中","广元","乐山","绵阳","德阳","攀枝花","雅安","宜宾","自贡","甘孜州","达州","资阳","广安","遂宁","眉山","南充"});
model.put("广东", new String[]{"广州","深圳","潮州","韶关","湛江","惠州","清远","东莞","江门","茂名","肇庆","汕尾","河源","揭阳","梅州","中山","德庆","阳江","云浮","珠海","汕头","佛山"});
model.put("广西", new String[]{"南宁","桂林","阳朔","柳州","梧州","玉林","桂平","贺州","钦州","贵港","防城港","百色","北海","河池","来宾","崇左"});
model.put("云南", new String[]{"昆明","保山","楚雄","德宏","红河","临沧","怒江","曲靖","思茅","文山","玉溪","昭通","丽江","大理"});
model.put("海南", new String[]{"海口","三亚","儋州","琼山","通什","文昌"});
model.put("新疆", new String[]{"乌鲁木齐","阿勒泰","阿克苏","昌吉","哈密","和田","喀什","克拉玛依","石河子","塔城","库尔勒","吐鲁番","伊宁"});
}
}2. Définissez la méthode d'obtention des provinces, créez une collection Map, attribuez-lui la collection cartographique obtenue à l'étape précédente et utilisez la méthode keySet() du Collection de cartes pour obtenir la collection La collection Set composée de tous les objets clés de est la collection province. Créez un tableau unidimensionnel de type Object, utilisez la méthode toArray() de l'interface Set pour convertir la collection Set en un tableau. renvoie ce tableau comme paramètre de la liste déroulante de sélection de province.
3. Utilisez la méthode setModel() de la classe JComboBox pour ajouter des informations sur la province à la liste déroulante des provinces. Le paramètre est la méthode pour obtenir la province à l'étape précédente.
4. Définissez la méthode d'obtention des villes/comtés en fonction des provinces, créez une collection Map, attribuez-lui la collection cartographique obtenue à l'étape 1 et utilisez la méthode get() de la collection Map pour obtenir le valeur de la clé spécifiée, c'est-à-dire Pour la collection ville/comté, créez un tableau unidimensionnel de type String[] et attribuez la collection ville/comté au tableau.
5. Définissez l'événement de changement de statut d'option de la liste déroulante province Dans cet événement, obtenez la province sélectionnée via la méthode getSelectedItem() de la classe JComboBox. collection, puis utilisez la classe JComboBox. La méthode removeAllItems() efface la liste ville/comté, obtient le tableau ville/comté en fonction de la province sélectionnée et utilise enfin la méthode setModel() de JComboBox pour rajouter la valeur du liste des villes/comtés.
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
/**
* 带背景的面板组件
*
* @author ZhongWei Lee
*/
public class BackgroundPanel extends JPanel {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7758689434195492602L;
/**
* 背景图片
*/
private Image image;
/**
* 构造方法
*/
public BackgroundPanel() {
super();
setOpaque(false);
setLayout(null);
}
/**
* 设置图片的方法
*/
public void setImage(Image image) {
this.image = image;
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {// 重写绘制组件外观
if (image != null) {
int width = getWidth();// 获取组件大小
int height = getHeight();
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, width, height, this);// 绘制图片与组件大小相同
}
super.paintComponent(g);// 执行超类方法
}
} import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
/**
* Utility class for managing resources such as colors, fonts, images, etc.
*
* This class may be freely distributed as part of any application or plugin.
* <p>
* Copyright (c) 2003 - 2004, Instantiations, Inc. <br>All Rights Reserved
*
* @author scheglov_ke
*/
public class SwingResourceManager {
/**
* Maps image names to images
*/
private static HashMap<String, Image> m_ClassImageMap = new HashMap<String, Image>();
/**
* Returns an image encoded by the specified input stream
* @param is InputStream The input stream encoding the image data
* @return Image The image encoded by the specified input stream
*/
private static Image getImage(InputStream is) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte buf[] = new byte[1024 * 4];
while (true) {
int n = is.read(buf);
if (n == -1)
break;
baos.write(buf, 0, n);
}
baos.close();
return Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().createImage(baos.toByteArray());
} catch (Throwable e) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path relative to the specified class
* @param clazz Class The class relative to which to find the image
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(Class<?> clazz, String path) {
String key = clazz.getName() + '|' + path;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
if (image == null) {
if ((path.length() > 0) && (path.charAt(0) == '/')) {
String newPath = path.substring(1, path.length());
image = getImage(new BufferedInputStream(clazz.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(newPath)));
} else {
image = getImage(clazz.getResourceAsStream(path));
}
m_ClassImageMap.put(key, image);
}
return image;
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(String path) {
return getImage("default", path); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path
* @param section String The storage section in the cache
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(String section, String path) {
String key = section + '|' + SwingResourceManager.class.getName() + '|' + path;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
if (image == null) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
image = getImage(fis);
m_ClassImageMap.put(key, image);
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
return image;
}
/**
* Clear cached images in specified section
* @param section the section do clear
*/
public static void clearImages(String section) {
for (Iterator<String> I = m_ClassImageMap.keySet().iterator(); I.hasNext();) {
String key = I.next();
if (!key.startsWith(section + '|'))
continue;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
image.flush();
I.remove();
}
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path relative to the specified class
* @param clazz Class The class relative to which to find the icon
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(Class<?> clazz, String path) {
return getIcon(getImage(clazz, path));
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(String path) {
return getIcon("default", path); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path
* @param section String The storage section in the cache
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(String section, String path) {
return getIcon(getImage(section, path));
}
/**
* Returns an icon based on the specified image
* @param image Image The original image
* @return Icon The icon based on the image
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(Image image) {
if (image == null)
return null;
return new ImageIcon(image);
}
} import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.event.ItemEvent;
import java.awt.event.ItemListener;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.swing.DefaultComboBoxModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
import javax.swing.border.TitledBorder;
public class MainFrame extends JFrame {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4595347311922711984L;
private JTextField textField_3;
private JTextField textField_1;
private JComboBox comboBox_1;
private JTextField textField;
private JComboBox cityComboBox;
private JComboBox comboBox;
/**
* Launch the application
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sun.java.swing.plaf.nimbus.NimbusLookAndFeel");
MainFrame frame = new MainFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame
*/
public MainFrame() {
getContentPane().setLayout(null);
setBounds(100, 100, 518, 379);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//获取默认的市/县
String province=(String)getProvince()[0];
setTitle("输入指定省/直辖市查询对应的市县");
final BackgroundPanel backgroundPanel = new BackgroundPanel();
backgroundPanel.setImage(SwingResourceManager.getImage(MainFrame.class, "/images/background.jpg"));
backgroundPanel.setBounds(0, 0, 510, 380);
getContentPane().add(backgroundPanel);
final JPanel panel = new JPanel();
panel.setOpaque(false);
panel.setBounds(36, 126, 438, 70);
backgroundPanel.add(panel);
panel.setLayout(null);
panel.setBorder(new TitledBorder(null, "居住地", TitledBorder.DEFAULT_JUSTIFICATION, TitledBorder.DEFAULT_POSITION, null, null));
cityComboBox = new JComboBox();
cityComboBox.setBounds(245, 25, 124, 27);
panel.add(cityComboBox);
cityComboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getCity(province)));
comboBox = new JComboBox();
comboBox.setBounds(25, 25, 124, 27);
panel.add(comboBox);
comboBox.addItemListener(new ItemListener() {
public void itemStateChanged(final ItemEvent e) { // 选项状态更改事件
itemChange();
}
});
comboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getProvince())); // 添加省份信息
final JLabel label = new JLabel();
label.setText("省/直辖市");
label.setBounds(155, 30, 66, 18);
panel.add(label);
final JLabel label_1 = new JLabel();
label_1.setText("市/县");
label_1.setBounds(375, 30, 37, 18);
panel.add(label_1);
final JLabel label_2 = new JLabel();
label_2.setBounds(36, 43, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_2);
label_2.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_2.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_2.setText("姓 名:");
textField = new JTextField();
textField.setBounds(113, 38, 154, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(textField);
final JLabel label_3 = new JLabel();
label_3.setBounds(36, 84, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_3);
label_3.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_3.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_3.setText("性 别:");
comboBox_1 = new JComboBox();
comboBox_1.setBounds(113, 81, 66, 25);
backgroundPanel.add(comboBox_1);
comboBox_1.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(new String[] {"男", "女"}));
final JLabel label_4 = new JLabel();
label_4.setBounds(36, 212, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_4);
label_4.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_4.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_4.setText("详细地址:");
textField_1 = new JTextField();
textField_1.setBounds(113, 208, 367, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(textField_1);
final JLabel label_4_1 = new JLabel();
label_4_1.setBounds(36, 252, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_4_1);
label_4_1.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_4_1.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_4_1.setText("E-mail:");
textField_3 = new JTextField();
textField_3.setBounds(113, 248, 367, 27);
backgroundPanel.add(textField_3);
final JButton button = new JButton();
button.setBounds(159, 289, 75, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(button);
button.setText("保存");
final JButton button_1 = new JButton();
button_1.setBounds(265, 289, 75, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(button_1);
button_1.setText("重置");
//
}
/**
* 获取省、直辖市,自治区
*
* @return
*/
public Object[] getProvince() {
Map<String, String[]> map = CityMap.model;// 获取省份信息保存到Map中
Set<String> set = map.keySet(); // 获取Map集合中的键,并以Set集合返回
Object[] province = set.toArray(); // 转换为数组
return province; // 返回获取的省份信息
}
/**
* 获取指定省对应的市/县
*
* @param selectProvince
* @return
*/
public String[] getCity(String selectProvince) {
Map<String, String[]> map = CityMap.model; // 获取省份信息保存到Map中
String[] arrCity = map.get(selectProvince); // 获取指定键的值
return arrCity; // 返回获取的市/县
}
private void itemChange() {
String selectProvince = (String) comboBox.getSelectedItem();
cityComboBox.removeAllItems(); // 清空市/县列表
String[] arrCity = getCity(selectProvince); // 获取市/县
cityComboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(arrCity)); // 重新添加市/县列表的值
}
}L'effet est comme indiqué ci-dessous :
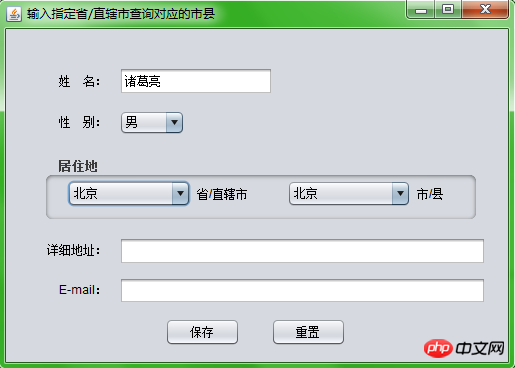
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

